Monopolistic Competition: Lecture Notes & Market Analysis
advertisement

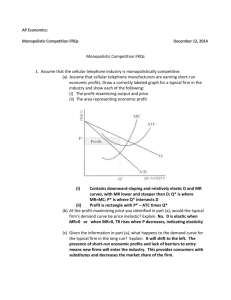
November 24, 2014 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Review HW: Activities 3-13, 3-14, 3-15 Lesson 3-9: Monopolistic Competition HW: Activity 3-16 No Current Event this week! Check Class Website for helpful videos on all Unit 3 Material! Monopolistic Competition • A mixture of Perfect Competition and Monopoly • Many firms sell similar but not identical products. • Relatively large # of sellers (not nearly as much as perfect competition) • Firms determine their own output are price makers. • Slightly differentiated products (distinguish from competition through reputation, customer service, location, brand name, etc.) • Examples: Retail clothing stores, restaurants, computers, apartments, fast-food, etc. • Easy entry and exit into industry Monopolistic Competition • Demand Curve downward sloping and MORE ELASTIC than Monopoly: Lower price to attract more customers due to competition. • Marginal Revenue Curve is steeper and below Demand Curve. • In the Short Run: 4 profit outcomes: 1. Positive Total Profit 2. Break Even 3. Loss but Not Shut Down 4. Shut Down • Firm MUST BREAK EVEN IN Long Run Monopolistic competitors in the short run (a) Firm makes profit (b) Firm makes losses Price Price MC ATC Price MC ATC ATC Price ATC Profit Demand Losses Demand MR MR 0 Profitmaximizing quantity Quantity 0 Lossminimizing quantity Quantity 4 The Long Run: Only a Normal Profit MC Price and Costs ATC P= ATC D MR = MC MR 0 Q3 Quantity Productive inefficiency: P > min ATC Allocative inefficiency: P > MC LO2 11-5 Monopolistic Competition: Inefficiency Price and Costs MC ATC P= min ATC P) Price is Lower D MR = MC Excess Capacity at Minimum ATC 0 MR Qm Qe Quantity Monopolistic competition is not efficient LO2 11-6