Slide 1
advertisement
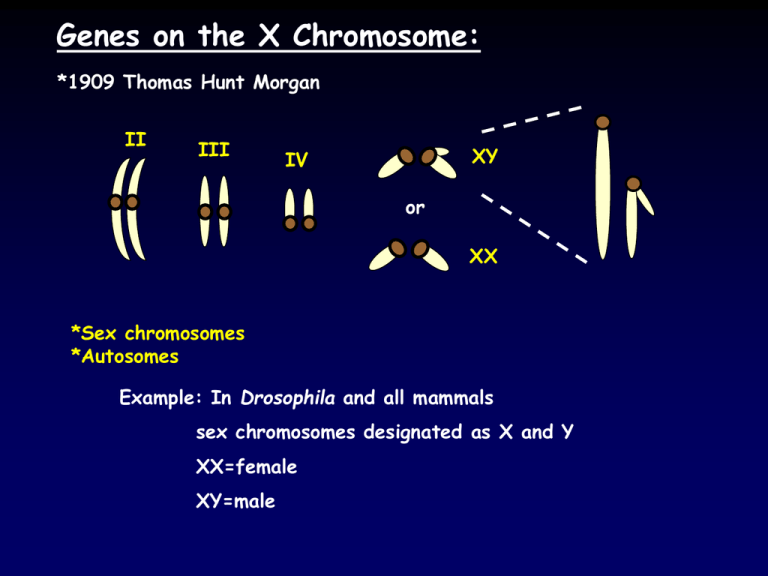
Genes on the X Chromosome: *1909 Thomas Hunt Morgan II III XY IV or XX *Sex chromosomes *Autosomes Example: In Drosophila and all mammals sex chromosomes designated as X and Y XX=female XY=male Modifications of Mendelian Ratios X-linkage - transmission and expression of genes on the X chromosome X-linkage in Drosophila: white mutation (eyes) sex-linkage - transmission and expression of genes on sex chromosomes Sex-limited Inheritance: *Sex-limited trait – trait that is expressed in only one sex even though the trait may not be X-linked. *holandric genes: genes on the Y chromosome Example: hypertrichosis (excess ear hair) *autosomal genes Example: milk production in mammals; L=lots, l=little Sex-influenced Inheritance: *Sex-influenced trait – phenotypic expression that is conditioned by the sex of the individual Examples: *cleft palate in humans *horns in sheep *pattern baldness in humans Summary: Sex-linked: on X or Y sex-chromosome Sex-limited: all or none expression by sex Sex-influenced: genotype + sex determines phenotype Phenotypic Expression: Gene expression often governed by genotype and environment *Penetrance – frequency with which individuals with a given genotype exhibit some degree of a phenotype associated with that trait. If 9/10 of individuals carrying an allele express the trait, the trait is said to be 90% penetrant *Expressivity – the degree or range in which a phenotype for a given trait is expressed *Temperature *Onset of genetic expression Chapter 7: Sex Determination Life cycles and reproductive modes *Asexual reproduction – formation of new individuals from the cell(s) of a single parent. *Sexual reproduction – reproduction through the fusion of gametes. *Alternation of generations – alternation of forms or of mode of reproduction in the life cycle of an organism. Some additional terms: *Primary sexual differentiation *Secondary sexual differentiation *Unisexual, dioecious and gonochoric *Bisexual, monoecious and hermaphroditic Chlamydomonas Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) X and Y Chromosomes: Early Studies 1906 Edmund B. Wilson and Protenor X and Y Chromosomes: Early Studies Wilson and Lygaeus X and Y Chromosomes: Early Studies Homogametic sex – sex which produces uniform gametes with respect to sex chromosomes. Heterogametic sex – sex which produces gametes with unlike sex chromosomes. *The male is not always the heterogametic sex… Examples: Moths, butterflies, most birds, some fish, reptiles, amphibians, at least one species of plants Chromosome Composition in Humans Karyotype XX XY








