writing and balancing equations
advertisement

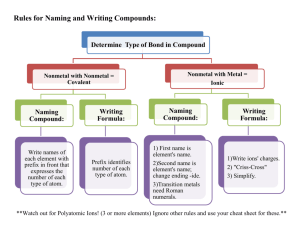
Chemical Reactions • A basic definition of a chem rxn is: • A Rearrangement of Atoms • Really - it is substance(s) changing into different substances Here is an Example • Notice the motion Evidence of Chemical Reactions • Visual Clues A. Color changes B. Formation of a solid (precipitate) C. Flame occurs D. Bubbles are produced (gas) • Temperature changes A. Heat is produced (exothermic) B. Heat is absorbed (endothermic) An Example • Eggs, flour, sugar, baking soda, and oil all in various amounts • combine together • to form Cake! A chemical reaction • The reactants (eggs, flour, etc.) have changed and are no longer eggs, flour, etc. • There is a new substances called a product cake in this case. How do we write these? • We write these reactions with + signs and signs. • Eggs + Flour + Baking Soda + Sugar Cake • Be Careful! The Eggs, flour, etc. are not the same. They don’t exist anymore!!!! Another Example • Hydrogen gas combined with oxygen gas will produce dihydrogen monoxide liquid • H2 + O2 H2O • More examples on Help Page Why the H2 and O2?!? • These are called Diatomic Molecules • Whenever you see hydrogen all by itself, it will be paired up! • There are 7 of them (see Periodic Table) • There are other examples of this: • Phosphorus all by itself is P4 • Sulfur all by itself is S8 Phases • In most cases, phases must also be written. You should always include symbols for reactions you observe in the laboratory! • Three common phases: • Solid ex: Cu(s) • Liquid ex: H2O(l) • Gas ex: Cl2(g) Weird Phases • • • • Plasma – not common Aqueous NaCl(aq) These are solutions Made of water and something dissolved in water • Mr. Wikrent’s favorite solution is soda. It has many healthy nutrients dissolved in the water of each delicious can. • What is the difference between Cu and Cu+2? What does a solution look like? • To the naked eye it looks like a liquid • Upon closer inspection it is many substances mixed together See an example See another example Back to our example • Hydrogen gas combined with Oxygen gas will produce Dihydrogen Monoxide liquid H 2 + O 2 H 2O • Should be: • H2(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) BUT, matter is always conserved, atoms must be conserved!!!!!!!! In order to make water, there needs to be 2 hydrogen molecules for every 1 oxygen molecule. 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(l) Let’s look back at the Help Pages • Help Pages WE MUST BALANCE!!! To correctly write and balance an equation: 1. Formulas MUST be correct 2. There must be the same number of each kind of atom on each side of the arrow. This is done by using coefficients (numbers in front of a formula). 3. Do not change formulas to balance atoms!! 4. Follow a trial and error process. Balance each species one at a time. Be prepared to erase!! Balancing simple equations K + Cl2 KCl Fe + O2 Fe2O3 LiCl Li + Cl2 NaN3 Na + N2 NiO + Al Al2O3 + Ni C4H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O Ag2O Ag + O2 B2O3 + Mg B + MgO KBr + Cl2 KCl + Br2 Balancing Reactions containing polyatomic atoms • Example Li3PO4 + MgCO3 Li2CO3 + Mg3(PO4)2 1. Keep the polyatomic ions together on both sides 2. Balance the metal ions first, or if they are balanced, the polyatomic ions first, metals last If your formulas are correct, the equation should balance Balance: Cu + AgNO3 Ag + Cu(NO3)2 NaI + Pb(NO3)2 NaNO3 + PbI2 Ca(CH3COO)2+ K2CO3 CaCO3+ KCH3COO Word equations (writing equations from observations) Water is decomposed by electricity to produce hydrogen and oxygen gases through a process called electrolysis. When copper(II)chloride is dissolved in water and reacts with aluminum metal, copper metal and an aluminum chloride solution is produced. Lead(II)nitrate solution reacts with sodium sulfate solution to produce lead(II)sulfate solid and sodium nitrate solution. Aluminum iodide solution reacts with lithium hydroxide solution to produce aluminum hydroxide solid and lithium iodide solution. tetracarbon decahydride (butane) gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. Ammonia gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce nitrogen gas and liquid water. Remember the following: 1. Diatomic elements hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, oxygen gas AND all halogens in their elemental form 2. The formulas and charges of the polyatomic ions WOW • The key is that Formulas MUST be correct and there must be the same number of each kind of atom on each side of the arrow. • Now go be reactive and produce some good work. • Assignment is: (depending on how well you work)