Photosynthesis Notes
advertisement

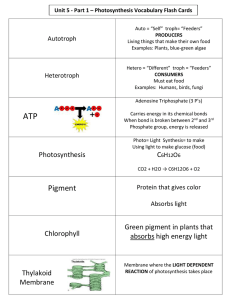
Draw this in your notes: Energy Transformations & Photosynthesis Most energy transformations can be traced back to the sun: the original source of energy for life on earth. Photosynthesis A process by which plants turn the radiant energy of sunlight into chemical energy in the form of sugars (glucose). Radiant energy from the sun enters the ecosystem at the producer level. Why this happens: First, leaves take in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air through their stomata (pores found in leaves) and take in water (H20) through their roots. Why this happens: Second, Plants absorb light (radiant energy) by a green pigment called chlorophyll in organelles called chloroplasts, the site for photosynthesis. Why this happens: Finally, Glucose a form of chemical energy (C6H12O6) is created and stored for the plant to use as food and Oxygen is produced and released (O2) through their stomata. Components of Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide and Water are the reactants in the reaction. They are the substances actually reacting. Glucose and Oxygen are the products of the reaction. They are the substances actually produced. REACTANTS PRODUCTS 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + Light C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Sunlight is fuel that drives the entire reaction. Without light, photosynthesis cannot take place. Exit Ticket Where does the original source of energy for life on earth come from? a. Water b. Wind c. Sun d. Plants When plants make glucose, they are converting the sun’s radiant energy: a. Into ATP b. Into chemical energy that can be stored c. In a process known as cellular respiration d. Into chlorophyll