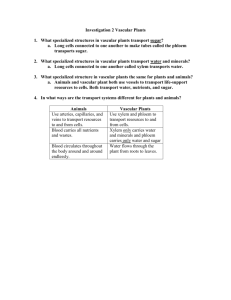
Science Study Guide for Plant and Animal Test PLANTS belong to
advertisement

Science Study Guide for Plant and Animal Test PLANTS belong to the Domain Eukarya and the Kingdom Plantae. Plants are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic. Plant cells have cell walls for strength and structure. Plants also have a cuticle which is a waxy covering to help the plant keep from drying out. There are 4 types of plants: Nonvascular: do not have vascular tissue (no pipes!) they can only absorb water through the processes of osmosis and diffusion, grow low to the ground. ex: mosses and liverworts. Vascular, seedless: have vascular tissue xylem and phloem (pipes!). These plants move water and nutrients through the plant using their vascular tissue and/or the processes of osmosis and diffusion. Grow taller than moss and do not have seeds but use spores to reproduce. ex: ferns, horsetails and club mosses Gymnosperms: like pine trees, have vascular tissue xylem and phloem (pipes) to transport food and water through the plant. Gymnosperms can also use the processes of osmosis and diffusion to move food and water. They have seeds but no flowers. They reproduce using cones and seeds. Pollen is carried from male cone to female cone by the wind. ex: pine trees, conifers, evergreens Angiosperms: have vascular tissue xylem and phloem (pipes), seeds and flowers. They use their vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) as well as osmosis and diffusion to transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. Ex: daffodils, apple trees, tulips, grass. Plant Structures The individual parts of the plant are adaptations that help plants to live on land. Petals: attract pollinators Cuticle: protects the plant from drying out Roots: absorb water and minerals from ground, anchor plant in the ground, and stores excess food. There are two types of roots: taproots and fibrous roots. Taproot Fibrous root Stems: help the plant to stand upright, transports water and food up the plant and supports the plant. There are two types of stems: woody and herbaceous. Woody Stem: rigid, covered in bark Herbaceous stem: thin and flexible Reproductive parts of the plant Stamen: male part of the plant that holds the pollen Pistil: female part of the plant that is fertilized by the pollen Bees carry pollen from the stamen to the pistil where the pollen travels down to the ovules and fertilize them and turn into seeds. The ovary then turns into a fruit. ANIMALS belong to the domain Eukarya and the Kingdom Animalia. Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular and heterotrophic. Animals without a backbone are invertebrates. Animals with a backbone are vertebrates. Animals are consumers. Animals mainly use sexual reproduction to have offspring. The 6 animal phlum: Phlum Physical characteristics Most distinguishing Examples characteristics Cnidarians no skeleton, no backbone stinging cells jellyfish, hydra radial symmetry Mollusks no skeleton, no backbone foot, mantle, visceral mass, snails, clams, octopus, slugs soft body, bilateral shell symmetry Annelids no skeleton, no backbone segmented body earthworms, bristle worms bilateral symmetry leeches Echinoderms endoskeleton, no backbone spiny skin sea stars, sea urchins, sand radial symmetry, dollars, sea cucumbers Arthropods exoskeleton, no backbone, jointed limbs, segmented Insects, spiders, crabs, well-developed nervous body, exoskeleton, centipedes, crustaceans system, bilateral symmetry compound eyes Chordates have backbone, backbone fish, mammals, reptiles, endoskeleton, very complex hollow nerve cord birds, humans nervous system, bilateral symmetry Animals can communicate with each other in different ways. Animals can use their vocal cords: make noises, talk Animals can use pheromones: own scent is used to either attract mates or keep predators away Animals can use touch as a way of communicating Animals can use body language as a way of communicating Animals exhibit either innate or learned behaviors. Innate behaviors are behaviors that are coded in the DNA. Yawning, babies crying, breathing are all examples of innate behaviors. Learned behaviors are learned by observation or experiences like language, (speaking) playing a sport, or reading. Animals can exhibit seasonal behaviors. Hibernation is when animals go into a long period of inactivity during the winter. Bears hibernate Estivation is when animals hibernate in the summer. Desert squirrels estivate. Survival behaviors Animals use poisons/ toxins and stingers to ward off predators Animals can use warning coloration to ward off predators. The organism may or may not be poisonous but the coloring of the organism makes predators think it is poisonous. Animals can camouflage themselves to escape predators. Animals use different ways to get food to survive. Organisms are made up of small cells which are part of bigger tissues, which are part of larger organs, the organs together make up organ systems and all together they are considerd an organism. Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organisms