CHAPTER 7 A TOUR OF THE CELL
advertisement

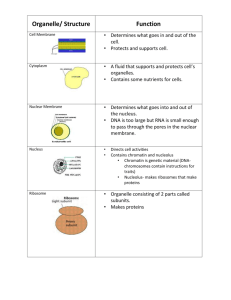
CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Cytology: science/study of cells Light microscopy resolving power~ measure of clarity Electron microscopy TEM ~ electron beam to study cell ultrastructure SEM ~ electron beam to study cell surfaces Cell fractionation ~ cell separation; organelle study Ultracentrifuge ~ cell fractionation; 130,000rpm A cell is a living unit greater than the sum of its parts • While the cell has many structures that have specific functions, they must work together. Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells AP Biology Eukaryote plant cells Cell Types: Prokaryotic Nucleoid: DNA concentration No organelles with membranes Ribosomes:protein synthesis Plasma membrane: (all cells); semi-permeable Cytoplasm/cytosol(all cells) Cell types: Eukaryotic Nucleus:membrane enclosed organelle containing chromosomes Membrane bound organelles of specialized form and function Generally larger than prokaryotic cells Cell Size As cell size increases, the surface area to volume ratio decreases Rates of chemical exchange may then be inadequate for cell size Cell size, therefore, remains small Why organelles? Specialized structures specialized functions mitochondria cilia or flagella for locomotion Containers partition cell into compartments create different local environments chloroplast separate pH, or concentration of materials distinct & incompatible functions lysosome & its digestive enzymes Membranes as sites for chemical reactions unique combinations of lipids & proteins embedded enzymes & reaction centers Golgi chloroplasts & mitochondria AP Biology ER Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? make proteins proteins control every cell function transfer energy for daily life for growth make more cells growth repair renewal AP Biology Proteins do all the work! proteins cells DNA AP Biology organism Repeat after me… Proteins do all the work! Cells functions Building proteins read DNA instructions build proteins process proteins folding modifying removing amino acids adding other molecules AP Biology e.g, making glycoproteins for cell membrane address & transport proteins Building Proteins Organelles involved nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus vesicles The Protein Assembly Line nucleus AP Biology ribosome ER Golgi apparatus vesicles Nucleus DNA Function chromosome protects DNA Structure histone protein nuclear envelope double membrane membrane fused in spots to create pores allows large macromolecules to pass through nuclear pores What kind of molecules need to pass through? AP Biology nuclear pore nucleolus nuclear envelope AP Biology Nucleolus Function ribosome production build ribosome subunits from rRNA & proteins exit through nuclear pores to cytoplasm & combine to form functional ribosomes large subunit small subunit AP Biology rRNA & proteins ribosome nucleolus large subunit Ribosomes Function small subunit protein production Structure rRNA & protein 2 subunits combine 0.08mm Ribosomes Rough ER Smooth ER AP Biology Types of Ribosomes Free ribosomes suspended in cytosol synthesize proteins that function in cytosol Bound ribosomes AP Biology attached to endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins for export or for membranes membrane proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum Function processes proteins manufactures membranes synthesis & hydrolysis of many compounds Structure AP Biology membrane connected to nuclear envelope & extends throughout cell Types of ER rough AP Biology smooth Smooth ER function Membrane production Many metabolic processes synthesis synthesize lipids oils, phospholipids, steroids & sex hormones hydrolysis hydrolyze glycogen into glucose in liver detoxify drugs & poisons in liver ex. alcohol & barbiturates AP Biology Synthesize components of the Endomembrane System Build new membrane synthesize phospholipids builds membranes ER membrane expands bud off & transfer to other parts of cell that need membranes AP Biology Rough ER function Produce proteins for export out of cell protein secreting cells packaged into transport vesicles for export Which cells have lot of rough ER? AP Biology Golgi Apparatus AP Biology Vesicle transport protein vesicle budding from rough ER ribosome AP Biology migrating transport vesicle fusion of vesicle with Golgi apparatus Any Questions!! AP Biology 2007-2008