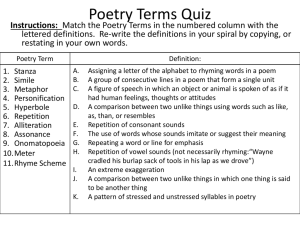
File - Mrs. Roberts' website
advertisement
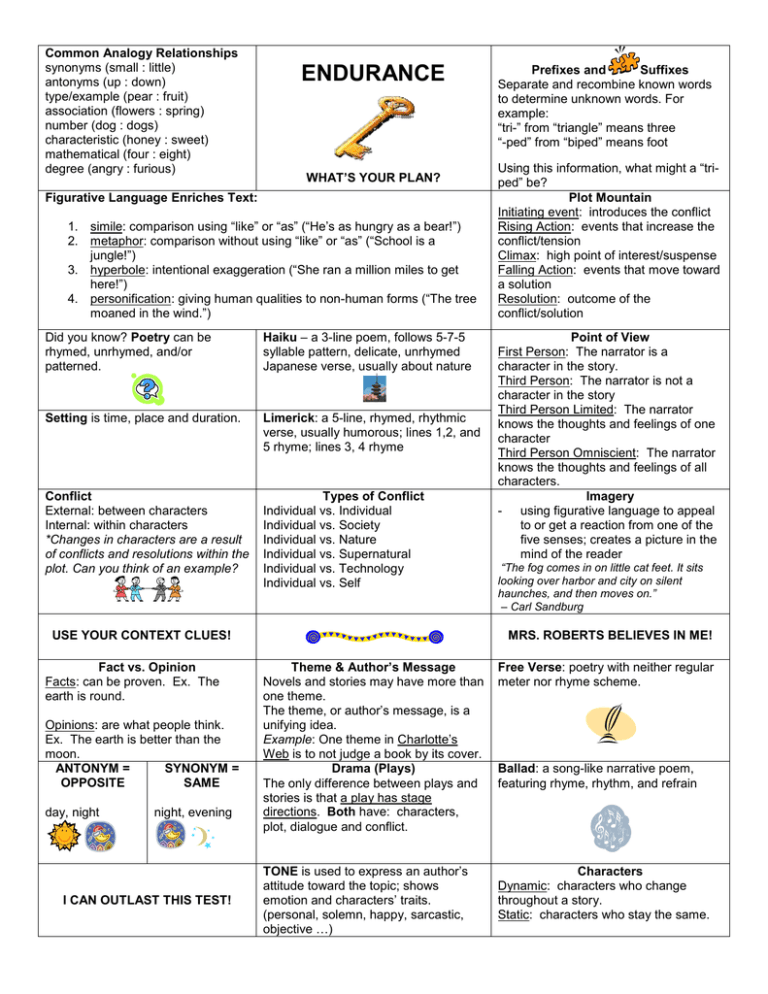
Common Analogy Relationships synonyms (small : little) antonyms (up : down) type/example (pear : fruit) association (flowers : spring) number (dog : dogs) characteristic (honey : sweet) mathematical (four : eight) degree (angry : furious) ENDURANCE WHAT’S YOUR PLAN? Figurative Language Enriches Text: 1. simile: comparison using “like” or “as” (“He’s as hungry as a bear!”) 2. metaphor: comparison without using “like” or “as” (“School is a jungle!”) 3. hyperbole: intentional exaggeration (“She ran a million miles to get here!”) 4. personification: giving human qualities to non-human forms (“The tree moaned in the wind.”) Did you know? Poetry can be rhymed, unrhymed, and/or patterned. Haiku – a 3-line poem, follows 5-7-5 syllable pattern, delicate, unrhymed Japanese verse, usually about nature Setting is time, place and duration. Limerick: a 5-line, rhymed, rhythmic verse, usually humorous; lines 1,2, and 5 rhyme; lines 3, 4 rhyme Conflict External: between characters Internal: within characters *Changes in characters are a result of conflicts and resolutions within the plot. Can you think of an example? Types of Conflict Individual vs. Individual Individual vs. Society Individual vs. Nature Individual vs. Supernatural Individual vs. Technology Individual vs. Self USE YOUR CONTEXT CLUES! Fact vs. Opinion Facts: can be proven. Ex. The earth is round. Opinions: are what people think. Ex. The earth is better than the moon. ANTONYM = SYNONYM = OPPOSITE SAME day, night night, evening I CAN OUTLAST THIS TEST! Prefixes and Suffixes Separate and recombine known words to determine unknown words. For example: “tri-” from “triangle” means three “-ped” from “biped” means foot Using this information, what might a “triped” be? Plot Mountain Initiating event: introduces the conflict Rising Action: events that increase the conflict/tension Climax: high point of interest/suspense Falling Action: events that move toward a solution Resolution: outcome of the conflict/solution Point of View First Person: The narrator is a character in the story. Third Person: The narrator is not a character in the story Third Person Limited: The narrator knows the thoughts and feelings of one character Third Person Omniscient: The narrator knows the thoughts and feelings of all characters. Imagery - using figurative language to appeal to or get a reaction from one of the five senses; creates a picture in the mind of the reader “The fog comes in on little cat feet. It sits looking over harbor and city on silent haunches, and then moves on.” – Carl Sandburg MRS. ROBERTS BELIEVES IN ME! Theme & Author’s Message Novels and stories may have more than one theme. The theme, or author’s message, is a unifying idea. Example: One theme in Charlotte’s Web is to not judge a book by its cover. Drama (Plays) The only difference between plays and stories is that a play has stage directions. Both have: characters, plot, dialogue and conflict. Free Verse: poetry with neither regular meter nor rhyme scheme. TONE is used to express an author’s attitude toward the topic; shows emotion and characters’ traits. (personal, solemn, happy, sarcastic, objective …) Characters Dynamic: characters who change throughout a story. Static: characters who stay the same. Ballad: a song-like narrative poem, featuring rhyme, rhythm, and refrain Character traits are revealed by… …what a character says. …what a character thinks. …what a character does. …how others respond to him/her. (honest, trustworthy, evil, cruel …) Patterns of Text Text is organized several ways, depending on the information: 1. chronological or sequential (time order) 2. compare and contrast 3. cause and effect 4. problem and solution 5. description Narrative form = tells a story; has setting, character, plot, conflict, and theme Prose vs. Poetry Language is either prose or poetry. Prose is ordinary written or spoken language in paragraph form. Poetry has meter and rhythm and is written in stanzas. Sound devices alliteration: repetition of beginning sounds. Lucy licks lollipops. consonance: repetition of consonant sounds at the ends of words. East or west I am best onomatopoeia: when a word’s sound suggests its meaning (“buzz”) assonance: repetition of vowel sounds: the cat sat on the hat. Author’s Purpose Entertain Persuade Explain Inform Encourage Describe Relate Identifying Reference Sources Dictionary: definitions, pronunciations Thesaurus: synonyms Glossary: specialized dictionary at the back of a book (with key terms) Online Sources: search engines, websites, etc. Atlas: book of maps Almanac: collection of yearly facts What is repetition? What is repetition? Rhyme: recurring identical or similar final word sounds within or at the end of lines of verse Rhythm: recurring pattern of strong and weak syllables stresses Repetition: repeated use of sounds, words, or ideas for effect & emphasis Infer To infer is to draw conclusions based on what you’ve read, not only what the author has directly told you. Example: If I have a red, stuffy nose and am carrying a box of tissues, what can you infer about how I’m feeling (without me even telling you)? Literary Devices Flashback: the return to an earlier time to introduce prior information. Foreshadowing: the giving of clues to hint at coming events in a story. Irony: the unexpected happens - the police station is robbed. That’s ironic. Symbolism: One thing stands for another. The flag symbolizes freedom. Last, but not least… The 6 test taking strategies to use on the Reading SOL TEST SR3 S tudy the graphic Best 50/50 Not -3 R ead the question X out 2 ridiculous answers X out 3 answers that are the same ( R eturn to find the answer Examine the remaining answers have something in common.) R espond Choose the answer the author of the Use this strategy during The remaining answer is The Answer. questions thinks is the answer the entire test! 3D (What is the summary of this SEC (What is the theme of this 5W’s (What is the main idea of passage?) story?) paragraph 2?) 3 answers are detail sentences Make a list of the following: Reread the paragraph and identify: identifying setting details, event from the passage Who: details, and character details. Read The answer left over is the What: summary statement these again and again to determine Why: theme. What is the author trying to tell Then decide on the main idea. Don’t you? choose a detail! ENDURANCE is the key!