Mythology PowerPoint
advertisement

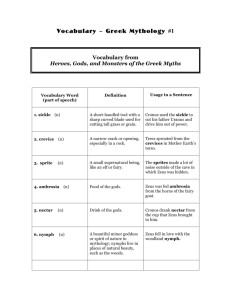
Introduction to Mythology Heroes, Gods, and Monsters of the Greek Myths Mythology A usually traditional story of events that serves to unfold part of the world view of a people or explain a practice, belief, or natural phenomenon . Myths often involve divine, supernatural, and/or heroic characters. Mythology OR A collection of fictional stories involving the actions of gods, goddesses and other imaginary characters, intended to explain the unexplainable. Classical Greek Mythology A collection of stories about a set of gods, based upon oral tradition, as told and recorded by the ancient Greeks Myths served as entertainment, a sense of national/regional pride, and religious education Oral Tradition The practice of passing along stories, tales, and folklore by word of mouth Oral tradition is responsible for many of the “inconsistencies” of ancient mythology. Fantasy Highly imaginative writing that contains elements not found in real life Many science fiction and fantasy books, movies and comic books are based upon the style and manner of myths. Legends • Definition: fictional stories loosely based upon real/historical people and events. • Also known as “tall-tales” • Are rooted in facts, but stories have been changed through the years…WHY? Fables • Definition: A brief story, often containing animal characters that teaches a lesson or moral • Fables deal with “useful truth” “The Classicists” Greek mythology existed for hundreds of years before these stories were ever recorded with written words. The scholars/poets who recorded the myths are known as “classicists.” The major classicists of Greek Mythology include Virgil, Homer, and Ovid. The Importance of Myths Myths were critical to the ancient Greeks These stories touched all aspects of Greek life, including art, music, architecture, military endeavors, religion, and education. Greek myths and sunlight are represented by moral quality. Heroes are set in sunlight, monsters belong to the darkness. Categories of Myths Myths of creation: these explain the beginning of time, space, and man Myths of explanation: these explain the great questions of the universe Myths of morality: these teach lessons and reinforce cultural morality Why Study Mythology? Greek myths are the foundations for the arts as we know them, including movies, television, commercial products, sports, music, and comic books. A knowledge of Greek mythology enhances a person’s ability to understand and appreciate the world as a whole. Mythology: A Brief Timeline The beginning: according to popular belief • Uranus was the “First One”, and he created the universe. • Uranus created and married Gaia, otherwise known as “Mother Earth.” • They lived on Mt. Olympus • Uranus and Gaia had many children: • Some were human-like giants, called the “Titans” • Some were hideous, disfigured monsters • The Titans lived for many years under Uranus’s cruel reign • Uranus’s most powerful son would soon challenge his rule. • Cronus killed his cruel father and assumed his role as “king of the Titans.” • Before Uranus died, he predicted that Cronus would be killed by one of his sons, just as he had been. • What is the logical solution to this problem? • Because he feared his sons, Cronus ate his first two sons whole • Fed up with his baby-gobbling, Rhea gave birth to her third son in secret • Rhea dressed a boulder up as a baby and Cronus ate the rock unknowingly • Zeus was sent as an infant to be raised in secret by human shephards •Cronus married his sister, Rhea, and had: -Three daughters: Hestia, Demeter, Hera -Three sons: Posiedon, Hades, and Zeus •These offspring were considered Titans, but would later become the gods and goddesses of Greek Mythology • Zeus returned to Mt. Olympus as a young man and poisoned Cronus • Cronus vomited up brothers Poseidon and Hades • Zeus was celebrated as a hero • An epic battle ensues between Cronus and his sons for the right to rule Mt. Olympus and the universe. The Great Battle! • Cronus is assisted in battle by his Titan brothers • Zeus and his brothers are assisted by the monsters Cronus had abused and tortured for years in captivity. • These monsters included the Cyclopes (3) and the Hundred-Handed Ones (3) Mythology and Classic Art • The Battle Between the Gods and the Titans by Wtewael Art Institute of Chicago, Chicago Cronus is Defeated! • The three sons roll dice to divide Cronus’ kingdom • Zeus wins, and chooses the empty sky. • Poseidon secretly wanted the sea. • Hades is left to bitterly receive “leftovers” In the underworld. Enter the Gods… • Magically and mysteriously, the children of Cronus become immortal, and become gods and goddesses. • Mythology offers no explanation for this important transformation! • The twelve main gods and goddesses are known as the Pantheon. The Pantheon • There are many gods, goddesses, demigods (half-gods) and supernatural beings in Greek Mythology. • The twelve main gods and goddesses are known as the Pantheon. Zeus Zeus: • King of the gods, ruler of Mt. Olympus • Also god of lightning • Was a powerful and aggressive ruler • Struck Earth with lightning bolt when upset • Waged constant war with wife and sisterHera • Cheated on wife countless times, and had numerous children with mortals, gods, and other creatures Zeus (continued) • Was a master of disguise, which aided him in his philandering • Was a complex character: capable of unspeakable acts of immorality and occasional acts of mercy Hera HERA • Queen of immortals, goddess of marriage and childbirth • Unhappy wife of Zeus • Disapproved of Zeus’ constant cheating • Held grudges against Zeus’ “children” • Often punished Zeus with childish pranks and vengeful schemes Athena Athena • Goddess of wisdom and warfare, mistress of strategy • Taught men how to use an ax, plough, wheel, sail. Taught women how to spin and weave (Arachne story...) • Mother was Metis, a Titaness • Zeus became paranoid that his child would harm him, so he eats her whole. • Zeus developed a splitting headache • Hephaestus split his head open with a chisel, and… The “Rebirth” of Athena • Athena jumped out of Zeus skull, full-grown and wearing battle armor. • One of the most popular and respected immortals • Athens, Greece is named for her Poseidon Poseidon • God of water • Never had children with sea nymph-Thetis because any son of Thetis would be greater than Poseiden • Thetis had a son from Peleus whose name was Achilles therefore the prophecy came true. • Difficult, quarrelsome, greedy, liked jokes • Thought up creature...octopus, squid, jellyfish, swordfish, dolphin, etc. • Was trying to perfect the horse for Demeter and that is why we have the camel, hippo, giraffe, donkey, and zebra •Ruled over seas, oceans, rivers and all the sea creatures •Did not live in the lost city of Atlantis •Invented many of the fish and sea monsters of mythology •Created the horse for Demeter (*) Hades HADES • God of the Underworld • Greeks buried their dead with a coin so that when they entered "Hades" they could pay the fare on their way to the river Styx • Cerberus- 3 headed dog that guarded the gate • 3 judges awaited the dead - Minos, Rhadamanthys and Aeacus. • > if judges were displeased - bad punishments • > if judges were pleased - Elysian Fields • Palace grounds were called Erebus- deepest part of the underworld Hades (continued) • Lived with his kidnapped wife, Persephone • The Eumenides or the " kindly ones" would wander the earth in search of evil-doers and ones that escaped punishment and their attention persuaded people to suicide Demeter Demeter • Goddess of the cornfield, mistress of planting and growing things • One of Zeus’ favorite females (also sister) • Had a daughter named Persephone • Demeter's daughter Persephone was kidnapped by Hades • Responsible for the winter and summer seasons, since Persephone ate the 6 pomegranate seeds, she will have to stay in the underworld with Hades for 6 months, and nothing will grow on earth because Demeter will mourn. Artemis Artemis • Born of Zeus and Leto (a nymph) • Zeus granted her whatever she wanted: remain a maiden, many names, silver bow and arrow, deerskin tunic, 50 ocean nymphs, 20 wood nymphs, hounds, mountains, and one city • Was Zeus’ favorite daughter • Went by Goddess of the Moon, Maiden of the Silver Bow, Lady of the Wild Things, Huntress, Maiden Apollo Apollo • God of the sun, patron of music, math, medicine and poetry. Preached moderation • Artemis’ twin brother • Hunted python who hunted his mother • Showed no mercy against the musician Marsyas ( unfair competition) The Flaying of Marsyas Hermes Hermes • Precocious • Stole Apollo's cattle and named himself the 12th god • Taught Apollo to play the lyre and traded Apollo pipes for his herdsman's golden staff • Apollo took Hermes to meet Zeus • Hermes became Zeus's messenger and known as the patron of liars, thieves, and gamblers, God of Commerce, framer of treaties, guardian of travelers, took newly dead to Tartarus • Invented the alphabet, scales, playing cards and card games • Told Zeus to disguise himself and join in on many adventures of the mortals Hermes • Messenger god, god of gambling, theivery and trickery • Has a sketchy creation: –Zeus child with a nymph –Zeus child with a goddess (unnamed) –Son of two enchanted mortals *Oral tradition is contributed to the many different creations of Hermes Hephaestus Hephaestus • Son of Zeus and Hera • Was born ugly and fitful • Hera kicked him from Mt. Olympus • Was reinstated by Hera for his masterful skill of jewelry-making • Hera gave him Cyclops for helpers and Aphrodite for a bride Hephaestus Strikes Gold… • Married to Aphrodite, the most beautiful of all goddesses • Had no children with his wife • Endured Aphrodite’s many affairs and constant flirtations • Was emotionally scarred by Aphrodite’s affair with Ares, the god of war 52 Aphrodite • Goddess of love and beauty, desire • Never distracted from her duties • Born out of primal murder - when Cronus killed his father Oranus/Uranus a body floated up from the foam and taken to Olympus • Hera wanted her married immediately, Aphrodite chose Hephaestus because he worked late ( though she planned to meet her other suitors) Aphrodite’s Creation • Version #1: Aphrodite was the son of Zeus and a Dione • Version #2: Aphrodite was born of Zeus and the daughter of one of his arch enemies But both of these stories are less-thanaccurate twists on the real version… Aphrodite (con’t.) • Discovered by fishermen and taken to Mt. Olympus as a gift to Zeus • Hera, fearing a relationship between Zeus and Aphrodite, insisted that she marry Hephaestus, her ugliest child • Aphrodite serves as a constant temptation for gods and mortals alike. • Her name literally means “from the foam” The Real Creation of Aphrodite • Aphrodite was born from the death of Uranus • Cronus castrated his father before death, and threw the “part” into the ocean • From the bubbling, boiling, bloody foam, Aphrodite appeared • She was accompanied at birth by sea nymphs and doves • Often depicted as having hatched from a seashell Ares • • • • • • Ares God of warfare Was violent, aggressive, and unlikeable Was Hera and Zeus’s most despised son Had an awkward love affair with Aphrodite Was actually a coward (traitor) Was feared, but not respected by Greeks