Work and Power
Work and Power
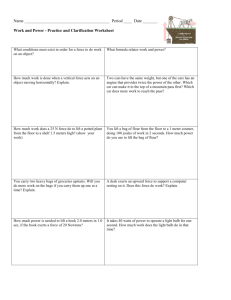
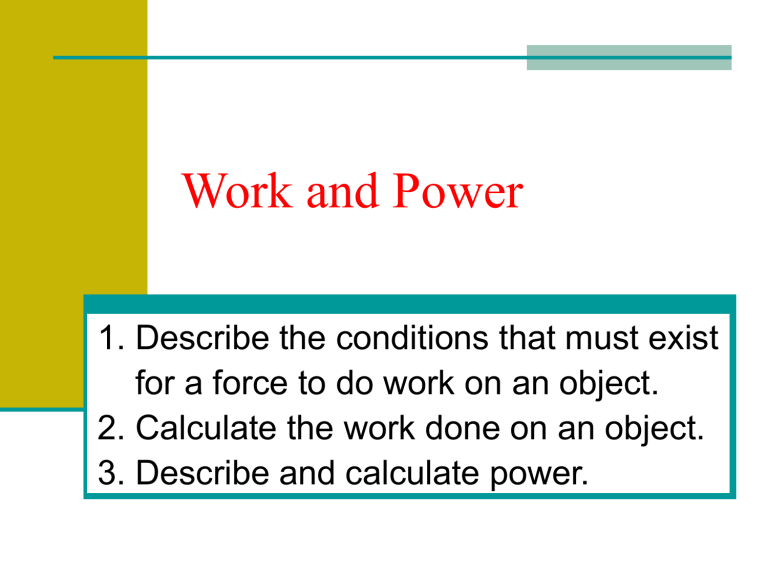
1. Describe the conditions that must exist for a force to do work on an object.
2. Calculate the work done on an object.
3. Describe and calculate power.
What is Work?
Work is the product of force and distance.
Work requires motion. If there is no movement then no work is done.
The force must act in the same direction as the object moves. Any part of a force that does not act in the direction of motion does no work on an object.
Calculating Work
Work = Force x Distance
Units of Work
The Joule (J) is the SI unit of work. It is the work of moving an object with the force of 1 Newton to a distance of 1 meter.
Practice using the Work Formula
A weight lifter lifts a 1600 N barbell over his head 2.0 meters high.
W = F x D
W = 1600 N x 2.0 m
W = 3200 J
What is Power
Power is the rate of doing work.
Doing work at a faster rate requires more power.
To increase power:
1. increase the amount of work done in a given time
2. do a give amount of work in less time.
Calculating Power
Power = Work / Time
Units of Power
The SI unit of power is the watt (W), which is equal to one joule per second.
How much work does a 25-newton force do to lift a potted plant from the floor to a shelf 1.5 meters high?
100%
A.
52 J
B.
48 J
C.
24 J
D.
38 J
0%
A.
0%
B.
0%
C.
D.
You lift a large bag of flour from the floor to a 1-meter-high counter, doing
100 joules of work in 2 seconds. How much power do you use to lift the bag of flour?
100%
A.
50 W
B.
52 W
C.
48 W
D.
42 W
A.
0%
B.
0%
C.
0%
D.
In which of the following cases is work done on an object?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Pushing against a locked door.
Suspending a heavy weight with a strong chain.
Pulling a trailer up a hill.
Carrying a box down a corridor.
0%
A.
4%
B.
83%
C.
13%
D.