sample questions
advertisement

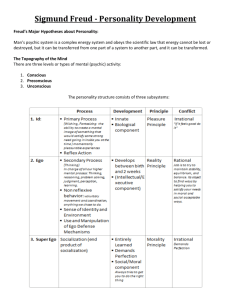
MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect MACROBUTTON HTMLDirect True/ False from chapter 12 A. Personality refers to one's typical way of behavior that differentiates a person from others. T B. A trait refers to a relatively enduring pattern of behavior that is relatively consistent across situations. T C. Acceptance is one of the Big Five personality traits. F D. People who live in individualistic cultures are more likely than people who live in collectivistic cultures to work hard to meet their own personal goals as opposed to the goals of others. T E. Freud's theory of personality is known as humanistic theory. F F. In Freudian theory, the phallic stage refers to a period of time when the genitals become a primary source of pleasure. T G. Karen Horney believed that Freud placed too much importance on sexual conflicts. T H. Self-efficacy refers to the idea that we learn from the environment but also that the environment changes because of us. F I. The internal force that motivates humans to grow and improve is known as inner-directedness. T J. The id is the subjective perception of who we are and what we are like. F K. If during a personality assessment the examiner merely watched the person being assessed, this would be an example of the use of the interview method. F L. Based on the research, projective tests are highly successful at predicting future behavior. F Multiple Choice Options The term ____________ refers to the sum total of all of the ways of acting, thinking, and feeling that are typical for a person and make that person different from all other individuals. D) a projective test based in the five-factor model. 2. Persons who score low on extraversion measures are said to be “Introverts”. 3. To prevent itself from being overwhelmed by excessive demands from the id and superego, the ego relies on A) reality principle; B) Pleasure principle; C) Oedipus Complex; D) Pleasure principle 4. Generally speaking, techniques such as the Rorschach and the TAT are ______ at predicting behavior. A) very good; B) not good; C) perfect; D) about 50% accurate 5. Generally speaking, techniques such as the Rorschach and the TAT are ______ at predicting behavior. A) permissive; B) divine; C) symmetrical; D) ancient 6. Most people intuitively understand that incest is wrong, even though they are not told this directly. Jung would explain that the incest taboo is part of the A) innate id; B) collective unconscious; C) collective superego; D) Electra complex 7. According to Freud, what are the three levels of consciousness? A) repressed conscious, preconscious, unconscious; B) unconscious, preconscious, personal conscious C) preconscious, collective unconscious, personal conscious; D) conscious, preconscious, unconscious 8. If you possess high levels of self-efficacy, this means that you A) can overcome feelings of anal-retentiveness; B) believe you are capable of achieving your goals; C) can control your own behavior in difficult environments; D) can communicate with others using fewer words 9. A major trait, like altruism, that dominates a person's life is described by Allport as a _______ trait A) dominant; B) central; C) primary; D) cardinal 10. Of Allport's categories of traits, which traits tend to describe a specific aspect of a person's personality? A) primary; B) secondary; C) cardinal; D) central 11. One personality theory called _______ suggests that behavior is consistent when the environment we inhabit remains consistent A) environmentalism; B) habitationism; C) situationism; D) socialization 12. The storage of primitive instinctual motives and memories and emotions threatening to the conscious mind are stored in the A) preconscious; B) conscious; C) unconscious; D) subconscious 13. Based on research, which of the following would best be attributed to someone living in a collectivistic culture? A) They are likely to resort to physical aggression when conflict occurs; B) They like to meet their own goals before meeting the company's goals; C) When they have time off, they spend it with friends or family; D) When they have conflict, they are likely to try to embarrass the other person 14. Children develop a superego through the process of A) repression; B) sublimation; C) fixation; D) identification 15. According to Maslow, self-actualized individuals have more ______ than non-self-actualized individuals A) sleepless nights; B) money and fame; C) peak experiences; D) inner directedness 16. According to Maslow, self-actualized individuals have more ______ than non-self-actualized individuals A) inner self is to outer self; B) self is to ideal self; C) symbolized self to idealized