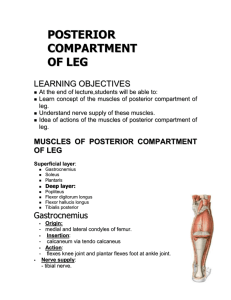
Lateral plantar nerve - Yeditepe University Faculty of Medicine 1st
advertisement
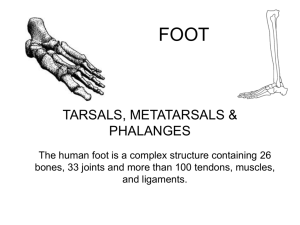
EXAM OF THE LOWER EXTREMITIES From A Practical Guide to Clinical Medicine University of California, San Diego 1 Region of the lower limb distal to ankle joint Subdivided into Ankle Metatarsus Digits Superior surface (dorsum of foot) Inferior surface (sole) Body's point of contact with the ground Provides a stable platform for upright stance. Supports the body weight and provides leverage for walking and running. Unique -constructed in the form of arches, adapt its shape to uneven surfaces. Serves as a resilient spring to absorb shocks, such as in jumping. 4 1…skin of the foot Skin of the dorsum of the foot thinner and less sensitive than that of the sole The subcutaneous tissue is loose deep to the dorsal skin Edema most marked on the dorsal skin especially anterior to and around the medial malleolus Entire sole is sensitive (“ticklish”), especially the thinner-skinned area underlying the arch of the foot. Ticklish? gargalesis Neurosci Res. 2010 Dec;68(4):285-9. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus enhanced by tickling stimulation with positive emotion. 2. Deep fascia of the foot & Plantar fascia Thin where it is continuous proximally with the inferior extensor retinaculum. Over the lateral and posterior aspects of the foot continuous with the plantar fascia, the deep fascia of the sole. Plantar fascia holds the parts of the foot together, helps protect the sole from injury, and helps support the longitudinal arches of the foot. 3. Compartments by the deep fascia Midfoot and forefoot Medial compartment of the sole Central compartment of the sole Lateral compartment of the sole Forefoot 4th compartment interosseous compartment of the foot Dorsal compartment of the foot 5th compartment between dorsal fascia of the foot & tarsal bones & compartment; Transverse section of the foot: 1, lateralhttp://home.comcast.net/~wn dorsal interosseous fascia compartment; of the midfoot3,and or/soleoffoot.htm 2, central medial compartment; forefoot 4, interosseous compartment. Arrows indicate the highpressure areas that often lead to foot ulceration. 4. Tarsal tunnel Formed on the posteromedial side of the ankle by: A depression formed by Medial malleolus of tibia Medial &posterior surfaces of talus Inferior surface of sustentaculum tali Medial surface of calcaneus Overlying flexor retinaculum Contents from ant. to post. (Tom Dick ANd Harry) •Tibialis posterior tendon •Flexor digitorum longus tendon •Posterior tibial artery •Tibial nerve •Flexor hallucis longus tendon 5. Flexor retinaculum Attaches above to medial malleolus below to calcaneus 2 compartments on the posterior surface of medial malleolus for tibialis posterior & flexor digitorum longus tendons Laterally posterior tibial artery ,veins & tibial nerve through tarsal tunnel into sole of foot Lateral to tibial nerve tendon of flexor hallucis longus Pulse of posterior tibial artery through flexor retinaculum midway between medial malleolus and calcaneus 6. Extensor retinacula Prevent tendon bowing during extension of the foot and toes Superior extensor retinaculum Superior to the ankle Attached to anterior borders of the fibula & tibia Inferior retinaculum Y-shaped Attached to lateral side of calcaneus Extensor digitorum longus & fibularis tertius tendons Medially Dorsalis pedis artery Extensor hallucis longus tendon tibialis anterior tendon pass under extensor retinacula 7. Fibular (Peroneal) retinacula Bind the tendons of fibularis longus & fibularis brevis to lateral side of the foot Superior fibular retinaculum Between lateral malleolus & calcaneus Inferior fibular retinaculum Attaches to lateral surface of calcaneus around fibular trochlea 8. Plantar aponeurosis A thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot A thick central part Weaker medial and lateral parts Tougher, denser, and elongated than palmar aponeurosis Anchored to the medial process of calcaneal tuberosity Supports the longitudinal arch of the foot & protects deeper structures in the sole 9. Fibrous sheaths of toes Flexor digitorum longus, flexor digitorum brevis, & flexor hallucis longus tendons enter fibrous digital sheaths on plantar aspect of digits. Formed by fibrous arches & cruciate (cross-shaped) ligaments Hold the tendons to the bony plane and prevent tendon bowing when the toes are flexed. 10. Extensor hoods Extensor digitorum longus, extensor digitorum brevis, and extensor hallucis longus expand over the proximal phalanges to form complex dorsal digital expansions ("extensor hoods"). Many of the intrinsic muscles of the foot insert here. This allows the forces from these muscles to be distributed over the toes to cause flexion of the metatarsophalangeal joints while at the same time extending the interphalangeal joints. 15 20 individual muscles of the foot 14 located on the plantar aspect 2 on the dorsal aspect 4 intermediate in position Plantar muscles function primarily as a group during the support phase of stance, maintaining the arches of the foot Few delicate functions compared to hand muscles Concerned with supporting the arches of the foot Muscles in the dorsum Extensor digitorum brevis Attached to a roughened area on the superolateral surface of the calcaneus lateral to the tarsal sinus Extensor hallucis brevis The part of the muscle associated with the great toe Deep fibular nerve Muscles in the sole Organized into four layers From superficial to deep or plantar to dorsal First layer Medial to lateral Abductor hallucis Flexor digitorum brevis Abductor digiti minimi Second layer Quadratus plantae Lumbrical muscles Third layer Flexor hallucis brevis Adductor hallucis Flexor digiti minimi brevis Fourth layer Dorsal & plantar interossei Functions & innervations