Endrocrine Images
advertisement

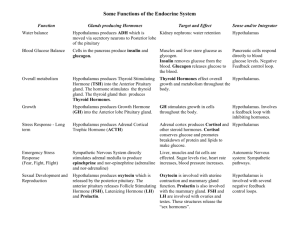
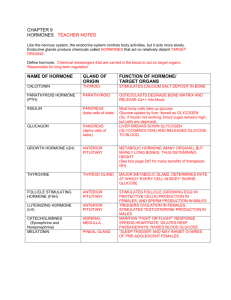
Endocrine System Figure 45.2a Blood vessel Response (a) Endocrine signaling Response (b) Paracrine signaling Response (c) Autocrine signaling Figure 45.2b Synapse Neuron Response (d) Synaptic signaling Neurosecretory cell Blood vessel (e) Neuroendocrine signaling Response Figure 45.4 Major endocrine glands: Hypothalamus Pineal gland Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands (behind thyroid) Organs containing endocrine cells: Thymus Heart Liver Adrenal glands (atop kidneys) Stomach Pancreas Kidneys Ovaries (female) Small intestine Testes (male) Figure 45.14 Cerebrum Pineal gland Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebellum Pituitary gland Spinal cord Hypothalamus Posterior pituitary Anterior pituitary Figure 45.5 Water-soluble (hydrophilic) Lipid-soluble (hydrophobic) Polypeptides Steroids 0.8 nm Insulin Cortisol Amines Epinephrine Thyroxine Figure 45.6-2 SECRETORY CELL Lipidsoluble hormone Watersoluble hormone VIA BLOOD Signal receptor TARGET CELL Cytoplasmic response Transport protein OR Gene regulation Signal receptor Cytoplasmic response NUCLEUS (a) (b) Gene regulation Figure 45.7-2 Epinephrine Adenylyl cyclase G protein G protein-coupled receptor GTP ATP cAMP Inhibition of glycogen synthesis Promotion of glycogen breakdown Protein kinase A Second messenger Figure 45.8-2 EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Hormone (estradiol) Estradiol (estrogen) receptor Plasma membrane Hormone-receptor complex NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM DNA Vitellogenin mRNA for vitellogenin Figure 45.9 Same receptors but different Different receptors intracellular proteins (not shown) Different cellular responses Different cellular responses Epinephrine Epinephrine Epinephrine receptor receptor receptor Glycogen deposits Glycogen breaks down and glucose is released from cell. (a) Liver cell Vessel dilates. (b) Skeletal muscle blood vessel Vessel constricts. (c) Intestinal blood vessel Figure 45.11 Example Pathway Negative feedback Low pH in duodenum Stimulus Endocrine cell S cells of duodenum secrete the hormone secretin ( ). Hormone Target cells Response Blood vessel Pancreas Bicarbonate release Figure 45.12 Example Pathway Stimulus Suckling Sensory neuron Positive feedback Hypothalamus/ posterior pituitary Neurosecretory cell Posterior pituitary secretes the neurohormone Neurohormone oxytocin ( ). Blood vessel Target cells Response Smooth muscle in breasts Milk release Figure 45.14 Cerebrum Pineal gland Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebellum Pituitary gland Spinal cord Hypothalamus Posterior pituitary Anterior pituitary Figure 45.16 Tropic effects only: FSH LH TSH ACTH Neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus Nontropic effects only: Prolactin MSH Nontropic and tropic effects: GH Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones Portal vessels Endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary Pituitary hormones Posterior pituitary HORMONE FSH and LH TSH ACTH Prolactin TARGET Testes or ovaries Thyroid Adrenal cortex Mammary glands MSH GH Melanocytes Liver, bones, other tissues Figure 45.15 Hypothalamus Neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus Neurohormone Axons Posterior pituitary Anterior pituitary HORMONE ADH Oxytocin TARGET Kidney tubules Mammary glands, uterine muscles Figure 45.17 Example Pathway Stimulus Cold Sensory neuron Hypothalamus Neurosecretory cell Hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH ). Releasing hormone Blood vessel Negative feedback Anterior pituitary Tropic hormone Endocrine cell Anterior pituitary secretes thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, also known as thyrotropin ). Thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormone (T3 and T4 ). Hormone Target cells Response Body tissues Increased cellular metabolism Hypothyroidism Goiter Hyperthyroidism Figure 45.20-2 Increases Ca2 uptake in intestines Active vitamin D Stimulates Ca2 uptake in kidneys PTH Stimulates Ca2 release from bones Parathyroid gland (behind thyroid) STIMULUS: Falling blood Ca2 level Blood Ca2 level rises. Homeostasis: Blood Ca2 level (about 10 mg/100 mL) Rickets Figure 45.21a (a) Short-term stress response and the adrenal medulla Stress Nerve Spinal cord (cross section) signals Hypothalamus Nerve cell Adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. Effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine: • Glycogen broken down to glucose; increased blood glucose • Increased blood pressure • Increased breathing rate • Increased metabolic rate • Change in blood flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive, excretory, and reproductive system activity Nerve cell Adrenal gland Kidney Figure 45.21b (b) Long-term stress response and the adrenal cortex Stress Hypothalamus Releasing hormone Anterior pituitary Blood vessel ACTH Adrenal gland Adrenal cortex secretes mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. Kidney Effects of mineralocorticoids: Effects of glucocorticoids: • Retention of sodium ions and water by kidneys • Proteins and fats broken down and converted to glucose, leading to increased blood glucose • Increased blood volume and blood pressure • Partial suppression of immune system Figure 45.13 Insulin Body cells take up more glucose. Blood glucose level declines. Beta cells of pancreas release insulin into the blood. Liver takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen. STIMULUS: Blood glucose level rises (for instance, after eating a carbohydrate-rich meal). Homeostasis: Blood glucose level (70–110 mg/m100mL) STIMULUS: Blood glucose level falls (for instance, after skipping a meal). Blood glucose level rises. Liver breaks down glycogen and releases glucose into the blood. Alpha cells of pancreas release glucagon into the blood. Glucagon