AP Biology Chapter 23 Worksheet Section A
advertisement

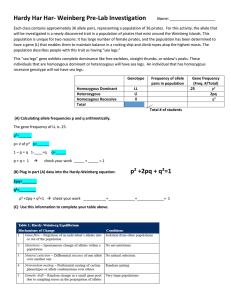
AP Biology Chapter 23 Worksheet 1. Do individuals evolve? Explain 2. Explain what microevolution is using an example. 3. What was missing in Darwin’s explanation of evolution? 4. Explain the theory of population genetics. 5. Explain the theory of modern synthesis. 6. Give the last names of the architects of modern synthesis. 7. Give the three main points of emphasis of the modern synthesis. 8. Explain the idea of gradualism. 9. Define the terms population and species. 10. Explain what is meant by a gene pool. 11. Explain what a fixed allele is. 12. Explain what the Hardy Weinberg Theorem describes. 13. Explain what this theorem states. 14. What do p and q represent in the Hardy Weinberg Theorem? 15. Give the formulas for the combined frequencies of each allele. 16. If we use wildflowers as an example and the probability of R is 80% and r is 20%. - calculate the probability of generating a homozygous dominant offspring. - calculate the probability of generating a homozygous recessive offspring. - calculate the probability of generating a heterozygous offspring. - show how these probabilities add up to 1 17. About 1 in 10,000 babies are born with phenylketonuria. Calculate the probability of producing each type of genotype. 18. Calculate the percentage of carriers produced in a population. 19. Explain how the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem plugs a hole in Darwin’s Theory. 20. Give the 5 conditions Hardy-Weinberg must satisfy. 21. According to this theory when does evolution occur? 22. How is the Hardy Weinberg theory used in evaluating an evolving population? 23. Explain what is meant by microevolution 24. When does microevolution occur? 25. Give the 4 factors that can alter the allele frequencies in a gene population. 26. Do they meet the Hardy-Weinberg criteria? 27. Why is natural selection the only factor that adapts a population to its environment. 28. Explain the concept of genetic drift and use an example in your answer. 29. Explain the concept of sampling errors. 30. Explain how a coin toss is analgous to sampling errors. 31. Give an example to help you explain the affect genetic drift can have on a small sample size. 32. Use an example to help you explain the bottleneck affect. 33. Use an example to help you explain the founder effect. 34. Explain how natural selection is a violation of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. 35. Explain why natural selection will lead some individuals to leave more offspring than others. 36. Use wildflowers as an example to help you explain number 13. 37. Explain the concept of gene flow and what causes it. 38. Explain how gene flow reduces differences in populations. 39. Explain what a mutation is and how it can change the gene pool. 40. Does a single locus mutation have a measurable affect on a population? Explain 41. Explain the concept of cumulative impact. 42. Explain how gene mutations serve as the raw material for natural selection