Roles of the President
advertisement

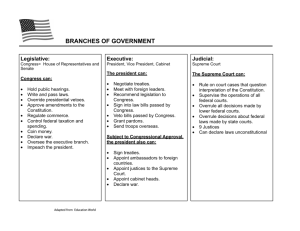
Chief Executive As Chief Executive, the president is in charge of 15 cabinet departments and more than 3 million government workers. The president appoints the heads of cabinet departments and large agencies (Senate must approve) Ex. Dept. of Defense, State Dept., Dept. of Treasury The president does not have any legislative powers (cannot make laws), but he can issue executive orders—rules or commands that have the force of law. Can be good for the nation—Ex. Order 9981 (1948) desegregates military Can be detrimental to the country—Ex. Order 9066 (1942) Japanese American Internment camps The president can appoint federal judges, including Supreme Court justices. This is important because the way the Supreme Court interprets laws greatly affects life in the U.S. Most presidents will appoint justices who share views similar to their own Influence will be felt long after they leave the White House The president can appoint federal judges, including Supreme Court justices. This is important because the way the Supreme Court interprets laws greatly affects life in the U.S. Most presidents will appoint justices who share views similar to their own Influence will be felt long after they leave the White House Chief Diplomat The president is responsible for directing foreign policy, or the country’s strategy on how we deal with foreign nations and the relationships we build Directs the U.S. in making key decisions about how we conduct ourselves in the world Makes treaties Makes foreign policy decisions with foreign leaders Makes treaties Makes executive agreements Agreement between president & leader of another country Does not require Senate approval Commander - in – Chief As commander-in-chief, the president is in charge of all branches of the armed forces. Congress and the president share the power to make war. Only Congress can declare war, but only the president can order soldiers into battle. Can order troops to end disturbances within the U.S Congress has declared war only 5 times, yet presidents have sent troops into action over 150 times. After the undeclared Vietnam War, Congress passed the War Powers Act (1973) The President must inform Congress he is sending troops into battle immediately & he must bring them home after 60 days unless Congress grants Chief Legislator Leads Congress in lawmaking Can write a bill but someone in Congress must introduce Gains support for legislation through the mass media Only Congress may introduce bills, but the executive branch proposes most legislation. All presidents have a legislative program that they want Congress to pass. The speeches they give to key members of Congress and the public is done so to build support for their programs. The presidents’ staff works on the laws with members of Congress. Ex. Patriot Act or tax cuts The president and Congress often disagree. A main reason for that the president represents the whole nation. Congress members only represent their states or districts Another reason is that the president can only serve two terms. Many Congress members win reelection many times and remain in office sometimes for decades. As a result, the president often wants to move faster on programs than members of Congress do. (Status Quo v. Change) Head of State/ Chief of State The president is the living symbol of the U.S. As head of state, the president is responsible for hosting visiting foreign leaders and carrying out ceremonial functions. Ex. Awarding medals or throwing out the first pitch at a baseball game. Economic Leader As a country’s economic leader, it is the presidents’ job to ensure that the economy is prospering. The president must plan the federal budget and try to deal with problems such as unemployment, rising prices (inflation), and high taxation. Makes sure the nation prospers Makes sound fiscal policy Party Leader The president is the face of his or her political party. Members of the political party work hard to elect the president into office. In return, the president gives speeches to raise campaign money and help fellow party members win political office in the Senate, House, and Governor’s seats Judicial Leader Appoints judges who serve for life Can pardon an individual Power to give pardons Pardons are forgiveness and freedom from punishment Commute sentences – person keeps the charge but doesn’t have to serve sentence Can give amnesty to a group Can delay punishment through a reprieve Roles of the President Chief Executive Chief Diplomat Commander-in-Chief Chief Legislator Head of State/Chief of State Economic Leader Party Leader Judicial Leader