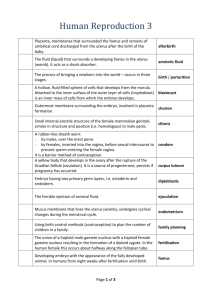
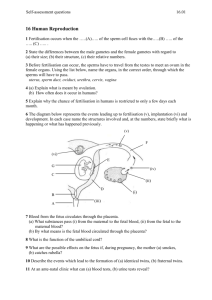
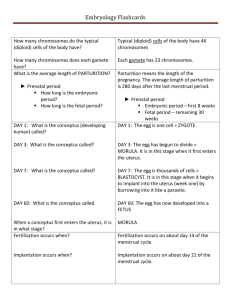
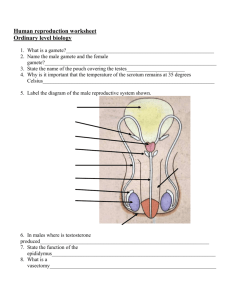
Spend out of placenta
advertisement
► Gestation periode beginning with fertilisation to end with parturition of foetus ► Gestation consist 3 class : ►ovum periode ►embryo periode ►foetus periode ► Ovum periode is periode from fertilisation to implantation ► Embryo periode is periode from implantation to early visceral organ formed. ► Foetus periode is periode from visceral organ formed, ekstremitas to partus Hafez (1974) statements : ► Ovum periode : from ovulation to fertilisation, Periode embrio dimulai sejak terjadi fertilisasi, ► Embryo periode : from fertilisation, implantation to visceral organ formed ► periode fetus : ekstremitas organ formed to parturition Placentation ►Placenta (Foetus membrane) is tissue connection between embryo & mom ►Placenta Function : Food pathway from mom to embryo ► Rubbish substance pathway from embryo to mom ► Early gestation Change of trophoblast morphology as : 1. Khorion (outer membrane) 2. Allantois (between khorion & amnion) 3. Amnion (inner membrane) ► Placentation consists of : 1. Placenta materna ; endometrium (Corunculae) 2.Placenta foetalis ; trophoblast (Cotyledone) MACROS & MICROS of PLACENTA ► After implantation of embryo at endometrium, next trophoblast & endometrium fused, is called PLACENTA. ► First nutrition of embryo from uterine milk (histotroph/ susu uterus). ► Placenta devided 3 part: Amnion : direct contact with foetus Alantois: between amnion & chorion Chorion : outer part membrane PLACENTA TYPE 1. 2. 3. 4. Cotyledonaria : Cow, ewe, goat have coruncula Difusa : Sow & Mare haven’t coruncula Zonaria : Dog Discoidalis : Monkey, human, rat, guinea pig, rabit Histologyst structure of placenta Epitheliochoriale (placenta difusa) : blood circulation between mom & foetus separated by 2 epithel layer, 2 endothel layer & 2 connective tissue from mom & foetus 2. Syndesmochoriale (plasenta cotiledonaria) : consists of 1 epithel layer, thiner than epiteliochoriale. 1. 3. Endotheliochoriale (placenta zonaria). blood circulation between mom & foetus separated by 3 layer from foetus (endothel, connective tissue & trophoblast epithel) & 1 layer from mom (endothel) 4. Hemochoriale (placenta diskoidale) blood circulation between mom & foetus separated by 3 layer conective cell from trophoblast 5. Hemoendotelial (plasenta diskoidale-kelinci) blood circulation between mom & foetus separated only by 1 layer endothel cell from blood vessel foetus gestation counted from fertilisation to parturition, but fertilisation didn’t know exactly. So… gestation counted from last mating to partus ► Long time of gestation influences by maternal factors, genetic, foetus & environment ► CHANGE OF FEMALE GENITAL ORGAN DURING GESTATION 1. Vulva & Vagina After retilisation, vulva & vagina not yet change. Edema vulva : 6-7 months of gestation in heifer 8,5 – 9 months of gestation in cow. Perubahan vagina terlihat adanya pertambahan vaskularisasi mukosa vagina. 2. Servik * After fertilisation : cerviks crypta produce mucous liquid * Older gestation increase mucouse * Approach of partus contraction of cerviks musculator * Cow : 2-5 days before partus cerviks musculatur relaxation & opened 3. Uterus * After fertilisation : Increase vascularitation of endometrium, glandulas growing prolongation, twisting & produce of uterus milk (histotroph) Condition of uterus quiet because influence of progesteron * After implantation pathway of nutrition & rubbish substance attachment of tropoblast – blood vasel at endometrium. 