2015 Answer Key to Classification Study Guide (Questions to be
advertisement
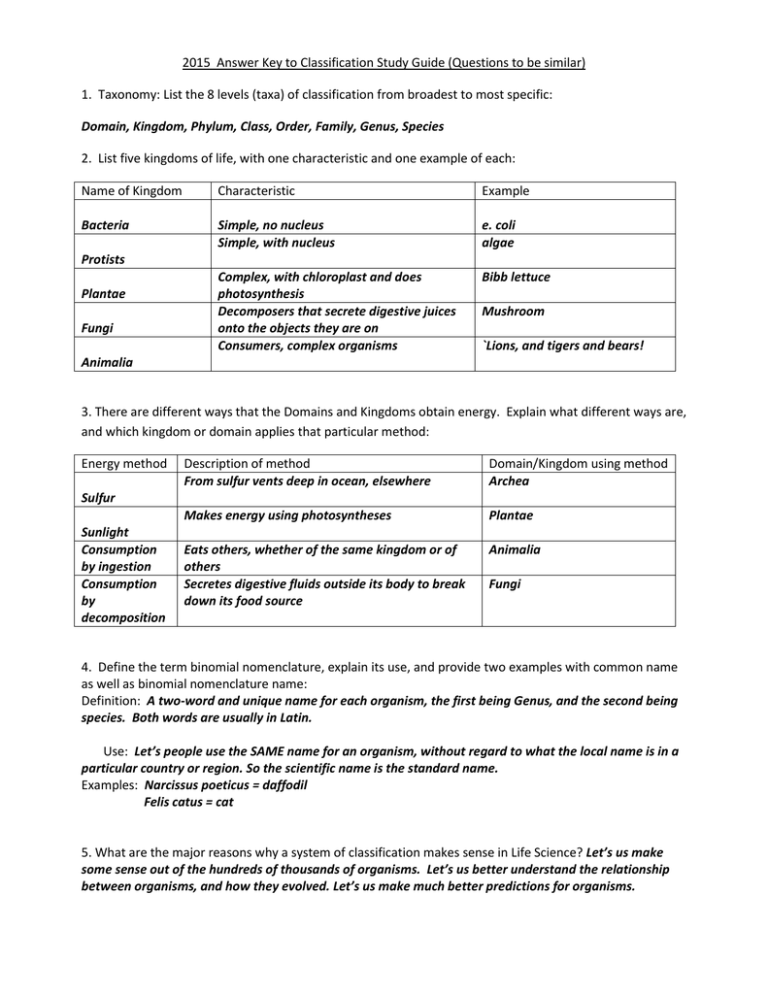
2015 Answer Key to Classification Study Guide (Questions to be similar) 1. Taxonomy: List the 8 levels (taxa) of classification from broadest to most specific: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 2. List five kingdoms of life, with one characteristic and one example of each: Name of Kingdom Characteristic Example Bacteria Simple, no nucleus Simple, with nucleus e. coli algae Complex, with chloroplast and does photosynthesis Decomposers that secrete digestive juices onto the objects they are on Consumers, complex organisms Bibb lettuce Protists Plantae Fungi Mushroom `Lions, and tigers and bears! Animalia 3. There are different ways that the Domains and Kingdoms obtain energy. Explain what different ways are, and which kingdom or domain applies that particular method: Energy method Description of method From sulfur vents deep in ocean, elsewhere Domain/Kingdom using method Archea Makes energy using photosyntheses Plantae Eats others, whether of the same kingdom or of others Secretes digestive fluids outside its body to break down its food source Animalia Sulfur Sunlight Consumption by ingestion Consumption by decomposition Fungi 4. Define the term binomial nomenclature, explain its use, and provide two examples with common name as well as binomial nomenclature name: Definition: A two-word and unique name for each organism, the first being Genus, and the second being species. Both words are usually in Latin. Use: Let’s people use the SAME name for an organism, without regard to what the local name is in a particular country or region. So the scientific name is the standard name. Examples: Narcissus poeticus = daffodil Felis catus = cat 5. What are the major reasons why a system of classification makes sense in Life Science? Let’s us make some sense out of the hundreds of thousands of organisms. Let’s us better understand the relationship between organisms, and how they evolved. Let’s us make much better predictions for organisms. 7. Complete a branching diagram showing the six organisms (o) pictured below in the appropriate location, with the appropriate 5 adaptations along the branch. Finch Lizard Feathers Salamander Eel Claws Lungs Jaws hagfish salamander Wormlike hagfish eel Finch Lizard Adaptations: Claws, feathers, jaws, lungs, 8. Compare and contrast Linnaean taxonomy to Cladistic taxonomy, to include two specifics where the two systems would differ in classification. Compare: both classify organisms for many purposes. Contrast: Traditional Linnaean relies on similarities in appearance and function of organisms, while Cladistic relies on evolutionary progress. Birds and reptiles are examples of how they come out with different classifications. For the traditional Linnaean approach, the birds are in a totally different category from reptiles. For the cladistics approach, since birds evolved from reptiles, they are in the same broad clade. 9. Be prepared to make a dichotomous key similar to the one done in class.









