File
advertisement

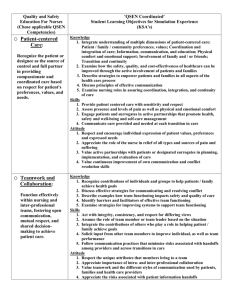
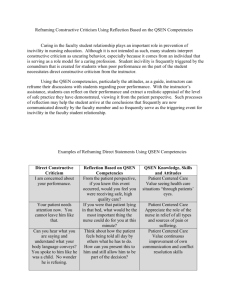
Nursing Practice Standards QSEN - 4 Quality and Safety Education for Nurses Nicole Chambers, Angela Helder, Kim Karwowski, Maggie Siler Ferris State University What is the practice standard of Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN)? According to the QSEN website: • The overall goal of this initiative is to educate all nurse's with the knowledge and abilities "to continuously improve the quality and safety of the healthcare systems within which they work". • It is funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. • The long term goal is to reshape nursing's outlook on the development of the necessary knowledge, skills, and attitudes (KSA's) regarding quality and safety competencies. • It is meant to improve competencies regarding: patient centered care, teamwork, collaboration, evidence based practice, quality improvement, safety, and informatics. (Quality and Safety Education for Nurses, 2011) The four initiatives on which QSEN is based are described below by the Francis Payne Bolton School of Nursing: 1. Defined quality and safety competencies for nursing and propose targets for the knowledge, skills, and attitudes (KSA's) to be developed in nursing pre-licensure programs for each competency: patientcentered care, teamwork and collaboration, evidence-based practice, quality improvement, safety, and informatics. 2. They also completed a national survey of baccalaureate program leaders and a state survey of associate degree educators to assess beliefs about the extent to which the competencies are included in current curricula, the level of satisfaction with student competency achievement, and the level of faculty expertise in teaching the competencies. 3. QSEN partnered with representatives of organizations that represent advanced practice nurses and drafted (in press) proposed knowledge, skills, and attitude targets for graduate education. 4. Funded work with 15 pilot schools who committed to active engagement in curricular change to incorporate quality and safety competencies. (Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing, Case Western Reserve University, 2010). Who Created Quality and Safety for Nurses (QSEN)? • QSEN was developed from a Robert Wood Johnson foundation grant. • The Grant has three phases. Each of the phases has a team of professionals that assist with the research and development of the phases initiative. • Linda Cronenwett and Gwen Sherwood are the principal investigators for phases I and II • Phase III led by Linda Cronenwett and Geraldine P. Bednash Who Created Quality and Safety for Nurses (QSEN)? (continued) • "Linda Cronenwett PH.D., F.A.A.N. dean at University of North Carolona at Chapel Hill School of Nursing"(QSEN, 2011) • "Gwen Sherwood, PH.D., RN, F.A.A.N., Associate dean for Academic Affairs and Professor University North CarolinaChapel Hill School of Nursing" (QSEN, 2011) • "Geraldine P. Bednash, PH.D. F.A.A.N. is the excutive director at the American Association of College of Nursing" (QSEN, 2011) Why was QSEN created? • The Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN) project was launched with a $590,000 grant in 2005. • The initial grant was used for evaluating and enhancing nursing curriculum involving safety and nursing issues(eHow.com, 2011). Why was QSEN created? (continued) There were three phases to the grant: • Phase I: defined six competencies crucial to health care quality and safety - Patient-centered care giving - Collaboration - Teamwork - Quality improvement - Evidence-based practice - Safety • Phase II: nursing schools integrated the six competencies into their curriculum -- Courses were refined and QSEN concepts were incorporated into clinical, lab and classroom settings. -- Continuing education courses for nurses included QSEN competencies • Phase III: developed ways for student assessment and aided faculty experts to spread QSEN through nursing education. -- Incorporated into textbooks and licensing exams -- Certification and accreditation requirements and continuing education standards were formulated How long has QSEN been around? QSEN began as an initiative in October, 2005 to correlate with the Institute of Medicine's (IOM) Health Professions Education report recommendation for transforming nursing education through curricula that support learning of the quality and safety competencies. • First phase of QSEN ended in early 2007: resulted in the determination of 6 learning objectives for quality and safety competencies, but the nursing faculties lacked the knowledge of fundamental concepts related to the competencies, how to identify, develop, assess, and implement the ideas. • Q SEN Phase II launched April 2007 and ran through October 2008: 15 pilot nursing schools were selected who were ready to design curricula and test teaching strategies to support quality and safety competency development among their nursing students. How long has