4. Ovarium * After ovulation korpus haemorrhagicum or korpus rubrum 2-3 days luteinisation proces Corpus luteum (CL). * Cow & Ewe 5 – 6 days after ovulation CL grow up. If didn‘t gestation CL regretion by PGF2 alfa from endometrium * If Gestation CL function constantly CL Graviditatum & constantly to function to last gestation (cow, ewe, goat, sow & buffalo). ROLE OF HORMON IN GESTATION PROCESS * Main Endokrine gland : Ovarium (CL & Folicle), Plasenta, Hipotalamus, & Hipofisa. * Support endokrine gland : tyroid & adrenal * Hipotalamus & Hipofisa Regulator gland * * * * CL produce P4 Folikel produce E2 Placenta produce P4 & E2 In Urine : Mare consist Estron, Estradiol 17 & β Goat & Ewe Estradiol 17 Sow Estron Cow Estron & Estradiol 17 * Placenta of Mare produce steroid & gonadotrophine (PMSG) FSH produce fol not ovulated lutein CL Ascesoris produce P4 EXAMINE OF GESTATION IN FARM ANIMAL ► CLINICALY 1. VISUAL INSPECTION 2. REKTAL PALPATION ► LABORATORIOSLY 1. HORMONE EXAMINATION 2. USG 3. RADIOGRAFI 4. IMUNOLOGY ► Gestation is physiologis process, how about gestacy of uterus to spend of foetus & placenta by ductus reproduction ► Strong stimulation from uterus musculatur, stomach & diafragma ► Before partus formerly with signs of partus ► PLACE OF FOETUS IN PARTUS TIME Normal Place 1. Anterior (letak muka) 2. Posterior (letak sungsang). Eutokia Easy partus process Distokia Difficult partus process need human help DISTOKIA (kaki depan) DISTOKIA (Kepala & 1 kaki) DISTOKIA (hanya ekor) PARTUS STAGES ► 1. EARLY STAGE / PREPARATION STAGE ► 2. FOETUS & PLASENTA EXPULSION / CONTRACTION / LABOR 2.1. PREPARE OF CONTRACTION 2.2. STRONG CONTRACTION FOR FOETUS EXPULSION 2.3. CONTRACTION FOR PLACENTA EXPULSION ► 3. PUERPURIUM EARLY STAGE / PREPARATION STAGE ► Normal Parturition Preparation stage longer incessant than contraction stage. ► Preparation stage can incessant several hours or days, whereas contraction stage can incessant in count minute. TEORY OF EARLY STAGE First : mechanic factor grow up of foetus Second : hormon factor P4, E2 dan Oxsitosyn. Third : intern foetus factor Fourth : combined of 3th teory above I. Mechanic Factor (If Normal Gestation) Foetus volume ↑ partus If Abnormal/ Patologik Condition Hydrops (Allantois Liquid ↑) partus Foetus twin in monotocous parturition faster II. Hormonal Factor Oksitocyne Role for begin contraction of myometrium Progesteron Take care of gestation with preventive contraction from musculator uterus until calm of uterus Estrogen Placenta grow up E2 ↑ Prostaglandin contraction from musculatur of uterus III. FOETUS FACTOR ► FOETUS GROW UP ► UTERUS REPEATEDLY STRECH OUT ► CORTISOL STIMULATE FROM FETUS IV. COMBINED OF TEORY ► ↑ P4 inhibiting of myometrium contraction ► ↑ Foetus Volume utereus repeatedly stretch out ► ACTH from foetus Cortex Adrenal produce Corticosteroid ► Corticosteroid stimulate PGF2↑ & E2 ↑ P4 ► E2 ↑ Sensitivitas myometrium toward Oxytocine ► Myometrium contraction ↑ (several hours to days) ► 2. CONTRACTION STAGE a. Prepare of Contraction stage Contraction for spend out of foetus Contraction for spend out of placenta b. c. ► Prepare of Contraction Intensitas contraction of myometrium ↑ until spend out of allantois from vulva ► Spend out of Foetus very quickly ► Spend out of placenta RETENSIO SECUNDINARUM Puerpurium Changes after parturition + spend out of placenta until Estrous again Changes in Puerpurium ► Regeneration of endometrium ► Involutio of uteri ► Estrous of postpartum Regeneration of endometrium (7weeks) ► After spend out of Placenta ► Crypta in endometrium become shorter ► Uterus blood vesel constriction Involusio of uteri ( 60 days) ► ► 1. 2. 3. Involutio of utery is smaller of uterus became normally size Consist to : Regeneration of endometrium epithel Smaller of myometrium Smaller of uterus blood vesel Estrous of post partum (30-70days) ► Regretion of Corpus Graviditatum fastly ► Puerpurium can extended : in mammalia Abnormalitas in parturition