ppt-Plant Classification & Structure
advertisement

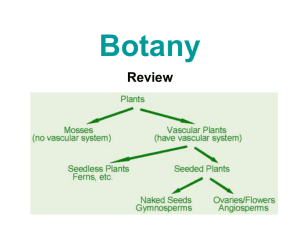
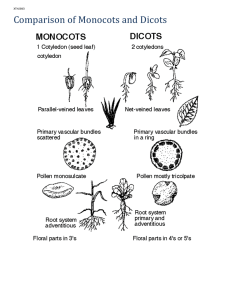
Chloroplasts NonvascularGametangia, need water to reproduce Cell walls Seedless, but vascular Monocots & dicots Adaptations to Terrestrial Life • • • • • • • • Stomata(gas exchange) Cuticle(prevention water loss) Lignin(support) Gametangia & seeds (reproduction) Pollen(reproduction) Vascular tissue(support & transport)-xylem & phloem Roots(water acquisition, support) Seed dispersal mechanisms General Structure PlantsGeneral Characteristics • Terrestrial • Photosynthetic • Alternation of generations charophyte bryophytes pteridophytes gymnosperms angiosperms Plant Morphology Organs tissues Leaves Stems Roots dermal vascular ground meristematic cells parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma Tissues 1. Dermal • • • • • Outer covering Protective Epidermal cells (cuticle) Guard cells Root hairs 2. Vascular • • 3. Transport & support Xylem & phloem Ground • • Bulk of plant Photosynthesis, storage, support 4. Meristematic – Embryonic tissuegrows throughout life of plant – Roots, shoots, stem(lateral) Cell Types Found in all 3 tissue types Thicker cell walls Heavy lignin phloem Found in vascualr bundl Include Fibers-bundles, support Scleroids-nut shells, seed Tracheids & vessels of xylem parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma Stems Functions • Transport between roots & leaves • Storage • support Stems-basic structure • Epidermis – Cuticle, stoma, photosynthetic • Body mostly parenchyma • Support tissuescollenchyma & sclerenchyma • Vascular tissues in bundles • Scattered (monocots) or in rings (dicots) • Can grow up or out Monocot stems scattered Epidermis______ Dicot Stems In ring, around pith Secondary growth-woody dicots only Produce a new layer of xylem & phloem each year Vascular cambium divides & differentiates Epidermis becomes cork cells, part of bark, along w/ phloem •Vascular cambiumundifferentiated cells •Pith & cortex parenchyma for storage •Phloem & xylem rays Transport H2O & nutrients Laterally •Primary xylem & phloem Non-functioning •Cork cambium Produces cork cells which replace epidermis-secrete suberin & die •Bark Phloem(living & dead), cork cambium & cork •Periderm •Cork cambium & cork Xylem = oldest Dead cells & suberin How does secondary growth happen? c=vascular cambium cell D=undifferentiated product of mitosis X=xylem P=phloem Roots Differentiation complete Responsible for lengthening of root Protection/lubrication 1st stage of differentiation Root Functions • Anchoring • Take up water & minerals • 1st part to develop • 2 types – Taproot(dicot) – Fibrous(monocot) • Basic Structure • Epidermis(dermal)-covers entire surface, including hairs – Absorption, protection – No cuticle • Cortex-mainly parenchyma – No chloroplast, but has storage plastids • Stele/vascular cylinder – Surrounded by endodermis-cells are highly selective – Xylem & phloem inside – Casparian strip – Pericycle – Pith(monocots) Thru cell walls Thru cytoplasm Lateral branch from pericycle Differences between monocots & dicots Monocots __________endodermis ____________pericycle Dicots ________ epidermis __________________ cortex Vascular Cylinder___ Endodermis___________ Pericycle________________ ________________xylem ________________phloem Leaves Functions • Photosynthesis • Maximize sunlight exposure • Gas exchange • Water conservation Special Leaf Adaptations • Specialized photosynthetic cells • Shape-most are broad & flat • Stomata • Pointed-water run off • Needle-shaped-cold & wind • Succulents-water storage • General Outer leaf 1. Cuticle(cutin) 2. Epidermis(upper & lower) 3. Stomata & guard cells Inner leaf 1. Mesophyll • Palisade parenchyma • • Spongy parenchyma • • 2. Densely packed, columnar, upper surface only Irregular shapes, large spaces for gas diffusion Bundle-sheath cells(C4 plants) Vascular bundles/veins Structure Monocots vs Dicots • Monocots – Parallel veins – No palisade layer – Vascular bundles appear scattered under ‘scope • Dicots – One large central vein, smaller veins branching off (perpendicular) – Palisade layer distinct monocot monocot dicot Palisade layer_______ _________spongy layer Main vein________ Leaf epidermis General Structure cont… fibers