PPT - Libertyville High School
advertisement

Libertyville HS
Key Questions
1. How do we
bring the South
back into the
Union?
2. How do we
rebuild the
South after its
destruction
during the war?
4. What branch
of government
should control
the process of
Reconstruction?
3. How do we
integrate and
protect newly
emancipated
black freedmen?
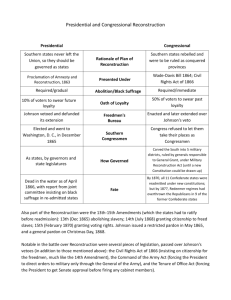
Republican Conflict
• President Lincoln view
– Saw war as “rebellion of
individuals”
– Believed Southern states never
legally left Union (unconstitutional
act)
– Second Inaugural address
• Republican Congress view
– “Radical Republicans”
– Saw war as rebellion of states
– Moral dimension to war: ending
slavery
– Punish the South!
Radical Congressional
Republicans
• Sen. Thaddeus Stevens
– South committed “state
suicide”
• Sen. Charles Sumner
– Southern states were
“conquered provinces”
President Lincoln’s 10% Plan
*
Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction
(December 8, 1863)
*
Replace majority rule with “loyal rule” in the
South
*
Pardon to all but the highest ranking military
and civilian Confederate officers.
*
When 10% of the voting population in the 1860
election had taken an oath of loyalty and
established a government, it would be
recognized.
*
Lincoln didn’t consult Congress regarding
Reconstruction
Wade-Davis Bill (1864)
Required 50% of the number of
1860 voters to take an “iron clad”
oath of allegiance (swearing they
had never voluntarily aided the
rebellion )
Senator
Benjamin
Wade
(R-OH)
Required a state constitutional
convention before the election of
state officials
Enacted specific safeguards of
freedmen’s liberties.
Congressman
Henry
W. Davis
(R-MD)
Wade-Davis Bill (1864)
President
Lincoln
Pocket
Veto
Wade-Davis
Bill
Pocket veto: if Congress sends a bill to President
within 10 days of adjournment, and President does
not act on the bill, it automatically dies
Freedmen’s Bureau (1865)
“Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen,
and Abandoned Lands”
Purpose = help black freedmen
adjust to freedom (food,
clothing, schools)
Congress authorized Bureau for
one year only; it existed from
1865-1868 (Johnson killed it)
Northerners who came to help
(or profit) from effort called
“carpetbaggers” by white
southern Democrats (INSULT!)
“Scalawags” = white, southern
Republican
Freedmen’s Bureau School
Assassination of Lincoln
• Civil War ended April 9,
1865
• Lincoln attended Ford’s
Theater on April 14, 1865
• Assassin: John Wilkes
Booth
– Background
– Conspiracy
– Death of Booth
• Lincoln died April 15,
1865
President Andrew Johnson
Jacksonian Democrat
Slave owner
Anti-Aristocrat
White Supremacist
Only Southern Democrat senator
to remain in Congress after
secession
Agreed with Lincoln
that states had never
legally left the Union
Picked to be VP by GOP in 1864
as reward, appeal to Democrats
13th Amendment
Ratified in December, 1865.
Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude,
except as punishment for crime whereof the
party shall have been duly convicted, shall
exist within the United States or any place
subject to their jurisdiction.
Congress shall have power to enforce this
article by appropriate legislation.
President Johnson’s Plan (10%+)
Johnson became President while
Congress was in recess, for 8 months
His plan was VERY generous to
South
Offered amnesty upon simple
oath to all except Confederate
civil and military officers
Civil, military officers and
Southerners with property worth
more than $20,000 had to apply
to give loyalty oath to Johnson,
directly
Allowed special congressional
elections, in 1865
President Johnson’s Plan (10%+)
Named provisional governors
in Confederate states and
called them to oversee
elections for constitutional
conventions (NO 10% loyalty
requirement)
In new constitutions, States
had to accept minimum
conditions: rejecting slavery,
secession and state debts
1. Disenfranchised certain leading Confederates.
EFFECTS?
2. Pardoned planter aristocrats were brought back
to political power to control state organizations.
3. Republicans were outraged that planter elite
were back in power in the South!
Growing Northern Alarm!
