It*s the Final Countdown!!!
advertisement

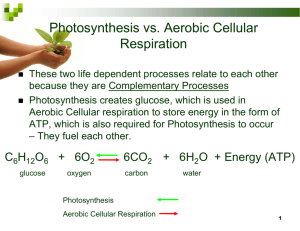
It’s the Final Countdown!!! Keystone Review Module 1 Basic Biological Principles The Chemical Basic of Life Bioenergetics Homeostasis and Transport Standards…… Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms Compare cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Cells Name the two major types of cells Cells Name the two major types of cells ANSWER: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells What type of organisms are prokaryotic and eukaryotic? Cells What type of organisms are prokaryotic and eukaryotic? ANSWER: Prokaryotic cells are Bacteria and Archaea ONLY. Eukaryotic cells are Animals, Plants, Fungi and Protists Cells Okay speaking of cells what 4 structures do ALL cells have? Cells Okay speaking of cells what 4 structures do ALL cells have? ANSWER: Cell membrane, DNA, cytoplasm and ribosomes Cells….Standard Check Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cell have the capacity to a. Assemble into multicellular organisms b. Establish symbiotic relationships with other organsims c. Obtain energy form the Sun d. Store genetic information in the form of DNA Cells….Standard Check Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cell have the capacity to Eukaryotic cells are capable of specialization and forming multicellular organisms a. Assemble into multicellular organisms b. Establish symbiotic relationships with other organsims c. Obtain energy form the Sun d. Store genetic information in the form of DNA Cells….Standard Check Inside eukaryotic cells are membranebound structures called a. Cell walls b. Cilia c. Organelles d. cytoplasm Cells….Standard Check Inside eukaryotic cells are membranebound structures called Remember membrane bound structures are organelles a. Cell walls b. Cilia c. Organelles d. cytoplasm Standards…… Describe and interpret relationships between structure and function at various levels of biological organization (i.e. organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ system and multicellular organisms.) Organization of Living Things What are life’s levels of organization? Organization of Living Things What are life’s levels of organization? ANSWER: Cell-tissue-organ-organ system-organism Organization of Living Things Give me an example of each level of organization for humans. Organization of Living Things Give me an example of each level of organization for humans. Cells Organization of Living Things Give me an example of each level of organization for humans. Tissues Organization of Living Things Give me an example of each level of organization for humans. Organs Organization of Living Things Give me an example of each level of organization for humans. Organ System Organism Really I think you can get this ONE! Biological Organization Standard Check Which statement best explains why these cells have structural differences? A. The cells have different functions B. The cells evolved in different organisms C. One of the cells develops into the other type of cell D. One of the cells is more primitive than the other cell. Biological Organization Standard Check Which statement best explains why these cells have structural differences? A. The cells have different functions B. The cells evolved in different organisms C. One of the cells develops into the other type of cell D. One of the cells is more primitive than the other cell. Biological Organization Standard Check Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms. The cell walls of these microorganisms serve as barriers to chemicals that might affect the processes that occur within a bacterial cell. Antibiotics are a type of substance used to stop bacterial growth. Some antibiotics cause the bacterial cell wall to rupture. NOTE: Use this information to answer the following questions: Biological Organization Standard Check The function of which human organ is most like the cell walls of bacteria? A. Skin B. Liver C. Heart D. pancreas Biological Organization Standard Check The function of which human organ is most like the cell walls of bacteria? A. Skin B. Liver C. Heart D. Pancreas NOTE: the cell walls of bacteria act as regulatory structures similair to the skin of humans. Biological Organization Standard Check Which statement best describes how antibiotics affect cellular homeostasis? A. Antibiotics remove chloroplasts from plant cells to cause starvation. B. Antibiotics interfere with the transport of intracellular and extracellular materials C. Antibiotics increase the rate of DNA replication in human cells by forming nucleotides. D. Antibiotic decrease the rate of cellular respiration in animal cells by producing oxygen. Biological Organization Standard Check Which statement best describes how antibiotics affect cellular homeostasis? A. Antibiotics remove chloroplasts from plant cells to cause starvation. B. Antibiotics interfere with the transport of intracellular and extracellular materials C. Antibiotics increase the rate of DNA replication in human cells by forming nucleotides. D. Antibiotic decrease the rate of cellular respiration in animal cells by producing