Respiratory System PowerPoint
advertisement

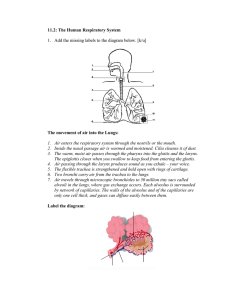
The Respiratory System • The respiratory system is the group of organs that takes in oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide • Respiration is another name for breathing • Respiration is the transport of oxygen from outside the body to cells and the transport of carbon dioxide and wastes away from the cells • When we inhale, oxygen in the air moves into the blood from the lungs • Oxygen is used for cellular respiration The O₂/C O₂ Exchange • When we exhale, carbon dioxide is released from the body • When we inhale, O₂ in the air moves into the blood from the lungs • O₂ leaves the blood and enters the body cell through the capillaries • O₂ is used for cellular respiration • When we exhale, CO₂ is released from the body • CO₂ moves from the body cells to the capillaries • Blood carries CO₂ through the heart and to the lungs • CO₂ moves out of the lung capillaries and into the lungs to be exhaled Parts of the Respiratory System • Air enters your respiratory system through your nose and your mouth • Air flows into the pharynx, or throat • The pharynx branches into two tubes • One tube leads to the stomach • The other tube leads to the lungs • The larynx is the part of the throat that holds the vocal chords • When air passes across the vocal chords, they vibrate, making a voice Parts of the Respiratory System • The larynx is connected to the trachea, or windpipe • Air flows from the larynx through the trachea to the lungs • The trachea splits into two branches called bronchi (bronchus, singular) • The bronchi connect to each lung • The bronchi branch off into smaller tubes called bronchioles • Bronchioles lead to tiny sacs called alveoli • Alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels • Gases move between the blood vessels and alveoli Parts of the Respiratory System • As you breathe, air is sucked into and forced out of the alveoli • Breathing is carried out by the diaphragm and the rib muscles • The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle below the lungs • When you inhale the diaphragm contracts, or moves down • The volume of the chest increases • This creates a vacuum and air is sucked in • Exhaling is the reverse process Disorders of the Respiratory System • Asthma – condition in which airways are narrowed because of inflammation of the bronchi • Pneumonia – inflammation of the lungs that is usually caused by bacteria or viruses – alveoli fill with fluid • Emphysema – alveoli have been damaged so oxygen cannot pass across into the blood as well as it should – often linked to long term use of tobacco