QSEN been around? Continued • QSEN Phase III was funded in November 2008: Plans were to continue working, evaluating, and sharing the six IOM/QSEN competencies, working with faculty expertise development, and to create mechanisms to sustain changes. QSEN provides guidelines for nursing practice competencies. It is a nursing practice standard that is continually evolving and shapes the practice of current and future nurses. The 2012 Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN) National Forum will take place in Tuscon, Arizona from May 30 at 1 pm through June 1, 2012 at 12 pm. Further details are available at: http://www.qsen.org/conferences/2012/ Sources: http://0-www.sciencedirect.com.libcat.ferris.edu/science/article/pii/S0029655409001778 http://www.qsen.org/overview.php Want to learn more? Introduction to the QSEN Competencies: A Self-Paced Tutorial: https://evolve.elsevier.com/cs/Satellite/Article/Introduction+to+the+QSEN+Compete ncies+A+SelfPaced+Tutorial?cid=700000001286413&Audience=Faculty Nicole Chambers RN In my current practice of neonatal intensive care nursing (NICU) QSEN influences my practice every day. We have multiple protocols that we are required to know and follow. We also have yearly competencies that are required by our institution. Every new nurse to the NICU is required to complete a program called Didactic. This program is a 12 week long program that is taught by the nurse practitioners. They discuss each system in the neonate and go through an assessment. Our newest initiative is relationship based care RBC. Monthly meeting are conducted to discuss ways we can improve this area. I am also part of a program called The Inpatient Satisfaction Team. The Idea of this team is to improve patients stay while in the hospital. The team incorporates many disciplines in all departments as well as management to improve care throught out the institution. Angela Helder, RN I am a recent graduate of an ADN program and just began my nursing career about two months ago working in the area of Women's Health/OB/GYN in a medical office. QSEN practice standards play an important role in the office setting. Some examples include: • Completion of an orientation program with required competency testing. • Specific phone protocols put into place for the triage nurses. • Nurses performing NST's (Non Stress Tests) are required to have taken a Fetal Monitoring Class offered through the hospital as continuing education. Paying attention to detail, staying up to date with the current evidencebased practice and advocating for patients are all a part of quality nursing care. Kim Karwowski, RN In my current practice area of cardiovascular, the QSEN practice standards influence my nursing practice in numerous ways: • Our unit uses Situation, Background, Assessment, & Recommendation or SBAR communication strategies for discussions with and calls to physicians. • Ongoing educational requirements for our unit include SHLIO or online learning modules. • We have mandatory yearly competency cruises, which consist of a skills review and competency validation requirement held on the unit, off site for skill stations, and online quizzes. • Our unit requires current basic and advanced cardiac life support (BLS and ACLS). • It is encouraged to attend progressive care classes and to pass the exam for certification. Our unit cares for patients with Left and BiVentricular Assist Device and the hospital is undergoing certification for heart transplants and there are additional required mandatory classes to care for the machines and patients. • The change of current methods are driven by evidence based practices. Maggie Siler RN, CCRN, RCIS In my current practice area of the cardiac catheterization laboratory the QSEN nursing standard influences my practice in a number of ways. We have a large assortment of coronary and peripheral interventional equipment for which we are held highly accountable to knowing detailed application and use. There are x-ray safety and vascular access competencies to name a few! Also included are hospital wide competencies such as critical care skills and safety days to ensure our knowledge of more general topics. One of the more recent quality initiatives we have started is Relationship Based Care (RBC). My hospital is a magnet institution which includes a clinical ladder. Both require ongoing education and quality engagement. I am also part of our regional STEMI committee and am beginning my service learning project involving public education on that topic. References Cronenwett, L., Sherwood, G., Gelmon, S., (2009). Quality and safety education. Nursing Outlook, 57 (6), 304-312. doi:10.1016/j.outlook.2009.09.004 eHow health. Quality & Safety Education in Nursing. (2011). http://www.ehow.com/facts_7392552_quality-safety-educationnursing.html Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing (2010). http://fpb.case.edu/QualSafe/qsen.shtm Quality and Safety Education for Nurses. (2011). http://www.qsen.org/about_qsen.php