Southern states met Johnson’s easy
requirements to re-join union
Johnson granted 13,500 special
pardons to Southern white leaders
Revival of southern defiance: white
leaders passed laws to restrict
African Americans’ rights
BLACK CODES
Black Codes
Purpose (for White South)
Guarantee stable labor
supply now that blacks
were emancipated
* Restore pre-emancipation
system of race relations
*
*
*
Effect: re-establish slavery
(curfews, labor ks, only live in
rural areas = plantations)
Forced many blacks to
become sharecroppers
[tenant farmers]
Congress , President Split
Congress refused to seat Southern
congressional delegations in early
1866
Joint Committee on Reconstruction
created
February, 1866: President vetoed
continuing the Freedmen’s Bureau
bill
March, 1866: Johnson vetoed the
1866 Civil Rights Act, designed to
overturn Black Codes
Congress passed both bills over
Johnson’s vetoes: 1st in
U. S. history!!
th
14
Amendment
Ratified in July, 1868.
*
Declared all persons “born or naturalized” in US
citizens
*
Prohibited states from making laws interfering with
rights of citizens
*
Also prohibited states from depriving any person of
life, liberty, or property, without due process
*
Assured equal protection of laws to all citizens
Southern states would be punished for denying
the right to vote to black citizens
Confederates disenfranchised
The 1866 Congressional Election
A referendum on Radical Reconstruction
Johnson went on a propaganda tour around the
country to push his reconstruction plan (bad idea)
Republicans
won a 3-1
majority in
both houses
and gained
control of
every northern
state.
Johnson’s “Swing around
the Circle”
The Balance of Power in South
State
White Citizens
Freedmen
SC
291,000
411,000
MS
353,000
436,000
LA
357,000
350,000
GA
591,000
465,000
AL
596,000
437,000
VA
719,000
533,000
NC
631,000
331,000
Radical Plan: Reconstruction Acts
of 1867
1866 - Southerners had rioted
against blacks, killing hundreds
Congress: civil authorities (police,
etc) in the South were subject to
military supervision
Required new southern state
constitutions to include black
suffrage and ratification of the 13th
and 14th Amendments
In March, 1867, Congress
authorized the military to enroll
eligible black voters to begin the
process of constitution making
White Southerners disenfranchised
Reconstruction Acts of 1867
Military Reconstruction Act
*
Restarted political Reconstruction in the 10 Southern states
that refused to ratify the 14th Amendment (Tennessee
excepted)
*
Divided the 10 “unreconstructed states” into 5 military
districts.
Reconstruction Act of 1867:
Southern Reaction
• Southerners resented
Reconstruction
governments
– Graft
– Corruption
• Southerners couldn’t fight
back with ballots, chose
violence
– Knights of the White
Camellia
– Ku Klux Klan
Increasing Tension
Congress prepared for showdown with
President
Command of the Army Act
*
The President was required to issue all
Reconstruction orders through the General
in Chief, Ulysses Grant
Tenure of Office Act
*
The President could not remove
any officials, esp. Cabinet members,
without the Senate’s consent, if the position
originally required Senate approval
Designed to protect radical
members of Lincoln’s government.
Unconstitutional act
Edwin Stanton
President Johnson’s Impeachment
Johnson removed Stanton in February, 1868 (as secretary of war,
Stanton in charge of military in south)
Johnson replaced generals in the field who were more sympathetic
to Radical Reconstruction
The House impeached him on February 24, before even
drawing up the charges
by a vote of 126 – 47!
The Senate Trial
11 week trial
Impeachment political
Johnson acquitted
35 to 19 (one short of
required 2/3 vote)
The Election of 1868
• Johnson cast aside
by GOP
• They enlist U.S.
Grant instead
• GOP strategy
– “Wave the bloody
shirt”: draw
connection between
democrats, CSA
– “Vote as you shot”
– And the winner is…
Results
Grant:
Seymour:
214 ECV / 3,012,833
80 ECV / 2,703,249
500,000 freedmen voted!
Note: “Unreconstructed states” had not met
Congressional requirements to participate in
elections
President Ulysses S. Grant
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Born in OH
West Point graduate, 1843
Career military until 1854
He and his wife owned five
slaves (released one, 1859)
Worked for dad in leather
shop in Galena, IL until CW
Lincoln promoted Grant, rose
quickly in Western theater
Became General in Chief,
1864
Difficult relationship with
Johnson
Grant and his family
Grant Administration Scandals
Grant presided over an era
of unprecedented
growth and corruption
Credit Mobilier Scandal
1867-68: transcontinental RR stock
and bond swindle
(Grant’s VP, cabinet
involved)
1872 “Salary Grab”: 50%
Congressional pay raise,
retroactive two years prior!
