Chemical Formulas
advertisement

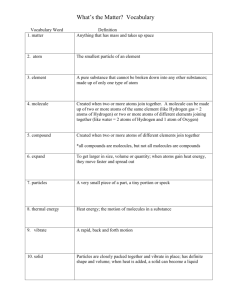
Chemistry Unit 2 Wear your safety goggles! Chemistry Unit 1 Structure of an Atom Protons and an Atoms identity Valence Electrons and Reactivity The Periodic Table Chemistry Unit 2 Chemical Formulas Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Law of Conservation of Mass Teks for Unit 1 and 2 • (5) Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: • Unit 1 • • • (A) describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud; (B) identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity; (C) interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements; • Unit 2 • • • (D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; (E) investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed; and (F) recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. 8.5 D Questions • The chemical formula for water is H2O. What do the H and O represent? What does the subscript 2 mean? • The chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide is H2O2. What does the chemical formula tell you about the hydrogen peroxide molecule? • Is CO the same as CO2? Explain. • One calcium (Ca) atom combines with two chlorine (Cl) atoms to make calcium chloride. What is the chemical formula of calcium chloride? • Suppose that all you know about a molecule is its chemical formula. What can the chemical formula tell you? 8.5 D Key Concepts • An element is made up of only one type of atom. Hydrogen, helium, and oxygen are examples of elements. Elements are pure substances. A pure substance is matter that has the same chemical composition throughout and cannot be separated into its parts by physical means. Elements form compounds. A compound is a pure substance that forms when two or more elements join chemically in a fixed proportion. • Just as an element is made up of one kind of atom, a compound is made up of one kind of molecule. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by very strong chemical bonds. These bonds form between atoms that share or transfer electrons. A molecule is the smallest unit of a compound that has all the properties of that compound. • A molecule can be made up of more than one atom of the same element. For example, two atoms of oxygen join to form a molecule of oxygen gas. • A molecule can also be made up of two or more different elements. A water molecule is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The illustration below is a model of a water molecule. • Molecules are identified by chemical formulas. A chemical formula is a group of chemical symbols and numbers that shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in a molecule. • The formula for a water molecule is H2 O. H is the chemical symbol for hydrogen. O is the chemical symbol for oxygen. The number 2 in the formula is called a subscript. It shows that the molecule contains two atoms of hydrogen. The O has no subscript. That means that the molecule contains only one atom of oxygen. Chemistry Vocabulary, Unit 2, part 1 • • • • pure substance: matter that has the same chemical composition throughout compound: a substance that forms when two or more elements join chemically molecule: a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds chemical formula: a group of chemical symbols and numbers that shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in a molecule How many chemical formulas can you name? Matter Compound Pure Substance Smallest unit is a molecule Smallest unit is an atom H2O H Chemical Formulas Subscripts And Lettering carbon dioxide CO2 Chemical Formulas of Household Items Common Name Chemical Name Chemical Formula aluminum foil vitamin C aluminum ascorbic acid Al C6 H8 O6 vinegar acetic acid (diluted) CH3 COOH table salt sodium chloride NaCl road salt calcium chloride CaCl2 table sugar sucrose C12 H22 O11 baking soda sodium bicarbonate NaHCO3 wood alcohol (solvent) methanol hydrogen peroxide hydrogen peroxide H2 O2 (diluted) dry ice carbon dioxide CH3 OH CO2 nail polish remover acetone CH3 COCH3 chalk, some antacidscalcium carbonate CaCO3 lighter fluid butane C4 H10 tincture of iodine iodine I2 soda water carbonic acid (diluted) H2 CO3 Chemical Formula CaC03 Common Name calcite Atoms Present 1 Calcium 1 Carbon 3 Oxygen Chemical Formula CaC03 Common Name calcite Atoms Present 1 Calcium 1 Carbon 3 Oxygen Chemical Formula CaC03 Common Name calcite Atoms Present 1 Calcium 1 Carbon 3 Oxygen NaCl C8H10N4O2 Mg3Al2Si3O12 O3 C6 H12 O6 NaCl C8H10N4O2 Mg3Al2Si3O12 O3 C6 H12 O6 NaCl C8H10N4O2 Mg3Al2Si3O12 O3 C6 H12 O6 Chemistry Vocabulary, Unit 2 pure substance: matter that has the same chemical composition throughout compound: a substance that forms when two or more elements join chemically molecule: a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds chemical formula: a group of chemical symbols and numbers that shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in a molecule physical change: a change in the form or appearance of a substance without a change in the identity of the substance \ chemical reaction: a process in which chemicals react, or change, to form new types of matter precipitate: a solid that forms during a chemical reaction in a solution reactant: a substance that enters into a chemical reaction product: a substance that forms during a chemical reaction combustion reaction: a chemical reaction that occurs when oxygen combines with certain other substances to release heat rusting: a slow chemical reaction between oxygen and a metal chemical reaction: a process in which chemicals react, or change, to form new types of matter reactants: the chemicals that enter into a chemical reaction; also called reagents products: the chemicals that form during a chemical reaction chemical equation: a statement that shows the reactants and products of a 8.5 E Questions • What is a chemical reaction? • What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical reaction? • How can you tell that a chemical reaction has taken place? • Are the products of a chemical reaction the same as the reactants? Explain why or why not. • What types of chemical reactions are there? 