Document
advertisement
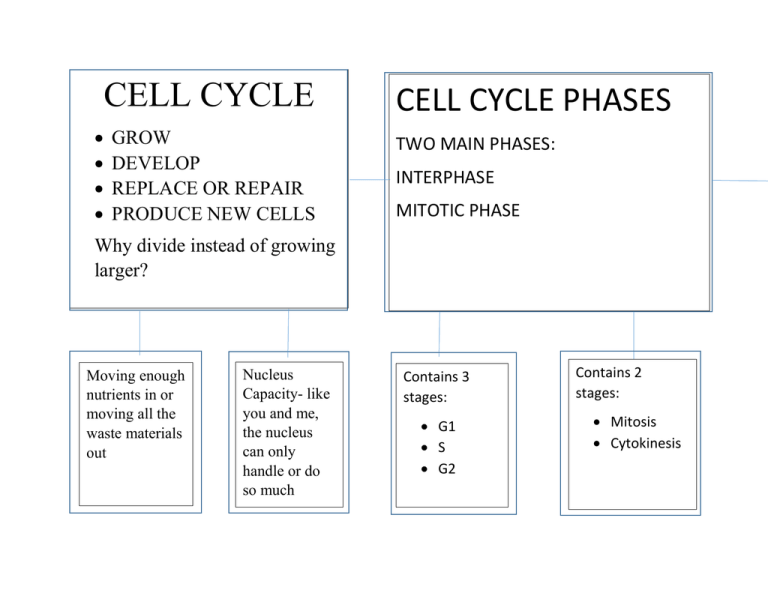
CELL CYCLE GROW DEVELOP REPLACE OR REPAIR PRODUCE NEW CELLS CELL CYCLE PHASES TWO MAIN PHASES: INTERPHASE MITOTIC PHASE Why divide instead of growing larger? Moving enough nutrients in or moving all the waste materials out Nucleus Capacity- like you and me, the nucleus can only handle or do so much Contains 3 stages: G1 S G2 Contains 2 stages: Mitosis Cytokinesis Phases of the cell cycle INTERPHASE Period of growth and development Most of the cell cycle DNA copied (chromatin) Cell prepares for division INTERPHASE-S STAGE Cell continues to grow Copies DNA DNA coils & forms a chromosome Identical join and DNA arranged in pairs called duplicated chromosomes INTERPHASE-G1 STAGE Rapid growth Normal cell functions occurs S STAGE CONTINUED Two identical chromosomes, called sister chromatids, make up a duplicated chromosome Sister chromatids held together by centromere If a cell has 11 duplicated chromosomes, how many chromatids does it have? INTERPHASE G2 STAGE ORGANELLE REPLICATION Period of growth and final prep for Mitosis Cell stores energy needed for Mitotic Phase Before division organelles are copied so new cells can function This copying occurs during all stages of interphase MITOTIC PHASE PHASES OF MITOSIS Mitosis: nucleus and contents divide Cytokinesis: cytoplasm and its contents divide Two daughter cells result Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase PROPHASE Coiled chromatin form visible duplicated chromosomes Nucleolus disappears Nuclear membrane bye! Spindle fibers form in cytoplasm METAPHASE Shortest phase Duplicated chromosomes line up in middle (equator) of cell (split occurs there) Incorrect genetic information can=cancer ANAPHASE Sister chromatids separate as spindle fibers pull apart into two identical single stranded chromosomes Cell gets longer during process Phase ends opposite end of cell TELOPHASE Spindle fibers disappear Chromosomes uncoil & nuclear membrane forms @ both ends (two new nuclei are formed) Described as reverse of Prophase CYTOKINESIS Cytoplasm divides forming two new daughter cells Division is different for plant and animal cells PLANT CELLS A new cell wall forms in the middle of the plant cell. Vesicles join form a cell plate Cell plate grows outward toward cell wall until two new cells form ANIMAL CELLS Membrane contract/squeezes causing furrow in middle of cell Furrow deepens until cell membrane comes together and divides the cell See page 102 RESULTS-CELL DIVISION Form of asexual reproduction for some unicellular organisms Allows multicellular organisms to grow & develop from one cell Worn out cells replaced (skin) Repair damage (broken bones)