The Human Genome
advertisement

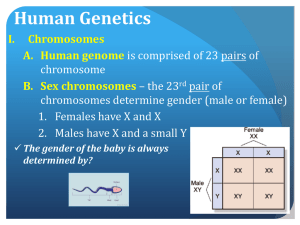
The Human Genome Chapter 14 Human Chromosomes • Karyotype: chromosomes arranged with their pairs in order. • Sex Chromosomes: two of the 46 chromosomes – XX = female – XY = male • Autosomes: the remaining chromosomes Human Traits • Pedigree: chart which shows the relationship within a family – box= a male – circle = a female – colored in = shows the trait – blank shape = does not have the trait – half color and half blank = carries the trait Hemophilia Pedigree • Hemophilia has played an important role in Europe’s history, for it suddenly cropped up in the children of Great Britain’s Queen Victoria. It became known as the “Royal disease” because it spread to the royal families of Europe through Victoria’s descendants. • It first appeared in Victoria’s family in her eighth child, Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany. Throughout his short life, he suffered severe hemorrhages, and always was described as “very delicate.” Leading the life of a normal youngster was impossible because any cut or bump could lead to death. It was necessary to keep him always under strict surveillance. In spite of all the protection, he died at the age of 31 as the result of a minor fall. Pedigree Problem • A man who had purple ears came to the attention of a human geneticist. In this family, purple ears proved to be an inherited trait due to a single genete. The man's mother and one sister also had purple ears, but his father, his brother, and two other sisters had normal ears. The man and his normal-eared wife had seven children, including four boys and three girls. Two girls and two boys had purple ears. Human Genes • The human genome: the complete set of genetic information that includes tens of thousands of genes. Sex-Linked Genes • found on the X chromosome • More than 100 genetic sex-linked disorders • In males: inherits an X chromosome from the mother that has the recessive gene • In Females: inherits X chromosomes that have the recessive gene from the mother and father Hemophilia • Two genes carried on the X chromosome control blood clotting • Caused by a recessive gene • 1 in every 10,000 males • Symptoms: bleed to death from minor cuts and bruises • Treatment: injections of clotting proteins Color Blindness • Three genes associated with color vision located on the X chromosome • recessive gene produces colorblindness • Symptoms: Inability to distinguish certain colors • red green color blindness Muscular Dystrophy • the progressive weakening and loss of skeletal muscle • 1 out of every 3000 males • Caused by a defective version of the gene that codes for a muscle protein • No cure as of now Problem • Cross a color blind male with a normal female. What is the genotype of their offspring? • A females father is color blind and she is not. Her husband is not color blind. What is the probability that they will have color blind children