File - Earth & Environmental Science
advertisement

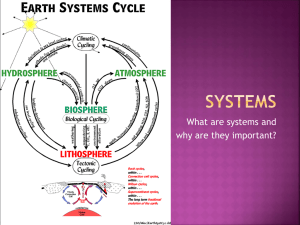
An Introduction to Earth Science Unit 1 - Chapter 1 What is Earth Science? Definition – the study of Earth and its neighbors in space. 4 subdivisions of Earth Science 1. Geology Definition – study of planet Earth 2 Areas of Geology Areas of Geology Physical Geology The examination of the materials that make up the Earth And the explanations for the processes that shape the Earth. Historical Geology Understanding Earth’s long history. 2. Oceanography •The study of the Ocean’s biology, chemistry and geology. 3. Meteorology •The study of the atmosphere, weather and climate. 4. Astronomy The study of the universe. Earth science is an ever evolving science because the Earth itself is CONSTANTLY changing! A new section of Earth science is environmental science. Environmental Science How humans interact/their relationship with the natural Environment. 40th anniversary of Earth Day Video The Earth is divided into 4 major spheres. Geosphere or 1. Hydrosphere Consists of all the water on the Earth. The oceans make up 97% of the water on Earth The other 3% is freshwater. (we must MAXIMIZE its use) Water is what makes our planet unique! We are the ONLY planet with liquid water. Water supports life No water = No life 2. Atmosphere Thin gaseous layer that surrounds the planet 100 kilometers thick. Provides the air we breathe Protects us from the Sun’s heat and radiation Provides our weather and climate 3. Geosphere Divided into 4 main parts 1. 2. 3. 4. The Crust The Mantle The Outer Core The Inner Core Geosphere Cont. 1. Lithosphere Rigid outer layer of the Earth – cool & solid Crust & uppermost part of mantle. 2. Asthenosphere Plasticity – warm & liquid Lower mantle 4. Biosphere Includes all life on Earth. Extends from the ocean floor to about a mile into the air Other Spheres 5. Cryosphere The Earth's surface where water is in a solid form 6. The Anthroposphere Humans and our constructions (also called anthrosphere). Interactions between the Spheres All of the spheres interact and influence the others The hydrosphere, geosphere and atmosphere ALL affect life Life affects and changes the hydrosphere, geosphere and atmosphere All the Spheres interact with Each other. Get into your assigned groups. Place all spheres together in a square formation. (they should slightly overlap) Cut out the different items or interactions and place them in the appropriate sphere or spheres. EARTH IS A SYSTEM!!!