Document

Introduction to Biology and Populations Ecology
JEOPARDY!!
Characterstics of Life Lab Skills Ecology Overview Population Structure and
Dynamics
Population Growth
10
Characteristics of Life
When it’s hot outside, you sweat.
10
Characteristics of Life
Living things need to maintain homeostasis.
20
Characteristics of Life
If you cut yourself, a scab will form .
20
Characteristics of Life
Living things must grow and develop.
30
Characteristics of Life
Change that occurs in a species overtime in response to the continuously changing environment
30
Characteristics of Life
Living things evolve.
30
Characteristics of Life
40
Characteristics of Life
A plant moves towards the sun.
40 Characteristics of Life
Living things must be able to respond to stimuli
50
Characteristics of Life
All living organisms share similar instructions to run cell processes and pass on hereditary information.
50
Characteristics of Life
Living things must have
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid (DNA)
10 Lab Skills
What is an independent variable?
10 Lab Skills
What the experimenter is testing, should only be 1!
20 Lab Skills
What is a dependent variable?
20 Lab Skills
The biological response or what the experimenter measures
30 Lab Skills
Why do we need controlled variables?
30 Lab Skills
To ensure we are testing only one independent variable
40 Lab Skills
What should you do with your hypothesis after your experiment?
40 Lab Skills
*Accept- data collected in the experiment supports it.
*Reject- data collected does not support it.
50 Lab Skills
What do we call the “placebo” group in an experiment, and why is it essential?
50 Lab Skills
The Control Group- to use as a standard for comparison.
10
Ecology Overview
List the ecological levels of organization from least inclusive (specific) to most inclusive (broadest)
10
Ecology Overview
Organism, Popululation,
Community, Ecosystem, Biosphere
20
Ecology Overview
Define Ecology.
20
Ecology Overview
The study of how organisms interact with their environment and each other.
30
Ecology Overview
A group of pigeons.
30
Ecology Overview
Population
40
Ecology Overview
In addition to populations, ecosystems include…
40
Ecology Overview
Abiotic Factors
50
Ecology Overview
The sum of all of the planet’s ecosystems…
50
Ecology Overview
Biosphere
10
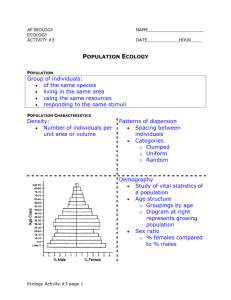
Population Structure
Define Population Density.
10
Population Structure
The number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume
20 Population Structure
How do scientists determine population density and why?
20
Population Structure
*Counting or
*Sampling Techniquesit’s often impossible and impractical to count all organism in an area.
30
Population Structure
Why would an organisms in a population take on clumped dispersion?
30
Population Structure
*Herding patterns
*social behavior
*uneven distribution of resources
*mating
40
Population Structure
What are survivorship curves?
40 Population Structure
*Graphs (curves) generated from life tables.
*Looks at average life span of organisms to make determinations about population growth.
50
Population Structure
What kind of distribution would a Cresotebush in the desert take and why?
50
Population Structure
Uniform- competition for water
10 Cells
My name is Bond, Ionic Bond;
Taken, not shared!
10
Population Growth
From: Mariano Cecowski
<MCecowski#NoSpam.sif.com.ar>
Q: if both a bear in Yosemite and one in
Alaska fall into the water which one disolves faster?
A: The one in Alaska because it is
HIJKLMNO
10
Population Growth
Alimentary: What Sherlock Holmes said to Dr. Watson.
Urinate: What a nurse would say if a patient asked her what room he's in.
Urine - The opposite of "You're out!"
Benign: What we want when we are eight.
Intestine - Currently taking an exam
CARDIOLOGY: advanced study of poker playing
TERMINAL ILLNESS: getting sick at the airport
10
Population Growth
What are the factors that limit population growth?
10
Population Growth
Density-dependent (competition, health, predation, physiological factors)
Density-independent (acidity, salinity, fires, catastrophes, weather conditions)
Boom and Bust cycles (pred/prey relationships, food supply)
10
Population Growth
20
Population Growth
What kind of growth model is represented below, and how is it possible?
20 Population Growth
Exponential Growth Model- conditions are ideal, birth rates exceed death rates
30 Population Growth
What are the characteristcs of the logistic growth model?
30 Population Growth
Idealized population growth slowed by limiting factors.
30
Population Growth
40
Population Growth
What is this? Analyze the data!
40
Population Growth
Age Structure Diagram-
*Decline in Population Growth
*Not enough children being born to replace those who die
50 Population Growth
What kind of growth do humans exhibit? Why is this a concern?
50 Population Growth
Exponential Growth.
*It’s ideal—and nothing’s perfect!
*resources will run out
*disease will spread
…?