Cell Cycle
advertisement

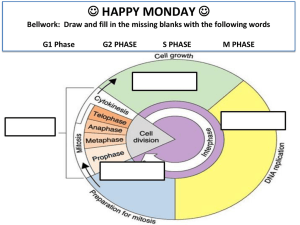
• • Cells grow by obtaining nutrients and discharging waste. Cells usually reach a certain size and then divide. An adult’s cells are no larger than a child’s, just that there are more of them. • • • • Smaller a cell is, the better for transporting gases and nutrients into the cell. Smaller Cell = More Surface Area Larger size is more demanding of nutrients Larger size put more demands on DNA Cell grows, prepares for division, divides to form two new daughter cells Interphase Divided into 3 phases (longest) 1. G1 Phase: period of activity where cells increase in size & synthesize new proteins & organelles Interphase cont. 2. S Phase: Chromosomes are replicated & synthesis of DNA molecules. 3. G2 Phase: DNA replication complete, the shortest phase begins. Organelles/molecules for cell division produced. Now M phase can begin. M Phase: Mitosis takes place or DIVISION OF CELL NUCLEUS! Later cytokinesis takes place M Phases-Mitosis: -Interphase -Prophase -Metaphase -Anaphase -Telophase Cytokinesis: Division of cytoplasm at end of mitosis Remember: IPMAT Chromosome: made of DNA which carry cell’s coded genetic info Centrioles: help organize spindle fibers Sister Chromatids: chromosome has 2 identical chromatids Centromere: holds sister chromatids together, separates chromosomes in anaphase Spindle fibers: fanlike microtubule, helps separate chromosomes Long, ¾ of time Remember: IPMAT Prophase • During prophase, the chromosomes become visible. The centrioles take positions in opposite sides of the cell and form the spindle. Back Prophase - Mitosis Metaphase • During metaphase, the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. • Microtubules connect the centromere of each chromosome to the two poles of the spindle. Back Anaphase • During Anaphase, the centromeres that joined the sister chromatids split becoming individual chromosomes. Back Telophase • The chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cell and a nuclear envelope forms around each group of chromosomes. Cytokinesis • The process in which the cytoplasm separates, forming completely the two new daughter cells. • It usually occurs about the same time as Telophase. • This occurs different in plants and in animals. Interphase Anaphase Prophase Metaphase Telophase Match word with definition The second stage, division of the cytoplasm. ( B ) a) Mitosis The first stage, division of the cell nucleus ( A ) b) Cytokinesis c) Chromatids One of the two identical “sister” parts of a duplicated chromosome. ( C ) Match word with definition Usually located in the middle of the chromatids (C ) Period of the cell cycle between cell divisions ( F) The series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide ( D) First and longest phase of mitosis ( A) Two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope ( E ) Fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes during mitosis ( B ) A. Prophase B. Spindle C. Centromeres D. Cell cycle E. Centrioles F. Interphase Mini-Test How do you call the process in which a cell divides into two new daughter cells? a) Cell Fractioning b) Cell Division What is the second stage in the cell cycle, where the cytoplasm divides? a) Mitosis b) Cytokinesis Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases, which are they? a) G1Phase, Sphase, G2Phase, cytokinesis b)Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase When are the chromosomes replicated, or “copied”? a) Before cell division b) After cell division