Behind the Demand Curve: Consumer choice
advertisement

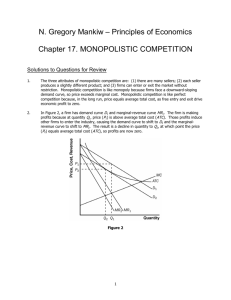
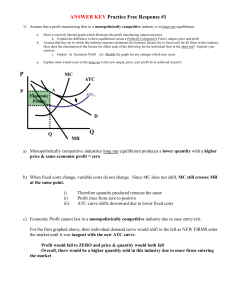
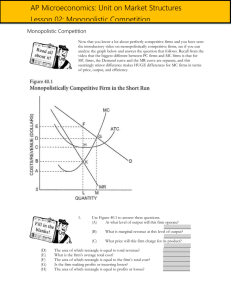
Monopolistic Competition Microeconomics TPS Write down a list of restaurants which serve basically the same food. Monopolistic Competition Defining Monopolistic Competition Somewhere between Perfect competition and an Oligopoly Many firms but NOT as many as PC Differentiated product Each firm has some ability to set the price of their product. No barriers to entry and exit. Inefficient market Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run Short-run economic profit encourages firms to enter the market TT = MR = MC at Q P = intersection of Q and MR = MC Positive economics profit is P > ATC Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run Firm Makes Profit Price MC ATC Price Average total cost Demand Profit MR 0 Profitmaximizing quantity Quantity Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run Short-run economic losses encourage firms to exit the market. Negative economics losses is P < ATC Monopolistic Competitors in the Short Run Firm Makes Losses Price MC ATC Losses Average total cost Price MR 0 Lossminimizing quantity Demand Quantity Homework Multiple Choice – 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 Short Answer - 21 Monopolistic Competition in Long-Run Equilibrium Firms will enter and exit until the firms are making exactly zero economic profits. Monopolistic Competitor in the Long Run Price MC ATC The demand curve is tangent to the ATC curve. P = ATC And this tangency lies vertically above the intersection of MR and MC. Demand MR 0 Profit-maximizing quantity Quantity Monopolistic Competition versus Perfect Competition Two differences Excess capacity Markup over marginal cost Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition Excess Capacity is … Firms produce less than the output at which ATC is minimized Monopolistic Competition versus Perfect Competition Monopolistically Competitive Firm Perfectly Competitive Firm Price Price MC MC ATC ATC P P = MC MR 0 Quantity produced Efficient scale P = MR (demand curve) Demand Quantity 0 Quantity produced = Efficient scale Quantity Monopolistic Competition versus Perfect Competition Markup over Marginal Cost Markup = P - MC More profit is generated Monopolistic Competition versus Perfect Competition Monopolistically Competitive Firm Perfectly Competitive Firm Price Price MC MC ATC ATC Markup P P = MC P = MR (demand curve) Marginal cost MR 0 Quantity produced Demand Quantity 0 Quantity produced Quantity Monopolistic Competition versus Perfect Competition Monopolistically Competitive Firm Perfectly Competitive Firm Price Price MC MC ATC ATC Markup P P = MC P = MR (demand curve) Marginal cost MR 0 Quantity produced Efficient scale Excess capacity Demand Quantity 0 Quantity produced = Efficient scale Quantity Homework Multiple Choice – 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 Short Answer - 22 Product Differentiation Differentiation by Style or Type Think pizza!! Deep-dish crust v. thin crust v. stuffed crust Consumers have different tastes Producers able to increase profits by differentiating their product. Product Differentiation Differentiation by Location Nearer to you is better than farther away. You may be willing to pay more when it’s closer/more convenient to/for you. Product Differentiation Differentiation by Quality Mercedes v. Kia Prices higher for Mercedes due to perceived/actual quality difference. Advertising Advertising delivers two different messages: Information persuasive Advertising Informative Store hours What we sell Extra services Advertising Persuasive ‘yummiest French fries’ ‘Just do it!’ ‘this house is charming and located in a lovely neighborhood.’ Use of humor, celebrities, special effects and/or musical jingles. Brand Names Brand Names are … Owned by particular companies Used to differentiate products in consumer’s minds We think Kleenex for facial tissue. Many other brands of facial tissue. Name brand v. store brand. Ingredients essentially the same Name brand cost more. Homework Multiple Choice – 13 - 19 Short Answer – 23, 24 Monopolistic Competition: Between Perfect Competition and Monopoly