Roman Life, Christianity & Fall (100 BC
advertisement

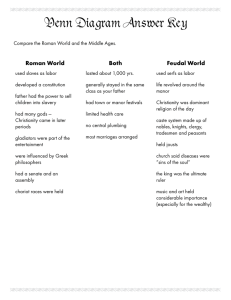
Roman Life, Christianity, Rome’s Fall (100 BC- 400 AD) I. Roman Life A. Homes B. Paterfamilia C. Religion D. Fun E. Slavery II. Christianity A. Rise B. Persecution III. Later Rome A. Constantine B. Why Fall? (476 AD) • • • • • • • • • • • • Key Terms Domus Larium Insulae Circus Maximus Colosseum Public Baths Spartacus Constantine Council of Nicea Theodosius Barbarian Invasions Bread & Circus Homes-Domus (Single-story homes for rich) Atrium (Often open to the sky with a basin to catch rainwater) Larium (A household shrine for special gods or ancestors of the family) Homes-Insulae (Multi-story apartments for commoners) Public Toilets-Not Much Privacy (Open to men & women at same time) Food/Diet • Wealthy = Bread, meat & fish were common; exotic meats, fruits & vegetables • Poor = Bread; some vegetables, pork on rare occasions Roman Family • Family = Paterfamilia • All family authority (including life & death) was held by the father. • Marriages were usually arranged. Mother & Child • Mothers/women had no political power, but did exercise authority over education of children. Religion • Prayers were recited on a regular basis each day. Larium (A household shrine for special gods or ancestors of the family) Religion • Prayers were recited on a regular basis each day. • Romans tolerated other religions, but all had to respect Roman gods. – Jewish temple in Jerusalem was destroyed in 70 AD – Jews were dispersed from Jerusalem in 73 AD • Simply took Greek gods and renamed them. Greek & Roman Gods Greek Zeus Roman Jupiter Greek & Roman Gods Greek Hera Roman Juno Greek & Roman Gods Greek Poseidon Roman Neptune Fun In Rome • Holidays: • Workday: 160-170 per year 6-7 hours Chariot Races (At Circus Maximus) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbQvpJsTvxU Teams Blue Green White Red Exotic Animals & Gladiators at Colosseum Public Baths Rooms At The Baths • Tepidarium • Calidarium • Frigidarium Pont du Gard - Aqueduct (France-178 feet high) Slavery • In 14 AD Italy’s population was 7.5 million; 1/3 were slaves (about 3 million). • Most were former prisoners of war and they worked producing food. • 73 BC Spartacus led a slave rebellion; at its height, it involved 120,000 men. Christianity • Grew out of Jewish belief a Messiah would come one day. • It is believed Jesus was born 4 BC. • Message-all (including poor) could be saved; established ethical standards. • Jesus was seen as subversive to Roman authority and executed around 29-33 AD. Gospels (Written 60-120 AD) • Synoptic Gospels (meant to be read together) – Mark (65-70 AD) • Written while disciples were alive (could have been contradicted); Goal = biography – Matthew (85-90 AD) • Goal = convert Jews; fulfills OT prophecy – Luke (90-100 AD) • Goal = convert non-Jews; several verses taken word-for-word from Mark & Matthew Gospels (Written 60-120 AD) • John (90-100 AD or later) – Contradicts earlier Gospels in places – Not biography; Goal = theological study with Christ as redeemer/creator Paul Of Tarsus • Traveled throughout the entire Roman world. – Used Roman road network. – Koine-Greek trade language. • Preached to Jews and non-Jews alike. • Wrote to Christians all over the Mediterranean world outlining religious teachings/doctrine. Persecution • Labeled as Atheists because many would not respect Roman gods. • Appeared to have odd religious practices… • Emperor Nero blamed Christians for the great fire in 64 AD. Christianity • Greek letters for word “fish” abbreviated: “Jesus Christ, Son of God, Savior.” Diocletian 1. Political Reform: The Empire was divided into four geographic regions 2. Social Reform: Christianity was outlawed 3. Economic Reform: The tax system was modified and taxes increased 284-305 AD Constantine 1. He consolidated power and ruled by decree 2. The capital of the Roman empire was moved to the East— Constantinople 3. The practice of Christianity was legalized 306-337 AD They Might Be Giants “Istanbul was Constantinople” http://vodpod.com/watch/3891206-istanbul-not-constantinople- Theodosius • Decreed Christianity was the official religion of Rome (380 AD). 379-395 Non-Christian Religions Prohibited Temple & Statue of Zeus in Olympia Temple of Zeus = Destroyed Council of Nicea (326 AD) • There were many views as to the nature of Jesus & Christian Doctrine. • Constantine called all religious leaders (Bishops) together • Nicene Creed: – Trinity: God, Jesus & Holy Spirit are one – Virgin birth of Jesus – He was crucified & rose from dead Why Did Rome Fall? (476 AD) 1. Barbarian Invasions a) Roman army wasn’t what it used to be 2. Bread & Circus! • People wanted “games” and free food. They became consumers; not producers 3. Administrative problems-the empire was simply too big to govern A Better Question: How/why was it able to last so long? Roman Life, Christianity, Rome’s Fall (100 BC- 400 AD) I. Roman Life A. Homes B. Paterfamilia C. Religion D. Fun E. Slavery II. Christianity A. Rise B. Persecution III. Later Rome A. Constantine B. Why Fall? (476 AD) • • • • • • • • • • • • Key Terms Domus Larium Insulae Circus Maximus Colosseum Public Baths Spartacus Constantine Council of Nicea Theodosius Barbarian Invasions Bread & Circus