8.5 E Key Concepts • A physical change alters the form or appearance of a substance without changing the identity of the substance. During a physical change, no changes occur in the elements or compounds that make up the matter. For example, when water boils, water vapor is released. The water changes from a liquid to a gas, but it is still water. A chemical reaction is a process in which elements and compounds combine in new ways to form new substances Usually a physical reaction can be easily reversed. For example, to change water vapor back into a liquid, you simply let it cool down. A chemical reaction, on the other hand, is not easily reversed. Some signs that indicate a chemical reaction has occurred include a change in color and the release of heat or light. Sometimes a precipitate forms. A precipitate is a solid that forms during a chemical reaction that takes place in a solution. • Some chemical reactions cause release of a gas. If you drop an antacid tablet into water, a chemical reaction occurs. The bubbles that you see in the water are carbon dioxide given off by a reaction between a compound in the tablet and the water. But release of gas does not always mean a chemical reaction has taken place. For example, when water boils, this change from liquid water to water vapor is a physical change, not a chemical change. • The reactants are the chemicals that enter into a chemical reaction. The products are the chemicals that form during a chemical reaction. For example, when acetic acid (vinegar) combines with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), acetic acid and sodium bicarbonate are the reactants. The products are a salt, water, and a gas—carbon dioxide. • A combustion reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs when oxygen combines with certain other substances to release heat. A combustion reaction takes place when something burns. When wood burns, water vapor and carbon dioxide are given off. The ash that remains is very different from the wood that burned. It is a new substance with different properties. Rusting is another example of a chemical reaction. Rusting is a slow reaction between oxygen and a metal. A nail contains iron. Over time, the iron combines with oxygen in the air to form rust. The surface of the nail changes from smooth and shiny to rough and reddish brown. The rust is a different substance from iron. Reaction Types • Physical Reaction • Chemical Reaction Types of Reactions Types of Reactions Types of Reactions Types of Reactions Types of Reactions Types of Reactions Combustion Reaction Combustion Reaction C25H52 + 38 O2 → 25 CO2 + 26 H2O 1. What are the reactants in the chemical reaction that occurs when a candle burns? 2. The products of the reaction are carbon dioxide and water vapor. What two types of energy are also released? 3. What happened when your teacher placed a glass jar over the burning candle? Why do you think this happened? C25H52 + 38 O2 → 25 CO2 + 26 H2O 1. What are the reactants in the chemical reaction that occurs when a candle burns? 2. The products of the reaction are carbon dioxide and water vapor. What two types of energy are also released? 3. What happened when your teacher placed a glass jar over the burning candle? Why do you think this happened? 4. Explain How do you know this is a combustion reaction? 4. Explain How do you know this is a combustion reaction? 5. Apply How do you know this is a chemical reaction and not just a physical change? 5. Apply How do you know this is a chemical reaction and not just a physical change? Evidence of a Chemical Reaction Precipitation Gas Bubbles Change in color or temperature N2 + H2 → NH3 Types of Chemical Reactions Oxidizing Combustion 8.5 F Questions • Why are coefficients included in a chemical equation? • What is the law of conservation of mass? How does it apply to a chemical reaction? • If 12 oxygen atoms enter a chemical reaction, must the same 12 oxygen atoms be included in the products of the reaction? How do you know? • How can you tell if a chemical equation is balanced or unbalanced? • When balancing a chemical equation, which element should you balance first? 8.5 F Key Concepts • • A chemical equation shows the reactants and products of a chemical reaction. The reactants are shown on the left side of the equation, and the products are shown on the right side. Here is an example of a chemical equation: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2 O This equation shows that methane (CH4) and oxygen (O2) react to form carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2 O). The equation above is an unbalanced equation, which means that the numbers of atoms on the left and right sides of the arrow do not match. The equation shows two oxygen atoms in the reactants (on the left side), and three oxygen atoms in the products (on the right side). Also, there are four hydrogen atoms in the reactants and only two hydrogen atoms in the products. The balanced form of the chemical equation shown above is as follows: CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2 O Placing a coefficient of 2 in front of H2 O makes four hydrogen atoms on both sides of the equation. Then, placing a coefficient of 2 in front of O2 makes four oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation. • A balanced chemical equation shows how a reaction agrees with the law of conservation of mass. Every atom has a specific mass, and that mass cannot be increased or decreased by a chemical reaction. So, if four oxygen atoms enter a chemical reaction, then four oxygen atoms must leave the reaction as well. • In balanced chemical equations, the coefficients show the ratios in which chemicals combine and form. In the reaction between methane and oxygen described above, the ratio of the reactants is 1:2—one methane molecule to two oxygen molecules. This shows that 10 methane molecules will combine with 20 oxygen molecules, or that 1,000 methane molecules will combine with 2,000 oxygen molecules. • When you balance an equation, remember the following: – If no coefficient is visible in front of a reactant or product, the coefficient of that reactant or product is 1. – You might not need to change every coefficient when balancing a chemical equation. – A coefficient in front of a reactant or product affects each element inside that reactant or product. For example, putting a coefficient of 2 in front of H2 O means that there are four hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. – Begin by balancing the element that appears in the fewest places in the equation. When you balance an equation, remember the following: • If no coefficient is visible in front of a reactant or product, the coefficient of that reactant or product is 1. • You might not need to change every coefficient when balancing a chemical equation. • A coefficient in front of a reactant or product affects each element inside that reactant or product. For example, putting a coefficient of 2 in front of H 2 O means that there are four hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. • Begin by balancing the element that appears in the fewest places in the equation. Balancing Chemical Reactions • Unbalanced Reaction – CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2 O • Balanced Reaction – CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2 O Evidence of a Chemical Reaction • • • • • • Color Change Temperature Change Release of Gas Bubbles Precipatate Light Odor