diversity in animal kingdom chapter 7 class ix - e-CTLT
advertisement

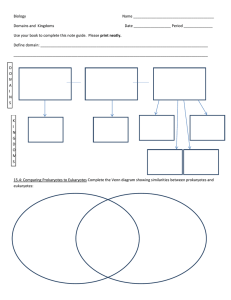
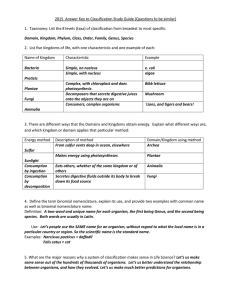
BY Ms SUMAN LATA TGT BIOLOGY , KV MIRC DEFINITION CLASSIFICATION- Biological classification, or scientific classification in biology, is a method of scientific taxonomy used to group and categorize organisms hierarchically according to their observed similarities/ differences and relationships. The Rank-based systems use a fixed number of levels in the hierarchy, such as kingdom, family, genus or species etc. Also known as Taxonomy TAXONOMY is the science of naming, describing and classifying organisms and includes all plants, animals and microorganisms of the world. Using morphological, behavioural, genetic and biochemical observations, taxonomists identify, describe and arrange species into classifications NEED FOR CLASSIFICATION Classification is important because it allows scientists to identify, group, and properly name organisms via a standardized system (Linnaeus Taxonomy); based on similarities found in the organisms DNA/RNA (genetics), Adaptations (Evolution), and Embryonic development (Embryology) to other known organisms to better study and understand the new organism as a whole. Several other branch of studies are also benefitted like Ecology, Forestry, Biogeography etc DIFFERENT APPROACH FOR CLASSIFICATION CLASSIFICATION (with example) k P C O F G S HEIRARCHY OF CLASSIFICATION GROUPS The groups in the classification are known as taxa (singular: taxon). Each taxon has a specific level of similarities and differences. Kingdom is the first category of taxon. A group of division forms kingdom. It is the largest group pf living organism. Differences are higher and similarities are very less in Kingdom Species: It is a group of organism that shows maximum similarities and capable of interbreeding. They are capable to give rise to fertile offspring. Genes: A group of species form genus that are having common ancestor. Family: A group of genera forms family that possesses certain common characters. Order: A group pf family who inter-related with each other forms order. Class and Division (Phylum): A group of orders forms class and group of class forms division. CELLS : DIFFERENTIATION Recall that there are two basic types of cells: eukaryotes and prokaryotes. EUKARYOTES are more complex in structure, with nuclei and membrane-bound organelles. Some characteristics of eukaryotes are: Large (100 - 1000 μm) DNA in nucleus, bounded by membrane Genome consists of several chromosomes. Most forms are multicellular Aerobic PROKARYOTES refer to the smallest and simplest type of cells, without a true nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria fall under this category. Some characteristics: Small (1-10 μm) DNA circular, unbounded Genome consists of single chromosome. Most forms are singular Anaerobic HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE : LEGENDARY TAXONOMISTS