AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
advertisement

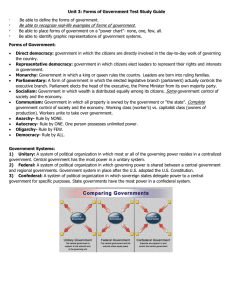
AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Red Flag Questions Pages 14-19 CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: Forms of Government By the end of this section, you will be able to answer these questions: 1. What are the classic forms of government? 2. How is national power organized differently in unitary, federal, and confederal systems? 3. In what ways do presidential and parliamentary systems differ? 4. What theories of rule have been put forth to explain government? THE CLASSIC FORMS Monarchy monarchy What is the difference between an absolute monarchy and a constitutional monarchy? autocracy Give an example of when placing the bulk of power in the hands of one person might be dangerous. Dictatorship dictatorship How is an absolute monarchy different from a dictatorship? How are totalitarian governments different from dictatorships? oligarchy theocracy Democracy What does “democracy” mean? direct democracy Why was Athens not a true democracy? Why is a direct democracy impractical for large industrial nations? Republic What is the main point of a representative democracy? ORGANIZING NATIONAL POWER Unitary Systems unitary systems What power does a unitary government hold over local governments? Federal Systems federal systems What is the significant feature of American federalism pertaining to national and local governments? In a federal system, which level of government do you think is most important? Why? Confederal Systems confederal system How suitable do you think the confederal system is as a form of national government? Explain your answer. PRESIDENTS AND PARLIMENTARY Presidential Systems presidential system What is an important strength and weakness of presidential systems? Parliamentary Systems parliamentary system What is an advantage and a disadvantage of parliamentary systems?