Mitosis Notes
advertisement

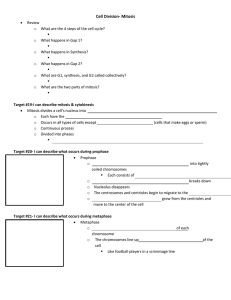
Mitosis Notes Mitosis is Asexual Reproduction • Produces genetically identical cells to the parent cell. •Done by somatic (body) cells in humans Somatic cells… • …Are diploid or 2n •Have two of each type of chromosome •Humans have 23 pairs or 46 total chromosomes Cell Cycle • Series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. 4 Phases: G1, S, G2, and M Interphase… • …consists of G1, S, and G2 •Cell Division = M Phase = Mitosis and Cytokinesis •Mitosis = Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase *Interphase • G1 = Cell growth •S = DNA Replication •G2 = Preparation for Mitosis •(more organelles produced) Prophase • 1st Phase of Mitosis, or M Phase – Longest •Chromosomes become visible •Condensed DNA Prophase (cont.) • Centrioles (in animals) move to the poles •Aster Microtubules form around centrioles •Spindle Microtubules Form •Attach to the centromere and help to move the chromosomes Prophase (cont) • Nuclear Membrane breaks down •Nucleolus disappears •Chromosomes moving towards the equator Prophase Asters Centrioles Spindle Chromosome Nuclear membrane breaking down Metaphase • 2nd Phase of Mitosis •Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Metaphase Anaphase • 3rd Phase of Mitosis •Centromeres Split •Sister chromatids now become individual chromosomes •Chromosomes move to the poles Anaphase Telophase • 4th Phase of Mitosis •Chromosomes begin to unwind and become chromatin again •Nuclear Membrane and Nucleolus reforms •Spindles and Asters break apart Telophase •Mitosis or division of the nucleus is complete •Cytokinesis has to occur to divide the cell or cytoplasm •Usually occurs during Telophase Animal Cytokinesis • Forms a furrow – “Pinches” from the Outside to Inside Plant Cytokinesis • Forms a cell plate made of cellulose – Starts from the inside and works to the outside Product • 2 Genetically Identical Daughter Cells •If not identical: 1. Cell will not function properly 2. Cell can die Importance of Mitosis 1. Growth 2. Healing 3. Regeneration