Ch15 Populations Study Guide
advertisement

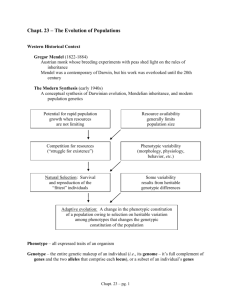
Ch.15 Populations Study Guide Vocabulary Words Gene flow: results from immigration an emigration Inbreeding: increasing the proportion of homozygous in a population Genetic drift: can result from a fire or landslide that leaves only a few survivors of a population Mutation: does not significantly change allele frequencies except over very long periods of time Natural selection: one of the most powerful agents of genetic change Directional selection: eliminates extremes from a range of phenotypes Stabilizing selection: increases the proportion of similar individuals in a population Essay If you were determining how the size of a population might change, what four features of the population would you examine? Population size, population density, growth rate, and dispersion What type of curve is produced when N in the equation AN = rN is plotted against time on a graph? An exponential growth curve Explain how stabilizing selection decreases genetic diversity. Stabilizing selection results in fewer individuals in a population that have alleles promoting extreme types. Individuals become more similar, and genetic diversity decreases. Concepts to Know When directional selection eliminates one extreme from a range of phenotypes, the alleles promoting the extreme trait becomes less common in the population. In the Hardy-Weinberg equation p2+2pq+q2=1, frequency of heterozygous individuals is what 2pq represents. A demographer studying the adult height in males finds that more men are of average height now than 100 years ago, and there are fewer men who are very short or very tall. Stabilizing selection explains this trend. In the U.S., the allele for sickle cell anemia is slowly decreasing in frequency. Allele frequency is least affected by mutations. Cheetahs are in danger of extinction because of the effects of genetic drift. Not all mutations result in phenotypic changes. The Hardy-Weinberg principle applies to all populations as long as evolutionary forces are not working, and the population is large enough that is members are not likely to mate with one another. The logistic model of population growth is usually associated with K-strategies. The statistical study of populations is called demography. Carrying capacity is the population size an environment can sustain over time. Barnacles crowded together on a rock exhibit a clumped dispersion. Populations of species that are r-strategists are characterized by exponential growth. In a population study, r is found to have a negative value, which means that the population is decreasing. Weather and climate are environmental conditions that affect populations, and are known as densityindependent factors.