self; D) self concept is to persona 17. If a child feels loved and secure, Horney believed the child will A) develop a weak personality; B) experience little or no conflict; C) develop the need to be perfect; D) be envious of power and privilege 18. What type of task might a person be asked to do if taking a projective test? A) answer true/false questions; B) make up a story; C) respond on a 1 to 5 scale; D) fill in a computer scanning sheet 19. The first psychosexual stage in Freud's personality theory is the ______ stage A) anal; B) oral; C) phallic; D) latent 20. The Freudian part of personality called the id operates on the ______ principle A) reality; B) pain; C) pleasure; D) guilt 21. Allie is very shy during one-on-one encounters, but tends to be very outgoing in a group. Which viewpoint best explains her behavior? A) Cattell’s trait theory; B) conditions of worth; C) reciprocal determination; D) person x situation interactionism 22. You took a personality test, and the results indicated you were high in extraversion and moderate in agreeableness. These are examples of A) situational questions; B) surface traits; C) the big five personality traits; D) projective test results 23. The third force in psychology is known as the ______ theory of personality A) humanistic; B) situational; C) psychoanalytic; D) behavioral 24. In Horney's theory of personality, anxious insecurity is most likely the result of A) defense mechanisms; B) inadequate parenting; C) feelings of inferiority; D) opposing mental elements 25. A young boy feels guilty after looking through some adult sex magazines. In Freud's theory, the source of this guilt is the A) id; B) anal stage; C) ideal self; D) superego 26. If you believed in humanistic personality theories, which of the following would you be most inclined to agree with? A) Humans are pleasureseeking creatures driven by lust, vengeance, and greed B) Each person is unique and strives to be valued for who she or he is; C) Human beings have no basic qualities; they are shaped by the environment; D) Each person is an individual and strives to develop the qualities that promote survival 27. In terms of the interests of society, the best form of displacement is referred to as: A) sublimation; B) regression; C) reaction formation; D) fixation 28. Which of the following Freudian terms is most closely synonymous with long-term memory? A) unconscious; B) preconcious; C) conscious; D) subconscious 29. The Oedipal complex and the Electra complex develop and are resolved during the: A) oral stage; B) anal stage; C) phallic stage; D) genital stage 30. According to Horney, the source of all psychological conflicts stems from: A) conflicts between the personal and collective unconscious; B) conflicts arising from inborn motives of the id. C) failure to symbolize unconscious thoughts.; D) the development of anxious insecurity 31. The personality theory attributed to Sigmund Freud is known as ______ theory. A) collectivistic; B) behavioral; C) humanistic; D) psychoanalytic 32. A humanist believes that the psychoanalytic view of the world, and especially personality, is: A) simplistic; B) on target; C) misguided; D) wrong 33. If you say that Karl will make a good college class president because he is outgoing and sensitive, you are subscribing to: A) humanism; B) trait theory; C) social learning theory; D) situationalism 34. If you knew someone with an extremely violent temper and aggressive attitude who became a boxer, you might suspect that the person was engaged in A) sublimation; B) repression; C) self-efficacy; D) a death instinct 35. Which of the following statements accurately describes a self-actualized person? A) they strive to be popular; B) they are committed to a cause; C) they work hard for their money; D) they are concerned about themselves 36. In Freud's analogy of the mind, the ______ mind is the tip of the iceberg visible above the surface A) conscious; B) preconscious; C) unconscious; D) subconscious 37. Generally speaking, collectivistic cultures tend to value: A) high-tech development over industrial development; B) membership as a part of a group; C) industrial development over agrarian development; D) the individuality of each person 38. When you are shown ambiguous pictures and you are asked to describe what you see and make up a story, then you are probably taking the: A) Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory; B) Thematic Apperception Test; C) Stanford Binet; D) Myers-Briggs Type Indicator 39. Among those who have revised Freud's psychoanalytic theory, who has been the most influential? A) Horney; B) Adler; C) Watson; D) Bandura 40. Enduring and distinctive thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are the core areas