Population Pyramids & Demographics: World Studies Assignment
advertisement

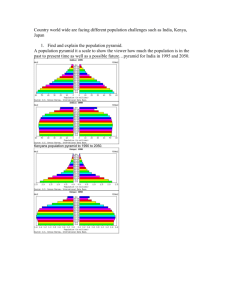
World Studies Hybrid 2/13 – Due Tuesday, 2/17 1. From the World Studies Edline Website, navigate to Notes, Unit 2 Population & Migration and review the powerpoint entitled “Population Pyramids”. 2. Read the blog post from the PRB about Population Pyramids and do the following: a. Compare the Population Pyramid for Zambia and for Japan (clickable links in the text). What are the different conclusions that can be drawn by looking at total numbers vs. percentages? Zambia has a large population of young people due to their high birth rate, and an increasingly low elderly population possibly do to high death rate/low life expectancy. Japan on the other hand has an aging population where many of their people are in the older ages on the pyramid and the base is rather small. Both countries have a relatively equal distribution between males and females. b. At the bottom of the document, click the link to the US Census Bureau International Data Base. c. Create Pyramids for China, India, US, Germany and South Africa for both the current year and for 2050. (Select Report: Population Pyramid Graph, Select Year: 2014 & 2050, click “Submit”) d. Draw 10 conclusions and comparisons between the countries that show the differences in the structure of the population of these countries. For example: China, as a result of the one child policy, has a much smaller ratio of people younger than age 20 than the other 4 countries. India has the greatest number of young people due to their large birth rate South Africa sees a dramatic drop in population size in the mid-30s, possibly due to lower life expectancy Most of the countries have a relatively equal distribution of gender, but India noticeably has more males than females Germany has a much larger population in their middle lives and few young people; low birth rate The united states has an equal distribution of ages until the 60s are hit China seems to be in the beginning stages of population aging, similar to Japan, as does Germany The distributions of South Africa and India are similar in shape, but India’s distribution is more even across ages All countries have very few people living past their 70s The more developed countries tend to have smaller bases and larger middles, the exception being the US and India Those countries with more young people means that women aren’t working, as is the case with India e. Screen shot the population pyramids and make sure they are properly labeled by country and year. Put your conclusions below the graphs. 3. We watched the first segment of World in the Balance, a case study about India’s population (023:00). Describe the population issues India must address regarding high birth rates, status of women and poverty. What does their population pyramid tell you about what needs to be done in the future to support their population adequately? India’s population is too large for their country to support because of their high birth rate. Young newlyweds say that they would be okay with only having 2 children regardless of gender, but most don’t think this is actually the case seeing as the culture is so dependent on having sons. Gender discrimination of childbearing has been made illegal so as to prevent the already outnumbered female population from becoming even smaller in proportion to the male gender. In order to lessen the pressure on women to bear many children, the culture of India must change in a way that prizes females as much as males, and it must allow women access to education and jobs as much as it does men. 4. Follow the link to: Lesson Plan: 2014 World Population Data Sheet. Complete Activity 1 (Questions 115), use the PRB Data Finder , charts and maps by topic, International section to view country rankings for each indicator. Activity 1: The World Population Data Sheet at a Glance Find answers to the following questions using the current World Population Data Sheet. 1.What is the population of the world? 7.2 billion 2.Rank the ten countries with the largest population (from largest to smallest). China, India, US, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh, Russia, Japan 3.Instead of absolute numbers, rates are often used to tell how frequently a population or demographic event is occurring — rates show how common an event is. List the type of information on the data sheet reported by a rate. Fertility, death, population in urban and rural areas 4.The crude death rate (CDR) is the annual number of deaths per 1,000 population. Which country (or countries) has the highest CDR? Which country (or countries) has the lowest? South Africa; Qatar 5.The infant mortality rate measures the number of deaths each year to infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births. Which country (or countries) has the highest infant mortality rate and what is that rate? Which country (or countries) has the lowest and what is that rate? Afghanistan, 187.5; Sweden, 3.4 6.The total fertility rate (TFR) is the average number of children women would have if they maintained the current level of childbearing throughout their reproductive years. Which countries (or countries) share the highest TFR and what is it? Which country (or countries) has the lowest TFR. What is it? Niger, 7.16; Singapore, .78 7.Which country (or countries) has the "youngest" population, that is, the highest proportion of population under age 15? Which country (or countries) has the "oldest" population, that is, the highest proportion of population over age 64? Niger; Monaco 8.In which country (or countries) are people expected to live the longest? Which country (or countries) has the lowest life expectancy? Monaco; Chad 9.In which African country (or countries) does the highest proportion of people live in urban areas? Gabon. In Asia? Singapore. In Latin America? Venezuela. In Europe? Paris. In Oceania? Australia. 10.Gross national income in purchasing power parity per capita (GNI PPP) converts income into "international dollars" and indicates the amount of goods and services one could buy in the United States with a given amount of money. Which country (or countries) is the wealthiest in terms of GNI PPP? Which is the second wealthiest? Norway, Luxemburg 11.A population grows because there are more births than deaths or more people are moving in than moving out. The difference between births and deaths is expressed as a percentage called the rate of natural increase. Which region is growing the fastest through natural increase? Which region is growing at the slowest rate? Niger; Ukraine 12.Which country (or countries) is growing the fastest through natural increase? Which country (or countries) is growing at the slowest rate? Niger; Ukraine 13.A population projection is a computation of future changes in population numbers based on assumptions about future trends in fertility, mortality, and migration. Which categories on the data sheet are shown as projections? Future population and development levels 14.Rank the 10 countries with the largest projected populations for both 2023 and 2050 (from largest to the smallest). Which country's (or countries') population is projected to drop out of the top 10 by 2050? Which country (or countries) is projected to be added to the top 10? Look back to the rankings for the current year. What are the major shifts in this ranking from now to 2050? The Congo and Ethiopia join the top 10 by 2050 while Japan and Russia drop from the list. All other countries currently on the list remain, just in a different order. Largest to Smallest: India, China, Nigeria, United States, Indonesia, Pakistan, Brazil, Bangladesh, Congo, Ethiopia. 15.Rank the regions according to population size (from largest to the smallest). Asia, Africa, Europe, Latin America/Caribbean, North America, Middle East, Oceania 5. Post answers to your website before Tuesday, 2/17.