Plant Tissues - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

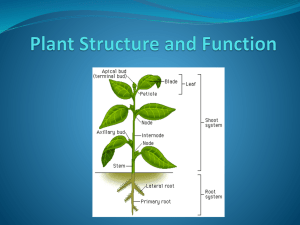
Plant Tissues There are 3 tissue systems in plants: • Dermal tissue • Ground tissue • Vascular tissue What are tissues made of? Tissues are a group of cells working together to perform a certain function. . Plant Tissues Neighboring cells are often connected by plasmodesmata. Plasmodesmata are strands of cytoplasm that pass through openings in cell walls and connect living cells. Label the Plant Tissues Dermal Tissue Acts similar to human skin. Function: Covers the outside of a plant, providing protection in a variety of ways. Details: Epidermis is made of live parenchyma cells. Can be made of dead parenchyma cells; makes the outer bark of woody plants. Cell types: Made of parenchyma cells Ground Tissue Surrounded by dermal tissue. Function: Provides support and stores materials in roots and stems. Details: Makes up much of the inside of the plant. Where you can find the chloroplasts in leaves. Made of all three cell types. Parenchyma is most common. Vascular Tissue Surrounded by ground tissue. Function: Transports water, mineral nutrients, and organic compounds to all parts of the plant. Details: Made of two networks of hollow tubes. Xylem and Phloem Cell types in Xylem – Tracheid cells and vessel elements Cell types in Phloem – Sieve tube elements, companion cells Xylem and Phloem Similar to our veins and arteries. Xylem: carries water and dissolved mineral nutrients up from roots to the rest of the plant. Phloem: the vascular tissue that carries the products of photosynthesis through the plant.