Module 4 Review Our Atmosphere: Things Happen Here!
advertisement

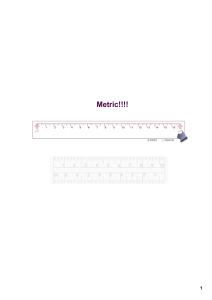
Key Points: -Keep a good notebook -Vocabulary words are in bold font -Icons will help alert you to important information -Questions: What do these icons indicate: Key Points: -Pace determines how quickly you complete the course. -Track tells if you are doing regular credit or advanced credit. -Question: How long does it take to finish the course (S1 and S2) with the traditional pace chart? What is different about the advanced track? Key Points: -Science is many things *a body of knowledge *a way of finding out about the world around us -Scientists have many shared characteristics: *curious *open minded *don’t give up easily *willing to learn new things -Question: Who can be a scientist? Key Points: Scientific Laws describe an observation. *cannot be broken Scientific Theories try to explain the observation. *they are supported by many years of experimentation and data *they can change if new data is discovered Question: What’s the most usual reason for a theory to be changed? A scientific theory is just a guess. True or False? Key Points: -Scientific Method is a process used in science. *Purpose – What you are trying to find out. *Hypothesis – Prediction about your purpose. *Experiment – Test designed to answer the purpose. (Data is recorded as well). - variables – the things that are changed - constants - the things that do NOT change *Analysis – Review and compare data from the experiment. *Conclusion – Determine whether the hypothesis is true or not. Questions: What are some other ways that scientists can investigate other than doing an experiment? What are some reasons that might explain why a scientist got different results when an experiment was repeated? Key Points: -A measuring system that is based on units of 10. -Used worldwide -Base units *length – meter *volume – liter *mass – kilogram *temperature – Celsius -common prefixes *kilo – 1000 *centi - .01 or 1/100 *milli - .001 or 1/1000 Question: Which metric unit is closest to a mile? Which metric unit would you use to measure the thickness of a dime? Key Points: -You can easily convert between metric units by moving the decimal point -Learn what the prefixes mean -practice, practice, practice Question: How many milliliters are in a liter? How many meters are in a kilometer? How many centigrams are in a gram? Key Points: -Graphs are used to organize data. -Line graphs are used to show how data changes over a period of time. - Bar graphs are used to compare data. - Labels and titles are very important. Question: Explain the data in this bar chart.