oxygen. Note: Homeostasis is maintained by different processes to regulate an organism’s internal conditions. The antibiotic describe in the scenario causes the cell wall to rupture and the cell to burst, so there can no longer be regulation of transport across the plasma membrane. Organization of Living Things Okay so you’re pretty smart but remember cells are made up of organelles, organelles are made up of macromolecules, macromolecules and made up of molecules and molecules are made up of ATOMS…. Organization of Living Things-Cell Organelles It is very important that you know all the structures and and their functions. Questions relating to this standard may ask you to describe the organelles function… Nucleus, nucleolus, cell membrane, golgi apparatus, er (smooth and rough), lysosomes, vesicles, vacuoles, chloroplast, mitochondria, cell wall, centrioles, cytoplasm,and everything else So let’s go Cell Organelles…Standard Check What organelle in the cell supplies energy to carry out the cells functions? a. Golgi apparatus b. Nucleus c. Mitochondria d. Chloroplast Cell Organelles…Standard Check What organelle in the cell supplies energy to carry out the cells functions? a. Golgi apparatus b. Nucleus c. Mitochondria d. Chloroplast Cell Organelles…Standard Check What organelle in the cell modifies, packages and ships protein and lipid products out of the cell? a. Golgi apparatus b. Nucleus c. Mitochondria d. Chloroplast Cell Organelles…Standard Check What organelle in the cell modifies, packages and ships protein and lipid products out of the cell? a. Golgi apparatus b. Nucleus c. Mitochondria d. Chloroplast Cell Organelles…Standard Check -allows waste to exit the cell -allows chemicals required for cellular respiration to enter the cell -regulates movement of water into and out of the cell The functions of which cell structure are described in this list? a. lysosome b. mitochondria c. the plasma membrane d. the endoplasmic reticulum Cell Organelles…Standard Check -allows waste to exit the cell -allows chemicals required for cellular respiration to enter the cell -regulates movement of water into and out of the cell The functions of which cell structure are described in this list? a. lysosome b. mitochondria c. the plasma membrane d. the endoplasmic reticulum NOTE: the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function in regulating the movement of water and other materials into and out of the cell Properties of Life Properties or characteristics of life All living things are made up of one or more cells All living things metabolize All living things maintain stable internal conditions All living thing contain DNA All living things reproduce Remember: living things also, evolve over time, respond to stimuli, grow and develop Properties of Life Standard Check Which characteristic of life is best shown by the diagram? a. b. c. d. DNA is the genetic code in an organism. An organism is made up of one or more cells An organism responds to changes in the environment Changes occur in an organism as it grows and develops Properties of Life Standard Check Which characteristic of life is best shown by the diagram? a. b. c. d. DNA is the genetic code in an organism. An organism is made up of one or more cells An organism responds to changes in the environment Changes occur in an organism as it grows and develops Properties of Life Standard Check A jackrabbit has large ears containing blood vessels that help it maintain a constant body temperature by adjusting heat exchange with the surrounding environment. Which characteristic of life is best described by this example? a. b. c. d. Growth Energy use Organization Homeostasis Properties of Life Standard Check A jackrabbit has large ears containing blood vessels that help it maintain a constant body temperature by adjusting heat exchange with the surrounding environment. Which characteristic of life is best described by this example? a. b. c. d. Growth Energy use Organization Homeostasis Note: The process of adjusting heat exchange is an example of maintaining a stable internal environment, which is homeostasis. Properties of Life Standard Explain how organisms maintain homeostasis (e.g. thermoregulation, oxygen regulation). NOTE: Organisms maintain their internal equilibrium by responding and adjusting to environmental stressors. Example: Aquatic organisms must respond to changes in water temp., sunlight, chemicals, and other organisms. Living cells must balance between materials entering and exiting the cell. It is important for a cell to maintain internal concentrations of water, glucose, and other nutrients, whole eliminating cellular wastes Standards…… Describe the unique properties of water, and how these properties support life on Earth (e.g. freezing point, high specific heat, cohesion) Properties of Water Water is the most abundant compound on Earth’s surface, constituting about 70% of the planet’s surface. In nature it exists in liquid, solid and gaseous states. Water is polar because the oxygen side is slightly negative and the hydrogen side is slightly positive. The three atoms are constantly at a “tug of war” for their electrons. This polarity helps water bond to other substances……… Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is cohesion? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is cohesion? ANSWER: When water sticks to itself, this is because of the hydrogen bonds that form between the negative oxygen side and the positive hydrogen side. Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is adhesion? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is adhesion? ANSWER: When water sticks to other polar substances such as leaves on a tree. Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? So remember cohesion vs adhesions Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is surface tension? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is surface tension? ANSWER: The top layer of water that is very strong, sue to the cohesion forces of the hydrogen bonds Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is capillary action? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is capillary action? ANSWER: Movement of water against gravity. Because of cohesion and adhesion water rise up narrow tubes in plant stems Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is high specific heat? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is high specific heat? ANSWER: Waters ability to resist change in temperature, important concept because it helps organisms retain body heat and resist freezing in cold temps. Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What do we mean by the following? Water is a universal solvent. Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What do we mean by the following? Water is a universal solvent. ANSWER: Water can dissolve many polar and ionic substances. This is important to life because of all the chemical reactions that take place in an aqueous environment. Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? Okay so water is the Universal Solvent, what do we mean by solvent, solute and solution? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? Okay so water is the Universal Solvent, what do we mean by solvent, solute and solution? Answer: Solvent is the substance that does the dissolving. Solute is the substance that is dissolved. Solution is the combination of the solute and solvent. Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is special about density and water? Properties of Water So what are the properties of water? What is special about density and water? ANSWER: Since solid water is less dense than liquid water, ice floats. Density is the measure of compactness of a substance.. Properties of Water Standard Check Which statement best describes an effect of the low density of frozen water in a lake? A. When water freezes, it contracts, decreasing the water level in a lake. B. Water in a lake freezes from the bottom up, killing most aquatic organisms. C. When water in a lake freezes, it floats, providing insulation for organisms below. D. Water removes thermal energy from the land around a lake, causing the lake to freeze. Properties of Water Standard Check Which statement best describes an effect of the low density of frozen water in a lake? A. When water freezes, it contracts, decreasing the water level in a lake. B. Water in a lake freezes from the bottom up, killing most aquatic organisms. C. When water in a lake freezes, it floats, providing insulation for organisms below. D. Water removes thermal energy from the land around a lake, causing the lake to freeze. Properties of Water Standard Check Which of the following is a property of water that allows a water strider to walk on the surface of water? A. B. C. D. Solubility Cohesion High specific heat Low freezing point Properties of Water Standard Check Which of the following is a property of water that allows a water strider to walk on the surface of water? A. Solubility B. Cohesion C. High specific heat D. Low freezing point Note: Cohesion is a property of water that describes the attraction of water molecules to one another, which creates high surface tension that keeps water strider on top of the water. Standard Explain how carbon is uniquely suited to form biological macromolecules. Describe how biological macromolecules form from monomers. Properties of Carbon Carbon is the second most abundant substance in living organisms. Carbon can share FOUR electrons, therefore it can bond to four additional elements. Carbon establishes covalent bond (high energy bonds) Carbon molecules have strength, flexibility, and can chemically react to other atoms. Properties of Carbon Properties of Carbon Standard Check Which statement correctly describes how carbon’s ability to form bonds makes it uniquely suited to form macromolecules? a. If forms short, simple carbon chains b. If forms large, complex, diverse molecules c. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms d. It forms covalent bonds that can exist in a single plane Properties of Carbon Standard Check Which statement correctly describes how carbon’s ability to form bonds makes it uniquely suited to form macromolecules? a. If forms short, simple carbon chains b. If forms large, complex, diverse molecules c. