Cells

Cells
History of the cell
When Robert Hooke viewed a thin cutting of cork he discovered empty spaces contained by walls, and termed them pores, or cells. The term cells stuck and Hooke gained credit for discovering the building blocks of all life.
Robert Hooke (Link)
Cell Theory in Pictures
Three parts to Cell Theory:
1. Cells are the Building Blocks of Life
= Cells
2. All life processes take place in Cells
3. New cells come from existing cells
= Organism
Two Different Cell types
• Prokaryotic- “simple” cells (ex. Bacteria)
• Eukaryotic- “complex” (complejo) cells
•
Prokaryotic
Most living things you are familiar with (including humans) have eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic
ANIMAL CELL
http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm
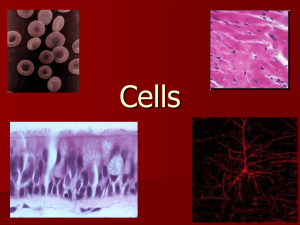
Cells under the Microscope
Cells under the Microscope
Blood Cells
Brain Cells Heart Cells
Lung Cells Egg Cells Sperm Cells
The Nucleus
(The Brain of the Cell)
Nucleus- The Control Center of the cell
Functions: directs all cell activities “the Boss,” contains DNA
Descriptions: Generally located in the center of the cell, surrounded by a membrane
Chromosomes- Threadlike material of DNA that contains genes
Gene- Piece of DNA that Contains information about organisms characteristics –
Eye color, height, etc.
So, What is DNA? (Click me to find out)
Cell Membrane
Description: Protective layer around all cells.
If the cell does have a cell wall the cell membrane is inside of it.
Function: Controls what comes in and out of the cell.
Water moves freely through this membrane.
Cytoplasm
Function: holds the organelles in place.
Description: Gel-like material; the “goop” of the cell
Cytoskeleton is found in cytoplasm. Helps cells change or keep their shapes.
Organelles are found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
Mitochondria
Description: peanut shaped in cells
Function: Energy is stored and released in the mitochondria (“Powerhouse” of cell).
Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates
Endoplasmic Reticulum “ER”
Endoplasmic reticulum (like factory conveyor belts)
Function: moves materials from one part to another in the cell.
Description: folded, or maze-like that goes from nucleus to cell membrane.
Smooth type: has no ribosomes
Rough type (pictured): has ribosomes in surface
Ribosomes
Function: creates proteins
Each cell contains thousands
Description: Found on ER and floating throughout the cell’s cytoplasm
Golgi Bodies
Golgi bodies (like the factory packing and shipping department)
Description: Stacked, flattened membranes
Function: Sorts, transports and packages proteins and other materials in the cell
Moves materials within the cell
Moves materials out of the cell
Lysosomes
Lysosomes (like the factory waste management dpartment):
“trash can” of the cell
Break down and recycle substances
Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal
Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes or ruptures
Vacoules
Description: membrane-bound sacks (the “storage container” of the cell)
Function: stores water, food, and waste products.Help
plants maintain shape- very large in plants
Chloroplasts (plants only)
Chloroplasts (like factory solar energy plants)
Description: Green and bean shaped organelles
Turns energy from the sun (with
CO
2 and water) into food
Function: Contains green chlorophyll and is where photosynthesis takes place
Cell Wall(plants only)
Description: Surrounds a plant cell
Function: protects the cell and gives it shape.
Cell membrane is still in plants, but the cell wall is the outer most layer.
PLANT CELL
http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm
http://news.discovery.com/videos/earth-frozen-fruit-death.html
What makes a plant cell different from an animal cell?
Chloroplasts – made from the chemical chlorophyll (C
55
H
72
O
5
N
4
Mg)
Used for Photosynthesis -
Makes food for the plant
Cell Wall-The rigid outermost cell layer found in plants
Bigger Vacuole
Rigid/Defined Shape
LAB TIME- Animal Cell
LAB TIME- Plant Cell
Reflection
Draw a cell and label at least 5 of the organelles.
Summarize the three parts to cell theory.
Compare and contrast the plant cell and the animal cell.
Point out the importance of why plant cells cannot freeze
Develop a plan of action to keep your cell healthy.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA, is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms.