Chapter 2 Vocabulary Types of Government
advertisement

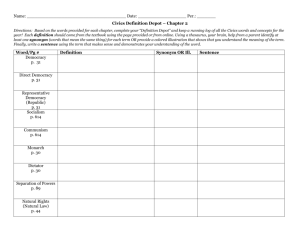
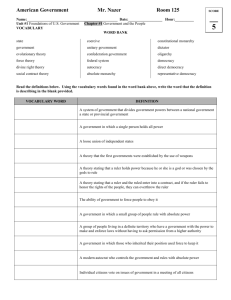
Chapter 2 Types of Government 1. Absolute/Traditional Monarchy • A form of government where the monarch rules without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. • Examples: Brunei, Oman, Swaziland, and Vatican City 2. Authoritarian • A form of government in which state authority is imposed onto many aspects of citizens' lives. • Examples: China, Cuba, Iran, Russia, and Syria 3.Communist • A system of government in which the government plans and controls the economy and a single - often authoritarian - party holds power; government controls are imposed with the end of private ownership of property or capital while claiming to make progress toward a higher social order in which all goods are equally shared by the people (that is, a classless society). • Examples: China, Cuba, North Korea, Laos, and Vietnam 4. Constitutional Monarchy • A system of government in which a monarch is guided by a constitution whereby his/her rights, duties, and responsibilities are spelled out in written law or by custom, and in which the government is run by a parliament. • Examples: United Kingdom, Japan, Spain, Thailand, and Sweden 5. Democracy • A form of government in which the supreme power is kept by the people, but which is usually exercised indirectly through a system of representation and delegated authority. • Examples: See direct democracy and representative democracy 6. Dictatorship • A form of government in which a ruler or small group hold absolute power (not restricted by a constitution or laws). • Examples: North Korea, Cuba, Russia, Ethiopia, and Syria 7. Direct democracy • A democracy in which the power to govern lies directly in the hands of the people rather than being exercised through their representatives. • Examples: Parts of Switzerland, and some small towns in New England states in the U.S. 8. Monarchy • A government in which the supreme power is in the hands of a monarch who rules over a state or territory, usually for life and by hereditary right; the monarch may be either a sole absolute ruler or a sovereign - such as a king, queen, or prince - with constitutionally limited authority. • Examples: See absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy 9. Oligarchy • A government in which control is exercised by a small group of individuals whose authority generally is based on wealth or power. • Examples: According to some, the United States, Greece, Russia, and Ukraine; in literature, Panem from the Hunger Games 10. Representative democracy • Variety of democracy founded on the principle of elected officials representing a group of people, as opposed to direct democracy. • Examples: United States, Germany, Ireland, and India 11. Republic • A representative democracy in which the people's elected representatives, not the people themselves, vote on legislation. • Examples: Iceland, United States, France, and Turkey 12. Theocracy • A form of government in which a deity (god) is recognized as the supreme civil ruler, but the deity's laws are interpreted by religious authorities; a government subject to religious authority. • Examples: Vatican City, Iran, and ISIS/ISIL (though not an official country at this time) 13. Totalitarian • A government that seeks to control not only all political and economic matters, but also the attitudes, values, and beliefs of its population. • Examples: North Korea, Cuba, and Venezuela