Muscle Contraction
advertisement
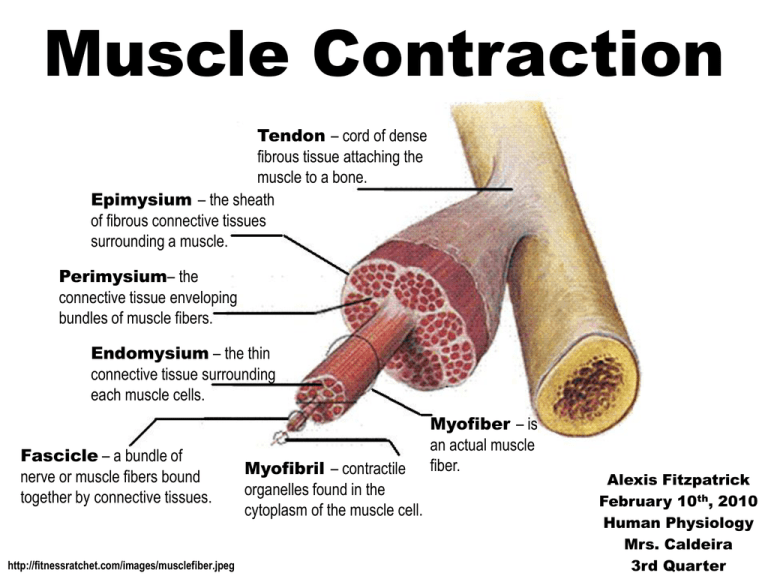
Muscle Contraction Tendon – cord of dense fibrous tissue attaching the muscle to a bone. Epimysium – the sheath of fibrous connective tissues surrounding a muscle. Perimysium– the connective tissue enveloping bundles of muscle fibers. Endomysium – the thin connective tissue surrounding each muscle cells. Fascicle – a bundle of nerve or muscle fibers bound together by connective tissues. http://fitnessratchet.com/images/musclefiber.jpeg Myofibril – contractile organelles found in the cytoplasm of the muscle cell. Myofiber – is an actual muscle fiber. Alexis Fitzpatrick February 10th, 2010 Human Physiology Mrs. Caldeira 3rd Quarter Anatomy of Myofiber & Myofibril •Myofilaments – are two myofibrils, is what actin and myosin are. •Actin – are a contractile protein of muscle. •Myosin – one of the principal contractile proteins found in muscle. •Z Line – the line that divides the sarcomere in a myofibril. •I band – are light bands or thin filaments of actin. •A Band – are dark bands or thick filaments of myosin. •Sarcomere – are thick filaments composed of protein myosin and has ATPase emzymes located in the distance between two z lines. •Sarcolemma – is a specialized plasma membrane. http://legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/images/Image286.gif Anatomy of the Neuromuscular Junction http://demo.classontheweb.com/CBSE/ClassX/images/NeuromuscularJunction.jpg Steps Of Muscle Contraction 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nerve impulse (electrical impulse) moves down the axon of a motor neuron towards the motor end plate of a neuromuscular junction. The axon terminal (end of axon) releases the neurotransmitter – acetylcholine (ACh). Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction. This causes the generation of a new action potential (electrical impulse) that spreads over the sarcolemma (muscle fiber). This impulse goes down the transverse tubules (T tubules) into the myofiber. http://www.bmb.leeds.ac.uk/illingworth/bioc1020/image36.gif Steps Of Muscle Contraction (Continue) 6. This impulse causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium. 7. Calcium binds to troponin on actin moving tropo,ysin and exposing the binding sites (on actin) for the crossbridges of myosin. 8. Myosin interacts with actin. 9. Crossbridges on myosin with Energy supplied by ATP (ATP=ADP+P+Energy) binds to actin and actin slides in between myosin (sliding filament theory). 10. Sarcomere shortens – myofiber shorten – entire muscle shortens. http://static.howstuffworks.com/gif/rigor-mortis-muscle.gif Steps Of Muscle Contraction (Continue) 11. Calcium returns (activily) to sarcoplasmic reticulum. 12. Troponin returns to its original position 13. Binging sites are covered by tropomyosin. 14. Actin slides back to a relaxed position 15. Muscle relaxes. http://www.biog1105-1106.org/demos/105/unit10/media/muscle-contraction.fig.jpg