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms d. It forms covalent bonds that can exist in a single plane Standard Compare the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids proteins and nucleic acids. NOTE: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are the foundation for the structure and function of every living cell in every organism. They are the building materials of the body and the storehouse for energy for every activity. Macromolecules Macromolecules Macromolecules NOTES: Carbohydrate- CHO ratio 1:2:1 Monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligiosaccharides and polysaccharides Examples: glucose, sucrose and starch In all living organisms, carbohydrates are broken down to provide usable chemical energy for all cells Cellulose is found in plants and provides structural support (cell wall) and fiber for us Macromolecules NOTES: Lipids: CHO a whole bunch of CHCHCHCHCHCH and a little O Lipids are commonly referred to as fats, oils and waxes They are insoluble in water due to the nonpolarity of the molecules Lipids are used by cells for long-term energy storage Lipids are a major component of cell membranes, phospholipids Macromolecules NOTES: Proteins C H O N and sometimes S This is the most diverse group They are large, complex polymers essential to life They are composed of chains of amino acids Proteins are important for muscle contraction, transporting oxygen in the blood, and the immune system, they are enzymes and they also are an important component of the cell membrane. Examples: collagen, enzymes, hemoglobin, insulin, and antibodies are examples of protein Macromolecules NOTES: Nucleic Acids Complex macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information in cells in the form of a code Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides The two types of nucleic acids ARE DNA and RNA NOTE: Nucleotides are the structural units of ATP and NAD+ and NADP+ Macromolecules Standard Check Which statement describes the formation of a protein molecule? a. Amino acids combine to form a protein chain b. Fatty acid monomers dissolve to form a protein chain c. Fatty acid monomers combine to form a protein chain d. Amino Acids dissolve monomers to form a protein chain Macromolecules Standard Check Which statement describes the formation of a protein molecule? a. Amino acids combine to form a protein chain b. c. d. Fatty acid monomers dissolve to form a protein chain Fatty acid monomers combine to form a protein chain Amino Acids dissolve monomers to form a protein chain Note: Proteins are biological macromolecules that form when multiple amino acid monomers are linked together with PEPTIDE BONDS Macromolecules Standard Check Student Organic Compound Description 1 Carbohydrates Complex compounds made of purines and pyrimidines that function as data-storage molecules 2 Lipids use the relatively high energy contained in C-H bonds to perform their primary function 3 Proteins chains of amino acids that can function as enzymes, hormones and antibodies 4 Nucleic Acids Compounds, produced through photosynthesis that contain carbon hydrogen and oxygen Standard Check Student 2 and 3 Student Organic Compound Description 1 Carbohydrates Complex compounds made of purines and pyrimidines that function as data-storage molecules 2 Lipids use the relatively high energy contained in C-H bonds to perform their primary function 3 Proteins chains of amino acids that can function as enzymes, hormones and antibodies 4 Nucleic Acids Compounds, produced through photosynthesis that contain carbon hydrogen and oxygen Enzymes Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme involved in the reaction of carbon dioxide with water to form a molecule that dissolves well in the liquid part of blood. How does carbonic anhydrase affect this reaction? a. By making the reaction reversible b. By changing chemical products of the reaction c. By increasing the time needed for the reaction to occur d. By decreasing the amount of energy needed to complete the reaction Enzymes Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme involved in the reaction of carbon dioxide with water to form a molecule that dissolves well in the liquid part of blood. How does carbonic anhydrase affect this reaction? a. By making the reaction reversible b. By changing chemical products of the reaction c. By increasing the time needed for the reaction to occur d. By decreasing the amount of energy needed to complete the reaction Note: An enzyme can act as a catalyst that regulates specific biochemical reactions and decreases the amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur Enzymes Don’t forget enzyme terminology -Active site -Substrate -Enzyme -Enzyme/substrate complex -Product Enzyme: Lock and Key Mechanism Enzymes Enzymes -are catalytic molecules -they speed up chemical reactions without being used up in the reaction -enzymes are PROTEINS - each enzyme catalyzes only one Specific type of reaction Enzymes Critical Thinking…… The rate of a reaction depends in part on the concentration of the enzyme. If the enzyme is diluted, its concentration is lowered, which