population genetics ppt
advertisement

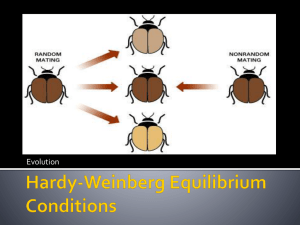
Breeding Bunnies Lab Observe the graph and discuss with your lab mate. • What is the data showing? • Does it make sense? Why? Population Genetics and Speciation MISCONCEPTION ALERT • Individuals DO NOT evolve! • Individuals do not change to match changes in the environment • POPULATIONS are acted upon by natural selection, where less fit individuals are less likely to pass on their genes • This causes a change in the genetic makeup of the population as a whole Genetic Variation within Populations • A healthy population is one with a wide range of genetic diversity, without which evolution CANNOT occur • A wide range of genetic diversity causes there to be many different phenotypes Genetic Variation within Populations • The greater the variation in phenotypes, the more likely it is that some individual can survive in a changing environment • Genetic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool – the combined alleles of all the individuals in a population • An allele frequency is a measure of how COMMON a certain allele is in a population Genetic Change within Populations • Genetic change can occur because of the variations within populations • Genetic change causes a shift in the allele frequencies of certain traits • Genetic change within populations over time can occur in several ways… Mechanisms of Genetic Change Over Time (Evolution) 1. Natural Selection • Occurs when nature selects for or against certain traits Mechanisms of Genetic Change Over Time (Evolution) 2. Gene Flow • When genes are added or removed from a population • Caused by migration (emigration or immigration) Mechanisms of Genetic Change Over Time (Evolution) 3. Genetic Drift • A CHANCE event that can cause the allele frequencies in a population (especially a small population) to change drastically • Can be caused by natural disasters such as fires, volcanoes, earthquakes and floods • Why? Genetic drift (random) Mechanisms of Genetic Change Over Time (Evolution) 4. Non-Random Mating • The cost of reproduction between males and females is different • Males produce many sperm continuously, while females are born with the number of eggs that they have • This allows females to be more choosy when it comes to selecting a mate • Non-Random mating occurs because certain traits in males increase mating success Mechanisms of Genetic Change Over Time (Evolution) 5. Mutations • A random mutation can add a new allele to a population Patterns of Natural Selection • When natural selection is NOT occurring, most populations have a normal distribution • If you were to collect one shoe from each student in your class and ordered and grouped them by size, you would probably form a hill-shape curve shown below, also known as normal distribution Patterns of Natural Selection • When natural selection DOES occur, populations can respond in three major ways… Patterns of Natural Selection • In directional selection, the “peak” of a normal distribution moves in one direction along its range • In this case, selection acts to eliminate one extreme from a range of phenotypes Patterns of Natural Selection • In stabilizing selection, the bell-curve shape becomes narrower • In this case, selection eliminates individuals that have alleles for any extreme type Patterns of Natural Selection • In disruptive selection, the bell-curve is pushed apart in two peaks. • In this case, selection acts to eliminate individuals with average phenotype values Speciation Through Isolation • Do you remember what defines a species? • A species is defined as a group of organisms that can successfully interbreed • It is important to remember that species are not permanent, stable things… Speciation Through Isolation • If gene flow between two populations stops for some reason, the populations are said to be isolated • As these populations adapt to their different environments, their gene pools may change • All of these changes add up over generations Speciation Through Isolation • With time, the isolated populations become more and more genetically different from each other and may no longer be able to mate with each other (they become reproductively isolated) • Reproductive isolation between populations is the final step of becoming separate species Speciation Through Isolation • • The rise of two or more species from one existing species is called speciation There are three ways in which population may become isolated 1. Behavioral Isolation: Caused by a difference in mating behaviors 2. Geographic Isolation: Involves physical barriers that divide a population into 2 or more groups 3. Temporal Isolation: Exists when timing prevents reproduction between populations Which type of isolation is this? Convergent vs. Divergent Evolution • Convergent Evolution – Occurs when different species evolve in similar environments – When this occurs, the different species often evolve to have similar traits – These traits are said to be ANALOGOUS Examples of Convergent Evolution Bird Insect ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES! (circle them in your notes!) Dolphin Shark Convergent vs. Divergent Evolution • Divergent Evolution – Occurs when closely related species evolve in different environments – When this occurs, the similar species evolve to have different traits – These traits are said to be HOMOLOGOUS Examples of Divergent Evolution HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES! Coevolution – The process in which two or more species evolve in response to changes in each other – Species that involve predator-prey or parasite-host relationships often develop adaptations in response to each other