Section 5.3 for 2011-2012
advertisement
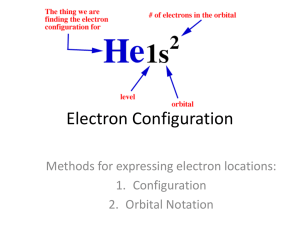
Electron Configurations SECTION 5.3 Electron Configurations Atom is in the ground state 3 rules or laws Aufbau principle Pauli Exclusion principle Hund’s Law Aufbau Principle Electrons occupy lowest energy orbital available All orbitals of a sublevel are equal energy Sublevels have different energies s < p < d <f Orbitals within one principal energy level can overlap orbitals of another Electron Filling Order Which orbital will fill first, 4s or 3d? Periodic Table Helps! Pauli Exclusion Principle Maximum of 2 electrons in an orbital, but only if they have opposite spin. Hund’s rule Electrons with same spin must occupy each equal energy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbital. Orbital Filling Order 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p Electron Configurations Three methods 1. Electron Configuration Notation 2. Noble Gas Notation 3. Orbital Diagrams Electron Configuration Notation Ex: N # of electrons? Start with the lowest energy, fill to capacity, go to next lowest energy, etc. Stop when you run out of electrons. Superscripts = total electrons Electron Configuration Notation You try … Zinc Electron Configuration Notation 2 2 6 2 6 2 10 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Assignment Write the electron configuration notation for the following elements: Boron (B), Neon (Ne), Sulfur (S), Magnesium (Mg), Vanadium (V), Silver (Ag) Noble Gas Notation Shorthand Find the noble gas closest to the element (without going over). Ex: For Gold (79): Xenon (54) We write [Xe] and start counting from there The first orbital after xenon is 6s Noble Gas Notation 2 14 9 [Xe]6s 4f 5d Check: (Xe’s atomic number) 54 + 2 + 14 + 9 = 79 (gold’s Atomic number)! You Try… Silver Assignment P.147 #79 Orbital Diagrams Draw a line for each orbital Designate each electron with an arrow = orbital with 1 electron = orbital with 2 electrons Orbital Diagrams Nitrogen: 1s22s22p3 Write notation of N 1s 2 s 2p Then we fill them with electrons using the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s law 1s 2s 2 p Orbital Diagrams You try another example: Cu Orbital Diagrams Answer 1s 2s 2 p 2 p 2 p 3s 3 p 3 p 3 p 4s 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d Assignment Draw orbital diagrams for beryllium, aluminum, nitrogen, and sodium, manganese, germanium, and europium. Electron Dot Structures Valence electrons Electrons in outermost energy level. Responsible for chemical properties Electron Dot Structures Valence electrons only Place ‘dots’ around element symbol 4 sides of element = orbitals Fill these orbitals one at a time (Hund’s) Electron Dot Structures Assignment P.141 #23(yellow box), 26, 28 P.147 #81




![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)