slows the reaction rate Enzymes Tell Me What this graph is showing! Enzymes Standard Check Food is commonly refrigerated at temperatures 20C to 70C to slow the rate of spoilage by bacteria. Which of the following best explains why refrigeration at these temperatures slows the spoilage of food? a. Bacteria that cause food spoilage are killed by these low temperatures b. Bacteria that cause food spoilage multiply rapidly at these temperatures c. The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are not active at these temperatures d. The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are denatured at these temperatures Enzymes Standard Check Food is commonly refrigerated at temperatures 20C to 70C to slow the rate of spoilage by bacteria. Which of the following best explains why refrigeration at these temperatures slows the spoilage of food? a. Bacteria that cause food spoilage are killed by these low temperatures b. Bacteria that cause food spoilage multiply rapidly at these temperatures c. The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are not active at these temperatures d. The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are denatured at these temperatures Standard Describe the role of ATP in chemical reactions ATP All life on Earth depends on the flow of energy. Primary source of energy is the Sun Photosynthesis convert solar energy to chemical energy (carbohydrates) and then the carbohydrates are broken down by the metabolism of organisms. ATP ATP is adenosine triphosphate ATP stores and releases the energy in its bonds in response to the energy need of the cell Stored energy is released when ATP is split into ADP ATP ATP By removing a phosphate group, energy is released for chemical reactions to occur in the cell, ATP becomes ADP. ATP Standard Check A protein in a cell membrane changed its shape to move sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradients. Which molecule was most likely used by the protein as an energy source? a. ATP b. ADP c. Catalase d. Amylase ATP Standard Check A protein in a cell membrane changed its shape to move sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradients. Which molecule was most likely used by the protein as an energy source? a. ATP b. ADP c. Catalase d. Amylase Standard Describe the fundamental roles of plastids (chloroplast) and mitochondria in energy transformations Compare the basic transformation of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Energy Cells use energy for making new molecules, building cell organelles, making membranes, maintaining homeostasis etc. Energy-Photosynthesis Plants, algae and other photosynthetic organisms are important to the maintenance and balance of life on Earth. They convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates NOTE: photosynthetic organisms must also break down carbohydrates to form ATP. Energy-Photosynthesis Energy-Photosynthesis Two Main Reactions of Photosynthesis 1. Light Dependent Reaction Theses reactions split water molecules, providing hydrogen and an energy source for the Calvin cycle. Oxygen is given off! 2. Calvin cycle, dark reaction or the Light Independent Reaction A series of reactions that form simple sugars using carbon dioxide and hydrogen from water. NOTE: The light reaction is the photo part of photosynthesis. The Calvin cycle is the synthesis part of photosynthesis. Energy-Photosynthesis Light Dependent Reaction Takes place in the chloroplasts at the thylakoid. A stack of thylakoids is called grana. The chlorophyll and other light-absorbing molecules absorb the energy from the sunlight. Energy-Photosynthesis Light Independent Reaction Takes place in the chloroplasts in the stroma. Carbon dioxide from the air combines with hydrogen from the light reaction to form simple sugars. Simple sugars form to make complex sugars, starches and cellulose. NOTE: AKA Dark reaction and Calvin Cycle Energy-Photosynthesis Energy-Cellular Respiration Two Main Reactions of Cellular Respiration 1. Krebs Cycle breaks down the products of Glycolysis to produce molecules used in the electron transport chain. 2. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) consists of a series of proteins in the mitochondrial membranes that convert ADP to ATP by transferring electrons Energy-Cellular Respiration 1. Krebs Cycle 1. Takes place in mitochondria and breaks down products of glycolysis 2. CO2 is released and 2 ATP’s produced 3. The main function of Kreb Cycle is to move high energy electrons to molecules for the electron transport chain Energy-Cellular Respiration 1. ETC 1. Takes place in and across the inner membrane of the mitochondria. 2. High energy electrons travel through the proteins and makes 32-34 ATP molecules 3. Releases carbon dioxide Energy-Cellular Respiration Energy-Cellular Respiration Respiration and Photosynthesis Standard Check In glycolysis, the first stage of cellular respiration, ATP molecules are produced. What is the net gain of ATP molecules (per molecule of glucose) from glycolysis? a. b. c. d. 1 2 4 36 Respiration and Photosynthesis Standard Check In glycolysis, the first stage of cellular respiration, ATP molecules are produced. What is the net gain of ATP molecules (per molecule of glucose) from glycolysis? a. b. c. d. 1 2 Remember 4 made two needed=2 net 4 36 Respiration and Photosynthesis Standard Check 1. 