evolution concept map
advertisement

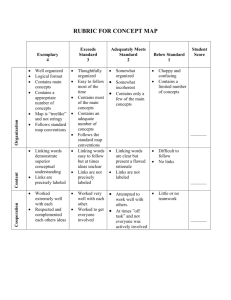
Assg: HON Name EVOLUTION CONCEPT MAP Date pd. Your task is to create one or a couple concept maps to show how the concepts are related. Include a brief description of the concept in the text box (shape) and put words on the arrows to show why you linked the certain concepts together. Use your notebook, worksheets, online activities, and resource textbooks to create your concept map. You need to read, process, and think how these concepts relate to how and why organisms change through time. RUBRIC FOR CONCEPT MAP Exceeds Standard Adequately Meets 9 Standard 8 Organization _______ Exemplary 10 Content ______ Cooperation _________ Well organized Logical format Contains main concepts Contains a appropriate number of concepts Map is “treelike” and not stringy Follows standard map conventions Linking words demonstrate superior conceptual understanding Links are precisely labeled Worked extremely well with each Respected and complemented each others ideas Approaching Standard 7 Thoughtfully organized Easy to follow most of the time Contains most of the main concepts Contains an adequate number of concepts Follows the standard map conventions Somewhat organized Somewhat incoherent Contains only a few of the main concepts Choppy and confusing Contains a limited number of concepts Linking words easy to follow but at times ideas unclear Links are not precisely labeled Linking words are clear but present a flawed rationale Links are not labeled Difficult to follow Links are vague Worked very well with each other. Worked to get everyone involved Attempted to work well with others. At times ”off task” and not everyone was actively involved Little or no teamwork Concepts to Include: adaptive radiation or divergent evolution homologous structure analogous structures homology artificial selection Lamarck’s idea of evolution binomial nomenclature (genus, species) macroevolution biogeography microevolution bottleneck effect molecular homologies coevolution mutations convergent evolution natural selection Darwin natural selection descent with modification Origin of Species directional selection paleontology disruptive selection phylogeny domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, population genetics species punctuated equilibrium evolutionary adaptation speciation founder effect stabilizing selection gene flow systematics gene pool taxon genetic drift taxonomy gradualism uniformitarianism vestigial organs Please add to your handout… Allopatric speciation Sympatric speciation Prezygotic barriers Postzygotic barriers Evidence of evolution Genetic variation