File
advertisement

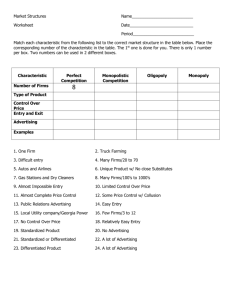
Monopolistic Competition & Oligopoly Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition • A relatively large number of sellers (Small Market Share, No Collusion, Independent Action) • Differentiated products (Product Attributes, Service, Location, Brands) • Easy entry and exit from the industry (Entry Eliminates Profits, Exits Eliminate Losses) • Advertising & Non Price Competition Monopolistically Competitive Industries • • • • Clothing Industry Restaurants Jewelry Consumer Electronics Price and Output in Monopolistic Competition (SR vs. LR) Monopolistic Competition and Efficiency • Productive efficiency is P= min ATC • Allocative efficiency is P= MC • Not productive or allocative efficiency • P>MC, meaning that resources are underallocated; not allocatively efficient • Firms do not produce where P= min ATC; therefore, not productively efficient • Marginal revenue curve will never coincide with D=AR=P Monopolistic Competition& Excess Capacity • Product differentiation creates excess capacity • means that fewer firms operating at capacity could supply the industry output • Excess capacity is the gap between the minimum ATC output and the profitmaximization output Monopolistic Competition & Product Variety • Firms are able to have profit from differentiation in the long run because no exact substitute). • Advertising may increase costs, but also demand, and help maintain long-run profit. • Satisfies a wide range of consumer tastes and encourages innovation to differentiate. • Max Profit is Price x Product x Advertising Characteristics of Oligopoly 1) A few large producers (Oil, Telecom, Soda). 2) Homogenous OR differentiated products (Oil and Gasoline versus Automobiles) 3) Price maker, but still mutually interdependent (Strategic Behaviour & Interdependance KEY!!) 4) Relatively high entry barriers Mergers • Merging of two or more competing firms is beneficial in that it may increase their market share significantly, and thus achieve greater economies of scale. • The larger firm that results from a merger would have greater control over market supply and price. Measures of Industry Concentration • Price Leadership • The Four Firm Concentration Ratio (determines whether a industry is monopolistic competition or oligopoly, magic number is 40%) • Herfindahl Index (Herfindahl-Hirschman Index or HHI) (the sum of the squares of the market shares of each individual firm) Oligopoly Behavior: A Game Theory Overview • Game Theory: study of how people/firms behave in strategic situations. • Game Theory Model: can be used to analyse the behaviour of oligopolists. • The “Payoff Matrix” and Collusive Behaviour. • Often the “Payoff Matrix” is represented by the Prisoner’s Dilemma, which is used to explain ologopoly behaviour. Prisoner’s Dilemma Mutual Interdependence Revisited • Oligopolistic firms can influence rival's profits by changing pricing strategies • Each firm's profit depends on their pricing strategy in relation to their rival's • Firms make decisions based on how they think other firms will react. They anticipate the next move • Collusion is best, but firms cheat : ( Oligopoly and Advertising • Positive Effects of Ads: > Low-cost means to obtain info on product > Diminishes monopoly power by providing info on competing goods • Negative Effects of Ads: > Manipulate or persuade consumers > May create a barrier to entry with costs of advertising Oligopoly and Efficiency • Remember the triple equality for economic efficiency: (P = MC = minimum ATC), Oligopolists do not achieve this. • Produce where P > minimum ATC so they are not productively efficient. • Produce where P > MC so they are not alocatively efficient. • Oligopolies can be less desirable than monopolies because no regulation.