Organic Chemistry
advertisement

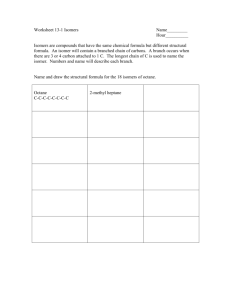
Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbons • Contain only carbon and hydrogen • Carbon (4 valence e ) will ALWAYS form four bonds Alkanes • Only single covalent bonds • C1-C4—gases at room temp. • C5-C10—liquids at room temp. • C11 and up—solids at room temp. • Nonpolar molecules, do not mix with water. Alkanes • CnH2n+2 is the formula for all alkanes • Structural— • Condensed— • Molecular-- Naming Alkanes • Find the longest “parent chain” in the molecule and name it. • Name any branches using the correct prefix and the ending “-yl” • Assign a number for the location on the parent chain where the branch is located. Isomers • Structural isomers have the same molecular formula, but different structures. • Since they are built differently, they have different properties and react differently with other compounds. Isomers • Build a model of C4H10 Isomers • Build a model of C4H10 • Does it look like this? Isomers • There is another form of C4H10 • And it looks like this: Same molecular formula (C3H8), but completely different construction. That’s isomers. Isomers • How many isomers are there for pentane? • How many are there for hexane? • Draw and name as many octane isomers as you can (as a group) before the end of class. (1 pt. each) • Do the isomers page for homework. Alkenes and Alkynes • Contain double (-ene) or triple (-yne) bonds. • Called unsaturated compounds. • How do we name them? Functional Groups • This is a specific arrangement of atoms attached to an organic compound. • The method we’ll use to introduce them will have the molecule represented as ‘R’ and the functional group attached. Halocarbons • This is a hydrocarbon with a halogen attached to it. R-Cl or R-Br • How do you name them? Alcohols • This is a hydrocarbon with a hydroxyl attached to it. R-OH • The carbon with the hydroxyl is numbered first, before any other attachment. • How do we name them? Ethers • This is a hydrocarbon that has an oxygen along the chain. R-O-R’ • How do we name them? • Unfortunately, there are two systems for naming ethers: Aldehydes & Ketones • They have a carbonyl group attached to them. -C=O • A ketone has the carbonyl along the middle of the chain, and an aldehyde has the carbonyl at the end of the chain. • How do we name them? Carboxylic Acids • Have a carboxyl group attached to them. • These acids donate hydrogen ions just like any other acid. • The carbon with the carboxyl attached to it is automatically carbon # 1. • How do we name acids? Esters • Product of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol • Often used as artificial flavors and fragrances. Amines and Amides • Contain the functional group –NH2 • Amines have the NH2 anywhere along the chain. • Amides have the NH2 at the end of the chain, attached to a carbonyl group. • And for the last time, how do we name them? Benzene Some benzene compounds Drug Compounds Ephedrine methamphetamine Caffeine Steroids Steroid Basis Andro Some others… • andriol Some others… dianabol Polymers • Large molecules formed by the repeated bonding of smaller molecules. • For example, polyethylene is formed by repeating ethene molecules; sometimes thousands of them. • Everything we know as plastic is some kind of polymer. Fatty Acids or Fats • Fats are carboxylic acids. • An acid with only single bonds along the chain is a saturated fat. • An acid with double bonds along the chain is an unsaturated fat. Fatty Acids • The double bond comes in two types, cis- and trans-. • The trans- bond keeps the chain straight, and the cis- bonds makes the chain bend. Omega 3 Fatty Acids Table of Fatty Acids Carbon Double Atoms Bonds Butyric acid 4 0 butanoic acid butterfat Caproic Acid 6 0 hexanoic acid butterfat Caprylic Acid 8 0 octanoic acid coconut oil Capric Acid 10 0 decanoic acid coconut oil Lauric Acid 12 0 dodecanoic acid coconut oil Myristic Acid 14 0 tetradecanoic acid palm kernel oil Palmitic Acid 16 0 hexadecanoic acid palm oil Palmitoleic Acid 16 1 9-hexadecenoic acid animal fats Stearic Acid 18 0 octadecanoic acid animal fats Oleic Acid 18 1 9-octadecenoic acid olive oil Common Name Scientific Name Sources Polymers • All of these polymers that make plastics and fabrics are made of molecules that were distilled from crude oil. Where a standard barrel of crude oil goes: • • • • • • • 47% Gasoline 23% Heating oil & Diesel fuel 18% Plastics, synthetic rubber, chemicals 10% Jet fuel 4% Propane 3% Asphalt If we quit driving cars today, we would still need oil for lots of things.