in describing someone's: A) psychoanalytic case history; B) superego development; C) personality; D) unconscious 41. It was Freud's emphasis of ______ that led Carl Jung to break away from Freud and continue to develop his own ideas about human behavior without Freud. A) sexual motivation; B) unconscious desire; C) oral-anal fixations; D) the Oedipal complex 42. Humanists believe that a person's psychological experience is best understood by A) asking the person about it and taking his or her word for it; B) interpreting the person’s dreams in order to discover hidden motivations; C) identifying, reinforcing, and punishing patterns of interaction within the person's family; D) analyzing each comment the person makes in terms of humanistic theoretical constructs 43. If you believed in humanistic personality theories, which of the following would you be most inclined to agree with? A) Humans are pleasureseeking creatures driven by lust, vengeance, and greed B) Each person is unique and strives to be valued for who she or he is; C) Human beings have no basic qualities; they are shaped by the environment; D) Each person is an individual and strives to develop the qualities that promote survival. 44. Which of the following theorists would believe that a human is neutral at birth (not good nor evil)? A) social learning theorist; B) psychoanalyst; C) humanist; D) cognitivist 45. Adler criticized Freud for denying the importance of the human need for healthy: A) sexual gratification; B) peak experiences; C) social relationships; D) repression 46. According to Freud, ______ is the key step in the development of the superego: A) repression; B) differentiation; C) sublimation; D) identification 47. In humanistic psychology, the ideal self is: A) the person I know I can become; B) the person my mother was; C) the person I wish I was; D) what comes from the environment 48. The theory known as interactionism posits that behavior is influenced by a combination of ______ and ______ A) operant conditioning; classical conditioning; B) neurotransmitters; hormones; C) id; ego; D) the person; the situation 49. When shown pictures of scenes that were happy or positive, highly extraverted people: A) showed less arousal than introverted person; B) showed more arousal than introverted people; C) tended to become more subject to later depressions; D) became dangerously manic in their behavior 50. If John is described as cruel, pushy, messy, and disorderly, Freud would refer to his personality a: A) oral aggressive; B) anal retentive; C) oral receptive; D) anal expulsive 51. t is one's ______ that encourages a person to grow, improve, and to become all they can. A) unconditional positive regard; B) inner directedness; C) reaction formation; D) anal expulsiveness 52. The traits of extraversion and neuroticism: A) were validated by MRI studies; B) were not validated by MRI studies; C) have been validated using PET scans only; D) showed lowered MRI scans indicating lower brain activity 53. Jung believed that certain motives, conflicts, and information have been repressed into the unconscious because they are threatening to us. He called this part of the mind the: A) collective unconscious; B) introverted consciousness; C) personal unconsiousness; D) reciprocal consciousness 54. If a child feels loved and secure, Horney believed the child will: A) develop a weak personality; B) experience little or no conflict; C) develop the need to be perfect; D) be envious of power and privilege 55. Which of the following Freudian terms is most closely synonymous with long-term memory?: A) unconscious; B) preconscious; C) conscious; D) subconscious 56. Based on research, which of the following would best be attributed to someone living in a collectivistic culture? A) They are likely to resort to physical aggression when conflict occurs; B) they like to meet their own goals before meeting the company's goals.; C) When they have time off, they spend it with friends or family D) When they have conflict, they are likely to try to embarrass the other person 57. What do humanists, psychoanalysts, and social learning theorists tend to agree on regarding personality? A) we guide our behavior by society’s standards; B) we are all born to be either good or bad; C) we operate on the reality principle; D) the unconscious mind holds the key to personality 58. If a child developed a need to be perfect, Horney would say that the child developed: A) feelings of inferiority; B) anxious insecurity; C) social interest; D) an ego ideal 59. The person you think you are is to the person you wish you were as: A) inner self is to outer self; B) self is to ideal self; C) symbolized self is to idealized self; D) self concept is to persona 