Major Works Data Sheet.ppt
advertisement

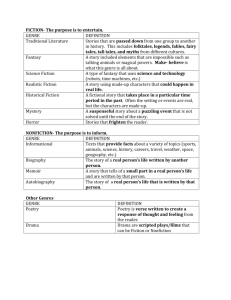
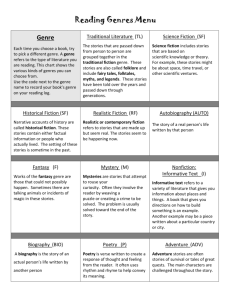
Major Works Data Sheet How do I do this? First Box MLA Book Citation Author (last name, first name). Title. City of original publication: Name of publisher, Date of original publication. Example: Tan, Amy. The Bonesetter’s Daughter. New York: Putnam, 2001. First Box (continued) Genre A division or type of literature. Literature is commonly divided into three major genres: Poetry Prose Drama Genre - Poetry Language in its most condensed form. Words are chosen and arranged to create a certain effect. Poetry uses a variety of sound devices, imagery, and figurative language to express emotions and ideas. Genre – Poetry (continued) Concrete Poetry Dramatic Poetry Epic Poetry - a long narrative poem about the adventures of gods or a hero. Epics address universal concerns such as good and evil, life and death, sin and redemption, or other serious subjects. Lyric Poetry Genre - Prose The ordinary form of written language. Most writing that is not poetry or drama is considered prose. One of the major forms of literature, prose occurs in two forms: fiction and nonfiction. Genre - Prose – Fiction Novel – a long work of fiction grouped by time period, subject/themes, or techniques used Adventure – An exciting undertaking involving risk and physical danger. The fast-paced plot focuses on the actions of the protagonist within the setting Robinsonade – simply described as a “desert island story”. The protagonist survives by his wits and the qualities of his cultural upbringing which also enable him to prevail in conflicts with fellow castaways. Genre - Prose – Fiction – Novel (cont.) Allegory – A figurative work in which a surface narrative carries a secondary, symbolic or metaphorical meaning. Bildungsroman – A novel of personal development in which the protagonist is initiated into adulthood through knowledge, experience, or both, often by a process of disillusionment. Genre - Prose – Fiction – Novel (cont.) Quest or Journey – The story of someone who undergoes great tests of character to become the embodiment of the values of his or her society. The protagonist sets off on an actual journey, encountering danger and intrigue, adventures that form him or her into the person that he or she is meant to be. Regional – A novel faithful to a particular geographic region and its people, including behavior, customs, speech, and history. Genre - Prose – Fiction – Novel (cont.) Social Realism – Literature that realistically depicts the life, struggles, and urban environment of the lower classes in the 20th century, and focuses on subjects of social and political concern, such as poverty and deprivation. Genre - Prose – Fiction (continued) Novella- (also called a short novel) is shorter than a novel, but longer than a short story. It generally has fewer conflicts than a novel, yet they are more complicated ones than those found in a short story. It is most often concerned with personal and emotional development. Genre - Prose – Fiction (continued) Short story- a brief work of fiction that can usually be read in one sitting. In most, the story has one main conflict that involves the characters, keeps the story moving, and keeps it interesting. Genre - Prose – Fiction (continued) Fable – a brief tale told to illustrate a moral or teach a lesson. Myth – a fictional tale, originally with religious significance that explains the actions of gods or heroes, or the causes of natural phenomena. Legend – a widely told story about the past, one that may or may not have foundation in fact Genre - Prose - Nonfiction Prose writing that presents and explains ideas or that tells about real people, places, objects, or events. Narrative Nonfiction – tells a true story that includes a real setting, all the elements of plot, actual people, and a point of view. It may also have a theme. And it is often told in chronological order. Genre - Prose – Nonfiction (continued) Autobiography – a form of nonfiction in which a person tells his or her own life story Memoir – a form of autobiographical writing in which a person recalls significant events in his or her life. Memoirs often include writers’ feelings and opinions giving the reader insight. Biography – a form of nonfiction in which a writer tells the life story of another person Genre - Prose – Nonfiction (continued) Essay – a brief composition on a single subject that usually presents the personal views of an author. Expository – used to explain something Narrative – tells a story Persuasive – used to convince Critical – evaluates Personal – expresses viewpoints by reflecting Genre - Prose – Nonfiction (continued) Speech – a talk or public address. The purpose of a speech may