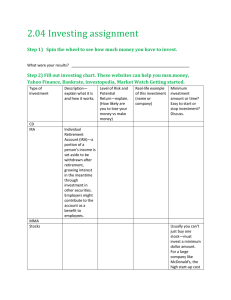
Personal Finance
FIN 235
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
1
Retirement Plan: Start Early
Why should you start ASAP?
A.
The longer you save, even amounts as small as $100
to $200 a month, the larger your retirement account
balance.
Consider saving $100 per month in an Index Fund.
Historical average return is 10.4% P.A.
1.
2.
After 30 years you will accumulate $246,277.
b. After 35 years, the accumulation is $421,143.
c. Plan “b” will provide an income of $3,946/mo.
d. If you save more as your income grows, it is entirely
possible that you can accumulate more than $750,000.
a.
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
2
Other Factors to Consider
Social Security benefits will very likely be
reduced and the retirement age increased by
the time you are ready to retire.
It’s a myth that you’ll spend less after
retirement:
A.
B.
1. More travel
2. Many decide to have two homes
3. Living expenses will continue to rise.
C.
FIN 235
You will live longer than your parents.
All Rights Reserved
3
Retirement Plans
Employer Sponsored
A.
Defined benefit
1.
a.
b.
c.
Vesting is an issue
Most do not permit employee contributions
Defined Contribution
Defined Contribution
2.
a.
b.
c.
401(k)
403(b) for non profits
Employer and employee contribute
Individual Plans
B.
1.
2.
IRA
SEP
Professionals and Small Business
C.
1.
FIN 235
Keogh
All Rights Reserved
4
US Govt. Retirement Plans
Social Security
A.
1. Financed by payroll taxes
2. Benefits a function of time and magnitude of
contributions.
3. Current Law: earliest is 62 with reduce benefits
4. Most younger Americans must wait until age 67
or 68 to enjoy full benefits.
5. Delaying increases the monthly check – going
early decreases the check.
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
5
Personal Retirement Plans
Regular IRA
A.
1. Make contributions until age 70 ½.
2. Must annuitize by age 70 ½ .
3. Current max contribution is $5000 / yr.
a. Catch-up provision for workers over 50
4. Contributions made with pre-tax dollars
5. Early withdrawals incur serious penalties and
taxes.
6. Distributions taxed as ordinary income.
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
6
Personal Retirement Plans
Roth IRA
B.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Contributions made with after-tax dollars
Contributions limited according to income and
marital status.
Must annuitize by age 70 ½.
Can begin drawing tax free benefits at age 59 ½.
Simplified Employee Pension Plan (SEP)
C.
1.
2.
3.
4.
FIN 235
Employer funded
Employee sets up account with financial institution.
Max annual contribution is $11,500.
Employee contributions made with pre-tax dollars.
All Rights Reserved
7
Personal Retirement Plans
Spousal IRA
D.
1. Contributions for non-working spouse.
2. May be fully or partially tax deductible.
Rollover IRA
E.
1. When you move funds from a 401(k) to an IRA
2. Make certain funds go from institution to
institution – otherwise it looks like a full
withdrawal – loads of tax implications.
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
8
Personal Retirement Plans
Education IRA (Coverdale ESA)
F.
1. Max $2000 per year.
2. Not tax deductible
3. Tax free distributions if used for educational
expenses.
Keogh Plan
G.
1. For self-employed and their employees
2. Used largely by doctors and lawyers and owners
of significant-sized businesses.
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
9
Employer Retirement Plans
401(k), 403(b), 457 Defined Contribution Plans
A.
1.
2.
Max contribution is $16,500
Plans typically offer a variety of investments
Defined Benefit Plans
B.
1.
2.
3.
Insurance annuities with fixed payouts
Payout as function of time in the plan.
Favored by unions (avoid market risk)
Cash Balance Plan
C.
1.
2.
FIN 235
A D-B plan that works as interest earning savings
100% employer funded
All Rights Reserved
10
HOMEWORK
Do The Math: 1 (a, b), 2
Be Your Own Personal Financial Planner
A.
B.
1. 2 – Calculate your retirement nest egg (w/s 65)
2. 4 – Questions to ask your employer (w/s67)
FIN 235
All Rights Reserved
11