60. When our view of self matches what we think we would like to be or what we ought to be, Rogers would say our self-concept is: A) self actualized; B) agreeable; C) congruent; D) symbolized 61. The MMPI-2 contains a total of ___ scales. A) 10; B) 8; C) 12; D) 6 62. A humanist believes that the psychoanalytic view of the world, and especially personality, is A) simplistic; B) on target; C) misguided; D) wrong 63. Which of the following statements accurately describes a self-actualized person? A) They strive to be popular; b) they are committed to a cause; C) they work hard for money; D) they are concerned about themselves 64. In Freud's analogy of the mind, the ______ mind is the tip of the iceberg visible above the surface A) conscious; B) preconscious; C) unconscious; D) subconscious 65. Generally speaking, collectivistic cultures tend to value A) high tech development over industrial development; B) membership as a part of a group; C) industrial development over agrarian development; D) the individuality of each person 66. It was Freud's emphasis of ______ that led Carl Jung to break away from Freud and continue to develop his own ideas about human behavior without Freud. A) sexual motivation; B) unconscious desire; C) oral anal fixations; D) the Oedipal complex 67. Humanists believe that a person's psychological experience is best understood by: A) asking the person about it and taking his or her word for it.; B) interpreting the person's dreams in order to discover hidden motivations; C) identifying, reinforcing, and punishing patterns of interaction within the person's family; D) analyzing each comment the person makes in terms of humanistic theoretical constructs 68. If you believed in humanistic personality theories, which of the following would you be most inclined to agree with?: A) Humans are pleasureseeking creatures driven by lust, vengeance, and greed; B) Each person is unique and strives to be valued for who she or he is; C) Human beings have no basic qualities; they are shaped by the environment; D) Each person is an individual and strives to develop the qualities that promote survival. 69. Which of the following theorists would believe that a human is neutral at birth (not good nor evil)? A) social learning theorist; B) psychoanalyst; C) humanist; D) cognitivist 70. When shown pictures of scenes that were happy or positive, highly extraverted people A) showed less arousal than introverted persons; B) showed more arousal than introverted people; C) tended to become more subject to later depressions; D) became dangerously manic in their behavior 71. If John is described as cruel, pushy, messy, and disorderly, Freud would refer to his personality as: A) oral aggressive; B) anal retentive; C) oral receptive; D) anal expulsive 72. It is one's ______ that encourages a person to grow, improve, and to become all they can A) unconditional positive regard; B) inner directedness; C) reaction formation; D) anal expulsiveness 73. The traits of extraversion and neuroticism (A) were validated by MRI studies; B) were not validated by MRI studies; C) have been validated using PET scans only; D) showed lowered MRI scans indicating lower brain activity 74. Carl Jung believed that certain motives, conflicts, and information have been repressed into the unconscious because they are threatening to us. He called this part of the mind the A) collective unconscious; B) introverted consciousness; C) personal unconscious; D) reciprocal consciousness 75. If a child feels loved and secure, Horney believed the child will: A) develops a weak personality; B) experience little or no conflict; C) develop the need to be perfect; D) be envious of power and privilege 76. Which of the following Freudian terms is most closely synonymous with long-term memory? A) unconscious; B) preconscious; C) conscious; D) subconscious 77. Based on research, which of the following would best be attributed to someone living in a collectivistic culture? A) they are likely to resort to physical aggression when conflict occurs; B) they like to meet their own goals before meeting the company’s goals; C) when they have time off, they spend it with friends or family; D) when they have conflict they are likely to try to embarrass the other person 78. What do humanists, psychoanalysts, and social learning theorists tend to agree on regarding personality? A) we guide our behavior by society’s standards; B) we are all born to be either good or bad; C) we operate on the reality principle; D) the unconscious mind hold the key to personality 79. When our view of self matches what we think we would like to be or what we ought to be, Rogers would say our self-concept is A) self actualized; B) agreeable; C) congruent; D) symbolized