Types of Government

Types of Government
The purpose and functions of government
Source: http://schoolwires.henry.k12.ga.us/cms/lib/GA01000549/Centricity/Domain/1296/Unit%201.ppt
SSCG19
The student will compare and contrast governments that are unitary, confederal, and federal; autocratic, oligarchic and democratic; and presidential and parliamentary.
Functions of Government
Types of Government
What is government?
The institution through which the state maintains social order!
Characteristics of Today's
States/Nations in the world
Population, Territory, & Government
Characteristics of Today's
States/Nations in the world
A state has to have
Population, Territory, and a Government in order to be recognized as a State!
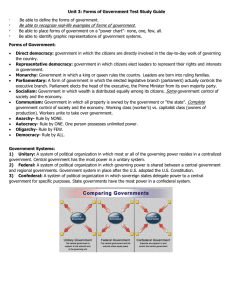
1. Federal Government
2. Unitary Government
Unitary Government
Gives all Key Powers to the
National Government
3. Confederal Government
Confederal Government
A loose union of independent states
4. Autocratic Government
Autocratic Government
The word autocracy comes from the Greek words “autos” meaning self and “kratos” meaning power.
In an autocratic government one person or group holds all power. Usually there no participation or consent from the people.
Autocracies can be theocratic (rule by religious leaders), dictatorial (rule by political leader), or a monarchy (rule by royal family).
5. Oligarchic Governmen
t
Oligarchic Government
Any system of government in which a small group holds the power!
6. Democratic Government
“Ruled by the People for the
People”
President Lincoln
The word democracy comes from the Greek words “demos” meaning people and “kratos” meaning power.
Have the most Freedoms!
a. Representative Democracy
Representative Democracy
A government in which people elect delegates to make law
Both Parliamentary and Presidential governments have are representative democracies.
b. Presidential Democracy
Led by a president that is elected by the citizens.
7. Parliamentary Government
Parliamentary Government
People vote for representatives. The political party that wins the majority of the seats in parliament chooses the leader, prime minister or chancellor.
The minority party serves as the opposition.
They challenge the majority party in an effort to balance power.
The prime minister stays in office until:
1.
2.
his party loses the majority his party loses confidence and votes to remove him.
Journal Assignment
Choose one of the following to compare and contrast. You may do this in paragraph form or using a Venn Diagram.
1.
unitary, confederal, and federal
2.
3.
autocratic, oligarchic, and democratic presidential and parliamentary