2. 3. 4. Cellular respiration and photosynthesis both involve water. Cellular respiration uses sugar, and photosynthesis produces sugar. Cellular respiration and photosynthesis both use light to produce energy. Cellular respiration requires light energy, and photosynthesis requires chemical energy. Which two statements correctly describe one similarity and one difference between cellular respiration and photosynthesis? a. Statements 1 and 2 b. Statements 1 and 4 c. Statements 2 and 3 d. Statements 3 and 4 Respiration and Photosynthesis Standard Check 1. 2. 3. 4. Cellular respiration and photosynthesis both involve water. Cellular respiration uses sugar, and photosynthesis produces sugar. Cellular respiration and photosynthesis both use light to produce energy. Cellular respiration requires light energy, and photosynthesis requires chemical energy. Which two statements correctly describe one similarity and one difference between cellular respiration and photosynthesis? a. Statements 1 and 2 b. Statements 1 and 4 c. Statements 2 and 3 d. Statements 3 and 4 Respiration and Photosynthesis Standard Check The diagram shows an energy transformation that typically occurs in plant cell plastids. Which statement best describes this role of plastids in the plant? a. Chloroplast transform light energy into chemical energy b. Mitochondria transform light energy into chemical energy c. Chloroplasts transform chemical energy into electromagnetic energy d. Mitochondria transform chemical energy into electronegative energy Respiration and Photosynthesis Standard Check The diagram shows an energy transformation that typically occurs in plant cell plastids. Which statement best describes this role of plastids in the plant? a. Chloroplast transform light energy into chemical energy b. Mitochondria transform light energy into chemical energy c. Chloroplasts transform chemical energy into electromagnetic energy d. Mitochondria transform chemical energy into electronegative energy Standard Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for the cell. Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane. Cell Membrane Cell Membrane: Function boundary and regulator As an active regulator the cell membrane helps to maintain the proper concentrations of substances inside the cell Selectively permeability Allows certain materials to pass through the membrane while keeping others out Cell Membrane Cell Membrane: Cell Membrane Transport of materials Cell Membrane: Cell Membrane Transport of materialsStandard Check Which of the following examples illustrates osmosis? a. Water leaving the tubules of the kidney in response to the hypertonic fluid surround the tubules b. Digestive enzymes are excreted into the small intestine c. White blood cells consume pathogens and cell debris at the site of infection d. Calcium is pumped inside a muscle cell after the muscle cell completes its contraction Cell Membrane Transport of materialsStandard Check Which of the following examples illustrates osmosis? a. Water leaving the tubules of the kidney in response to the hypertonic fluid surrounding the tubules b. Digestive enzymes are excreted into the small intestine c. White blood cells consume pathogens and cell debris at the site of infection d. Calcium is pumped inside a muscle cell after the muscle cell completes its contraction Cell Membrane Transport of materialsStandard Check CRQ- During physical education class, some students ran one mile. After their run, the students recorded changes they experienced. Changes Experienced Sweating Muscle cramps Decreased energy Increased heart rate Increased breathing rate Increased thirst Increased body temp Select three changes experienced by the students and explain how each change can represent a homeostatic mechanism. Cell Membrane Transport of materialsStandard Check CRQ Sweating an represent a homeostatic mechanism because when your body is hot it cools itself by activating the sweat glands which cool you by evaporation Increased heart rate….because when you run your muscles need more oxygen and blood so your heart pumps faster to abide to those needs Increased thirst….because it is caused by sweating out moisture which your body then wants to replenish causing your body to tell you to drink Decreased energy …because when you exercise your body uses all of its energy to do so, so you loose your energy and become tired until your body regains it WHAT IS? An educated guess/prediction; usually in “If…Then” form WHAT IS? An educated guess/prediction; usually in “If…Then” form ANSWER: hypothesis What is The factors that are measured in an experiment WHAT IS? The factors that are measured in an experiment ANSWER: variable (s) WHAT IS? The variable that you purposely change WHAT IS? The variable that you purposely change ANSWER: Independent WHAT IS? The variable that changes in response to changing the independent variable. WHAT IS? The variable that changes in response to