of the muscles of the foot 1st layer Abductor hallucis Flexor digitorum brevis Abductor digiti minimi 2nd Medial plantar nerve (S2, S3) Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) layer Quadratus plantae Lumbricals 3rd layer Assists flexor digitorum longus in flexing lateral four digits Flex proximal phalanges, extend middle & distal phalanges of lateral four digits 4th layer Flexor hallucis brevis Adductor hallucis deep branch Flexor digit minimi brevis superficial branch Plantar interossei (three muscles) Adduct digits (2-4) and flex metatarsophalangeal joints Dorsal interossei (four muscles) Abduct digits (2-4) and flex metatarsophalangeal joints 20 Supply of the foot Terminal branches of anterior tibial artery & posterior tibial artery dorsalis pedis artery & plantar arteries Posterior tibial artery in the sole divides into lateral & medial plantar arteries Lateral plantar artery +Dorsalis pedis artery Deep plantar arch Lateral & medial plantar arteries Lateral plantar artery Major branches of the deep plantar arch Digital branch to lateral side of little toe 4 plantar metatarsal arteries 3 perforating arteries Medial plantar artery Passes deep to the abductor hallucis Ends by joining the digital branch of the deep plantar arch Superficial branch Dorsalis pedis artery Major source of blood supply to forefoot Continuation of anterior tibial artery Begins midway between malleoli Runs deep to inferior extensor retinaculum between extensor hallucis longus & extensor digitorum longus tendons on the dorsum of the foot Dorsalis pedis artery Passes inferiorly as deep plantar artery Joins deep plantar arch in the sole of the foot. Branches lateral and medial tarsal branches arcuate artery first dorsal metatarsal artery 25 As in the rest of the lower limb, there are both superficial and deep veins in the foot. Unlike the leg and thigh, however, the venous drainage of the foot is primarily to the major superficial veins Medial side Great saphenous vein Lateral side Small saphenous vein 28 Tibial nerve Deep fibular nerve Superficial fibular nerve Sural nerve Saphenous nerve Tibial nerve All intrinsic muscles of the foot except for the extensor digitorum brevis, innervated by the deep fibular nerve Deep fibular nerve often also contributes to innervation of the first and second dorsal interossei. Tibial nerve Enters the foot through tarsal tunnel posterior to medial malleolus Lateral to posterior tibial artery Medial calcaneal branches heel Midway between medial malleolus & heel large Medial plantar nerve smaller Lateral plantar nerve Medial plantar nerves Larger & more anterior terminal branch Arises deep to the flexor retinaculum Major sensory nerve in the sole Compared to lateral plantar nerve, supplies more skin area but fewer muscles. Its distribution to both skin and muscles of comparable to that of the median nerve in the hand. Skin on most of the anterior two-thirds of the sole and adjacent surfaces of the medial three and one-half toes, which includes the great toe. Four intrinsic muscles- abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis, and the first lumbrical. Lateral plantar nerve Smaller & more posterior terminal branch Also courses deep to the abductor hallucis but runs anterolaterally between the 1st and 2nd layers of plantar muscles, on the medial side of the lateral plantar artery. Ends @ lateral compartment, dividing into superficial and deep branches. Lateral plantar nerve Superficial branch Two plantar digital nerves (one common and one proper) Skin of the plantar aspects of the lateral one and a half digits, the dorsal skin and nail beds of their distal phalanges, and skin of the sole proximal to them. Deep fibular nerve Passes deep to extensor retinaculum Enters dorsal aspect of the foot on the lateral side of dorsalis pedis artery. Muscles on dorsum of the foot When finally emerges as a cutaneous nerve, so far distal in the foot ; small area of skin remains available for innervation: web of skin between and contiguous sides of the 1st and 2nd toes Divides into two dorsal digital nerves Superficial fibular nerve Emerges as a cutaneous nerve about two thirds of the way down the leg Skin on the anterolateral aspect of leg Divides into Medial and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves Most of the skin on the dorsum of the foot Terminal branches Dorsal digital nerves (common & proper) Skin of the proximal aspect of the medial half of the great toe & that of the lateral three and a half digits. Sural nerve Cutaneous branch of tibial nerve Originates high in the leg Sural nerve formation: Medial sural cutaneous nerve (from the tibial nerve) Sural communicating branch of common fibular nerve Accompanies small saphenous vein Enters the foot posterior to the lateral malleolus ankle joint & skin on the lateral side of the foot and dorsolateral surface of the little toe. Saphenous nerve • Longest & most widely distributed cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve •Only branch to extend beyond the knee •Originates in the thigh Skin and fascia on the anteromedial aspect of the leg, ankle joint Skin along the medial side of the foot as far anteriorly as the head of the 1st metatarsal , medial side of the proximal foot Cutaneous innervation of the foot Medially Saphenous nerve distally to the head of 1st metatarsal Superiorly (dorsum of foot) Superficial (primarily) Deep fibular nerves Inferiorly (sole of foot) Medial & lateral plantar nerves Laterally Sural nerve Posteriorly (heel) Medial & lateral calcaneal branches of tibial & sural nerves, respectively 39 Medial superficial lymphatic vessels medial side of the dorsum & sole of the foot Accompany great saphenous vein Lateral superficial lymphatic vessels lateral side of the dorsum & sole of the foot Accompany small saphenous vein Deep inguinal lymph nodes Iliac lymph nodes