Grant Administration Scandals
Politicians
• “Treasury Department
Scandal” (Whiskey Ring)
– Profiteering on overdue
taxes
Business
Labor•
Erie Railroad Scandal (NY
state)
– Bribes to state legislators
• City scandals
– “Tammany Hall Ring”
– William Marcy Tweed
– Big city machine corruption
1872 Presidential Election
• Many GOP disgusted by
corruption of Grant
• Eight candidates,
including splinter party,
Liberal GOP (Greely)
• Democrats also
nominated Greely!
• Greely dies Nov. 24
• Grant re-elected
The Panic of 1873
Raised “the money question”
*
Debtors seek inflationary
monetary policy by
continuing circulation of
greenbacks (paper $)
*
Creditors, intellectuals
support hard money
(primarily gold coinage)
1875: Specie Redemption
Act
Country put back on
hard money basis
Favored creditors
Blacks in Southern Politics
Core voters were black veterans
Blacks were politically unprepared
Blacks could register and vote in states since 1867
The 15th
Amendment
guaranteed
federal voting.
15th Amendment
Ratified in 1870.
The right of citizens of the United States to vote
shall not be denied or abridged by the United States
or by any state on account of race, color, or
previous condition of servitude.
The Congress shall have power to enforce this
article by appropriate legislation.
Women’s rights groups were furious that they were
not granted the vote!
Black Senate & House Delegates,
1872
The Failure of Federal Enforcement
Enforcement Acts of 1870 & 1871 Amnesty Act of 1872
First protected freedmen voters
Allowed re Second allowed federal
enfranchisement of
supervision of southern elections
all but 500 top
Third increased penalties vs.
Confederate leaders
attacking blacks & their voting
rights – Pres. Could suspend
Allowed white home
habeus corpus (KKK Act)
rule (white
supremacy)
“Solid South” voted
Democratic in
reaction to Radical
GOP Reconstruction,
for 90+ years
The Failure of Federal Enforcement
• Result of Amnesty Act
– Poll tax
– Literacy tests
– “Grandfather clause”
– Collectively known as
“Mississippi Plan”
• Jim Crow laws
– Segregation of races
in public places
– Plessy v. Ferguson
(1896) (Separate but
equal upheld)
Emergence of the “New South”
• Diversified farming
– One crop economy
broken
– Tenant farming
– Sharecropping
Tenancy & the Crop Lien System
Furnishing Merchant
Tenant Farmer
Landowner
Loan tools and seed up
to 60% interest to
tenant farmer to plant
spring crop.
Plants crop, harvests in
autumn.
Rents land to tenant in
exchange for ¼
to ½ of tenant farmer’s
future crop.
Farmer also secures
food, clothing, and
other necessities on
credit from merchant
until the harvest.
Merchant holds “lien”
{mortgage} on part of
tenant’s future crops as
repayment of debt.
Turns over up to ½ of
crop to land owner as
payment of rent.
Tenant gives remainder
of crop to merchant in
payment of debt.
Triumph of Segregation
• Barriers such as poll
taxes, etc resulted in
disenfranchisement of
Blacks
• Blacks economically
powerless to resist
• Booker T. Washington
– “Atlanta Compromise”
– Emphasis on economics,
not politics
– Rejected as “Uncle Tomism”
The Civil Rights Act of 1875
Crime for any individual
to deny full & equal use of
public conveyances and
public places
Prohibited discrimination
in jury selection
Shortcoming: lacked a
strong enforcement
mechanism
No new civil rights act
was attempted for 90 years
16 African American Senators, Reps in 1875
Northern Support Wanes
“Grantism” & corruption
Panic of 1873 [6-year
depression]
Concern over westward
expansion and Indian wars
With Civil Rights Act, North
felt job in South was done
Key monetary issues
* Should the government
retire $432m worth of
“greenbacks” issued during the Civil War?
* Should war bonds be paid back in specie or
greenbacks?
1876 Presidential Election
• One of the most disputed &
vicious elections in history
• Democrat: Sam Tilden
• GOP: Rutherford Hayes
• Issues in election
– End corruption
– End Reconstruction
– Civil Service reform
• Rampant fraud in FL, LA,
& SC (total 19 ECV)
The Political Crisis of 1877
• Each party announced it
won the disputed states
• All votes went to Hayes
after bitter dispute
• Back room deal to end
dispute
• In return for Southern
states votes, GOP
agreed to pull troops
out of south
• Referred to as
“Compromise of 1877”
Reconstruction was over!