Memory - Reading Community Schools
advertisement

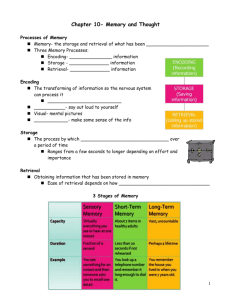
Memory Cody Reardon Human Behavior What is Memory and why is it Important? • Memory- is the process by which we recollect prior experiences, information, and skills learned in the past. – We classify memory by knowledge, skills, and events. Episodic Memory • The first type of memory is Episodic (or memory of a specific event that took place in the person’s presence) • Some memories are so surprising and significant to us that is as if a flashbulb went off. Flashbulb memory is something that can be remembered in great detail. • Examples? Generic Memory • Generic Memory (memory that is general knowledge that people remember) is less specific in the where and when. – Who was the first president? – When did you learn that? Procedural Memory • The third kind of memory Procedural Memory (consists of skills or procedures you may have learned) – What are some of these skills you can remember off hand? – How and when did you learn them? Three Processes of Memory • 1. Encoding (the translation of information into a form in which it can be stored) is a way for people to individualize how they place their memories in their memory bank. – Visual Codes (See the letters in your mind as a picture) – Acoustic Codes (read and repeat out loud or silently) – Semantic Codes (relating to meaning) Three Process of Memory • 2. Storage (the maintenance of encoded information over a period of time) – Maintenance Rehearsal- Repeating information over and over – Elaborative Rehearsal- relating new information to information already known – Organizational Systems- Memories you organize in your mind for future use (chronological) Three Processes of Memory • 3. Retrieval- locating stored information and returning it to conscious thought – Context dependent memory- The memories that come back to you in a certain place – State Dependent memory- Memories that are retrieved because of the mood you are in. – Tip of the tongue phenomenon- When we come close to retrieving information but the process in incomplete Three Stages of Memory • Sensory Memory- The First Stage of memory that consists of immediate, initial recordings of information through our senses – Iconic Memory- like snapshots are extremely brief, photographic memories that last a fraction of a second – Eidetic imagery- or what most of us refer to as photographic memories Three Stages of Memory • Short Term Memory- also known as working memory where info will remain in your sensory register where it can be held briefly – Primacy Effect- Remembering the first few items in a group – Recency Effect- Remembering the last few items in a group Short Term Memory (contd.) • Chunking- Grouping items into small manageable units • Interference- When new information appears in short term memory and takes the place of what is already there. Three Stages of Memory • Long Term Memory- the third and final stage of memory where you want to remember something more than just briefly. – The capacity of our memory is limited by how much we pay attention – Memory is Reconstructive and can be seen differently based of the experience – Schemas- Mental representations that we form of the world by organizing bits of information into knowledge Forgetting and Memory Improvement • Basic Memory Tasks – Recognition- identifying objects or events that have been encountered before. – Recall- When you try to bring something back to mind and reconstruct the event or object – Relearning- When we do not remember things that have already been taught to us, but are able to pick back up a skill very quickly Different Kinds of Forgetting • 1. Repression- Some memories may be so painful or unpleasant that they make us feel anxiety, guilt, or shame. – What kinds of actions may people want to forget. Different Kinds of Forgetting • Amnesia- severe memory loss caused by brain injury, shock, fatigue, ill, or repression – Infantile Amnesia- cannot remember things before the age of three – Anterograde Amnesia- memory loss forming from trauma that prevents a person from forming new memories – Retrograde Amnesia- forgetting the events leading up to a traumatic event. Improving Memory • Drill and Practice-repetition and practice seems to be the most basic way to improve memory • Relate to things you already know • Form unusual associations • Construct links • Use Mnemonic Devices-HOMES