be to entertain, explain, persuade, or inspire, or it may be any combination of these aims. Genre - Drama Serious Drama – a story written to be performed by actors; developed into a sophisticated art form by the ancient Greeks who created the forms of comedy and tragedy. The first English dramas were miracle plays, Bible stories; and morality plays that dealt with personified virtues and vices. Genre - Drama (continued) Comedy – a work of literature, especially a play, that has a happy ending; often shows ordinary characters in conflict with their societies; problems resolved through laughter, reconciliation, and the correction of moral faults or social wrongs. Tragedy – type of drama or literature that shows the downfall or destruction of a noble or outstanding person, traditionally one who possesses a character weakness called a tragic flaw Genre - Drama (continued) Biographical Drama – a work of dramatic fiction depicting the life story of a real person Courtroom Drama – a work of dramatic fiction about law, crime, punishment of the legal profession. Characteristics of the genre – Third Box The genre of each ORM book is listed for you on your course syllabus. From your notes, you are expected to list here the salient points for the identified genre. What is it about this piece of literature that makes it fit the particular genre you have indicated? First Box (continued) Point of View Refers to the method of narrating a piece of literature First-Person – the reader knows only what this character does or thinks Third-Person – a person outside the story narrates it Omniscient – the reader knows what all the characters think and do Plot Summary (two sentences to explain each) Exposition/Background Initial Conflict Rising Action Crisis/Climax Falling Action Biographical information about the author. This is where you will need to do a little research about your author. Focus your entry on information that helped shape the author. Historical information about the period of publication. Again you will need to do some research – this time about what was happening in the world at the time the book was published. Focus your entries on what was going on in the world that may have influenced the author to write this particular book. Characters Make them three dimensional State character’s full name Explain role in story – be specific Adjectives – make vivid specific choices State a quote from the novel that reveals something significant about this character MLA site the page number of the quote (4) Discuss the significance of this quote Memorable Quotes If you could only pick three lines from the book which tell your reader everything he needs to know, what three lines would they be? “MLA cite the page number of each quote” (4). Identify the speaker of each quote. Significance: Why were each of these three lines the most important in the book? Examples of Literary Techniques Choose three different Literary Techniques. “MLA cite the quote and the page number of each quote” (4). Identify the speaker of each quote. State and discuss each technique listed. Setting When and where did this book take place? What do you think the author had in mind when s/he chose this setting? Mood Describe the atmosphere or emotional condition created in you by this piece of literature Symbols A symbol stands for something else. Literary symbolism combines the literal and the abstract. The American flag is a symbol of the United States and its democratic ideals. The dove symbolizes peace. State at least two symbols in this work. Explain the meaning and significance of each of these symbols. Themes Remember a theme is: Similar to the moral of a fable, it is a life lesson, or an observation about life or human nature that the writer shares with a reader State it as a complete sentence including both a subject/topic AND your opinion about that subject. Theme itself does not include plot details, but the discussion of the theme must include them. Possible Themes (continued) Pick a topic such as maturity, friendship, love, desire, self-worth, thankfulness, superstitions, etc. Add your opinion about that topic. Loyalty, affection, and conscience are far more important than wealth and social position. Growing up and becoming a young adult is a painful process. Significance of opening scene. Why did the author choose to start the book this particular way? Significance = Importance Implication Consequence Worth Connotation Significance of closing scene Why did the author choose to end the book this way? Some closing remarks Completely respond to each topic Limit yourself to the allotted space for each response Make it neat and complete – this should be a final draft Turn it in as soon as you can once you finish reading the piece of literature