changing the independent variable. ANSWER: Variable Dependent WHAT IS? Things that are purposely kept the same in an experiment WHAT IS? Things that are purposely kept the same in an experiment ANSWER: Constants WHAT IS? A structured way to test a hypothesis WHAT IS? A structured way to test a hypothesis ANSWER: Experiment WHAT IS? Baseline measurement used to compare you data to WHAT IS? Baseline measurement used to compare you data to Answer: Control WHAT IS? Testable multi step process for solving problems WHAT IS? Testable multi step process for solving problems ANSWER: Scientific Method WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Either sexually or asexually WHAT IS? Either sexually or asexually ANSWER: Reproduction WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Maintaining internal conditions usually quite different than the external environment WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Maintaining internal conditions usually quite different than the external environment ANSWER: Homeostasis WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Traits that are passed on to offspring WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Traits that are passed on to offspring ANSWER: Heredity WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Smallest unit of life WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Smallest unit of life ANSWER: cell WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Get and use energy in order to carry out life functions WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Get and use energy in order to carry out life functions ANSWER: metabolism WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Ability of populations to change over time WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Ability of populations to change over time ANSWER: Evolution WHAT IS? Category: Characteristics Of Life Ability of populations to change over time ANSWER: Evolution WHAT IS? Group of cells that carry out a similar function WHAT IS? Group of cells that carry out a similar function ANSWER: Tissue WHAT IS? A single living thing WHAT IS? A single living thing ANSWER: organism WHAT IS? A group of organs that work together to perform a function (s) WHAT IS? A group of organs that work together to perform a function (s) ANSWER: organ system WHAT IS? A group of tissues that carry out a specialized function in the organism WHAT IS? A group of tissues that carry out a specialized function in the organism ANSWER: Organ WHAT IS? A group of organisms that look similar and can produce fertile offspring WHAT IS? A group of organisms that look similar and can produce fertile offspring ANSWER: species WHAT IS? A group of different species that live in the same habitat and interact with one another WHAT IS? A group of different species that live in the same habitat and interact with one another ANSWER: community biological WHAT IS? A community of organisms and their non living environment WHAT IS? A community of organisms and their non living environment ANSWER: Ecosystem WHAT IS? A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area and can interbreed WHAT IS? A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area and can interbreed ANSWER: Population WHAT IS? All of the world and its atmosphere that supports life is WHAT IS? All of the world and its atmosphere that supports life is ANSWER: biosphere WHAT IS? Characteristics Water of Water is _________ because it has an unevenly distributed charge WHAT IS? Characteristics of Water Water is _________ because it has an unevenly distributed charge ANSWER: Polar WHAT IS? Characteristics Bond of Water that forms between water molecules because they are polar is WHAT IS? Characteristics of Water Bond that forms between water molecules because they are polar is ANSWER: Hydrogen bond WHAT IS? Characteristics Property water of Water where water sticks to WHAT IS? Characteristics Property of Water where water sticks to water ANSWER: cohesion WHAT IS? Characteristics Property of Water where water sticks to other polar or charged substances is WHAT IS? Characteristics of Water Property where water sticks to other polar or charged substances ANSWER: adhesion WHAT IS? Characteristics Process of Water by which water travels up something…..due to cohesion and adhesion WHAT IS? Characteristics of Water Process by which water travels up something…..due to cohesion and adhesion ANSWER: capillary action WHAT IS? Characteristics Property of Water of water that allows bugs and lizards to walk on water WHAT IS? Characteristics of Water Property of water that allows bugs and lizards to walk on water ANSWER: surface tension WHAT IS? Characteristics Time of Water for a “thinkie” question Water has high heat capacity, why is that important to living organisms? ANSWER: surface tension WHAT IS? Characteristics of Water Time for a “thinkie” question Water has high heat capacity, why is that important to living organisms? ANSWER:High heat capacity means it takes a lot of energy to raise or lower its temperature, this is important because it helps organisms maintain homeostasis by keeping a constant body temp.