Chapter 20
advertisement

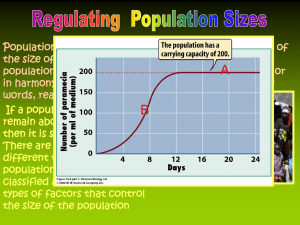
Chapter 5 Population Ecology Charateristics: geographical distribution, density and growth Population Density Measures is how crowded a population Unit examples? City vs Suburbs vs Rural Population Distribution Three main ways – Clumped – Random – Uniform/Even Most common? Rare? Distribution patterns Population Dynamics Birth rate = number of births over time Death rate = deaths over a period of time Life expectancy = how long individuals in pop. are expected to live – Take a guess: life expectancy for men and women in United States Men = 72 years Women = 76 years Population Growth Rate Growth rate= change in population size over time Depends upon the following: – Birth – Death – Immigration – Emigration Age Structures Effects of AIDS on a Population Questions- be ready to answer What is a rate? What is birth rate? What is death rate? What are two additional factors that cause a population to increase? Decrease? What does per capita or % annual growth rate mean? Growth Rate What is a rate? – Change over time – In math terms = slope What is birth rate? death rate? – Number of births over a period of time – Number of deaths over a period of time Growth Rate Two factors that increase population growth – Births – Immigration Two factors that decrease population growth – Deaths – Emmigration Growth rate % GROWTH RATE? - takes into account total growth (births and immigration) minus decline (death and emmigration) – Change in growth over time Look at fig 5-14 on page 132 What does ZPG mean? – Zero population growth What years had the highest % growth rate? Concept Map Section 5-1 Population Growth can be Logistic growth Exponential growth characterized by No limits on growth Unlimited resources represented by Constant growth rate J-shaped curve characterized by Limits on growth which cause a Falling growth rate represented by S-shaped curve Exponential Model for Population Growth Says that populations grow rapidly after only a few generations Bacteria follow this model Logistic Model Populations are limited by their environment Any factor that limits population growth is called a limiting factor Limiting factors include things like food, habitat availability, water, predators Carrying Capacity (K) The number of individuals the environment can support over a long period of time. This number is due to birth rates, death rates, and limiting factors Humans – how long? HW – CH 5 Study Guides due Tues! Section Outline 5–2 Limits to Growth Section 5-2 A. B. 1. 2. 3. 4. C. Limiting Factors Density-Dependent Factors Extinction Competition Predation Parasitism and Disease Density-Independent Factors Population Fluctuations 1. Density-independent factors- reduce population by the same proportion regardless of population size; ex. Cold winter effects the squirrel population – 2. It doesn’t matter the size of the population Density-dependent factors- resource limits due to increase in population density; ex. Shortage of food due to too many deer in the area causes some deer to starve. Fluctuations Change the Graph Extinction What if an organism went extinct? What would the graph look like? What about small populations? Very vulnerable to extinction Why is that? Inbreeding Something bad happens in the environment and too many die to sustain the population Ex. Cheetahs, sea otters, CA Condors, Siberian tigers Figure 5-7 Wolf and Moose Populations on Isle Royale Section 5-2 60 2400 50 2000 40 1600 30 1200 20 800 10 400 0 1955 1960 0 1965 1970 1975 Moose 1980 Wolves 1985 1990 1995 Human Populations Human Populations They have exploded over the last 1000 years The death rates have decreased and the birth rates have increased. This makes the overall growth rate increase. Do you think that this current human population is sustainable? Do you think that we are way past our carrying capacity and it will go down? Human Population Growth Section 5-3 Industrial Revolution begins Agriculture begins Plowing and irrigation Bubonic plague