Try these conversions, using the ladder method.
advertisement

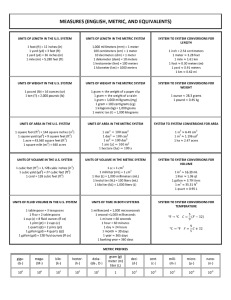
Metric Conversions Ladder Method T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ . Why Metric 1 A.Metric is easy because it’s based on POWERS OF 10! B.Our system (the English system) is all over the place C.All scientists use metric 2. WHAT DO I NEED TO KNOW? A.Our base units 1.Mass (gram == g) 2.Length (meter == m) 3.Volume (liter == L) UNITS OF MEASURE • What metric unit measures… • length? • Meter • volume? • Liter • mass/weight? • Gram • Volume of a solid • cm3 B.Our BIGGER prefixes 1.Kilo (k) – 1000 x base 2.Hecto (h) –100 x base 3.Deca (da) –10 x base C.Our SMALLER prefixes 1.Deci (d)—1/10 x base 2.Centi (c) –1/100 x base 3.Milli (m) –1/1000 x base Abbreviations Kilometers-km. Hectometers –hm. Dekameters- dam. Decimeters- dm. Centimeters- cm. Millimeters- mm. Kilograms-kg. Hectograms –hg. Dekagrams- dg. Decigrams- dg. Centigrams- cg. Milligrams- mg. Kiloliters-kL. Hectoliters –hL. Dekaliters- daL. Decileters- dL. Centiliters- cL. Milliliters- mL. 3. How do I remember this? KING HENRY DIED BY DRINKING CHOCOLATE MILK Conversion Practice Try these conversions using the ladder method. 1000 mg = _______ g 1 L = _______ mL 160 cm = _______ mm 14 km = _______ m 109 g = _______ kg 250 m = _______ km Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm 6m 7g 698 mg Metric Conversion Challenge Write the correct abbreviation for each metric unit. 1) Kilogram _____ 4) Milliliter _____ 7) Kilometer _____ 2) Meter _____ 5) Millimeter _____ 8) Centimeter _____ 3) Gram _____ 6) Liter _____ 9) Milligram _____ Try these conversions, using the ladder method. 10) 2000 mg = _______ g 15) 5 L = _______ mL 20) 16 cm = _______ mm 11) 104 km = _______ m 16) 198 g = _______ kg 21) 2500 m = _______ km 12) 480 cm = _____ m 17) 75 mL = _____ L 22) 65 g = _____ mg 13) 5.6 kg = _____ g 18) 50 cm = _____ m 23) 6.3 cm = _____ mm 14) 8 mm = _____ cm 19) 5.6 m = _____ cm 24) 120 mg = _____ g Compare using <, >, or =. 25) 63 cm 26) 536 cm 6m 53.6 dm 27) 5 g 28) 43 mg 508 mg 5g 29) 1,500 mL 30) 3.6 m 1.5 L 36 cm Check your answers! Try these conversions, using the ladder method. Conversion Challenge Abbreviations: 1. kg 2. m 3. g 4. mL 5. mm 6. L 7. km 8. cm 9. Mg 1. 2 g 2. 104000 m 3. 4.8 m 4. 5600 g 5. .8 cm 6. 5000 ml 7. 0.198 kg 8. 0.075 l 9. 0.5 m 10. 560 cm 11. 160 mm 12. 2.5 km 13. 65000 mg 14. 63 mm 15. 0.12 g 16. < 17. > 18. = 19. = 20. < 21. > Scientific Notation A way to express very small or very large numbers Example: 12345 = 1.2345 x 104 ____________ – the # of times the decimal was moved __________ – must be between 1 and 9 _________ 0.00456 = 4.56 x 10-3 (+) to the left (-) to the right Scientific Notation 56934 = 1280 = 0.0345 = 0.0000037 = Scientific Notation 2.347 x 10-3 = 8.98736 x 104 Reverse it! = 3.48763 x 10-4 = 5.7654 x 105 = (+) right (-) left BELL WORK With your partner, come up with 5 examples of metrics in everyday life. Compile the list in the “Notes” section of your binder. Be prepared to share with the class Some Examples of Metrics